How to add a white paper
The white paper collection is managed through a configuration file that contains information on registered white papers. This configuration can be automatically updated from GitHub by a script that will pull some meta information like the title, authors, and abstract. It will also grab the latest compiled PDF from the source repository that was created by a CI job.
To get started, head over to the white paper template repository. There should be a button toward the top right that says Use this template, which will allow you to create a copy of the template repository into a repository of your own.
Tip
You can get started by creating a whitepaper repository using the template
under your own account. However, when the document finalizes, consider
moving it into the ACTS organization (acts-project), which helps
management of documents.
The project will immediately start building the basic default note with dummy content using GitHub Actions. You can now clone and start making changes to the document and compile locally.
Tip
The easiest way to compile the document locally is latexmk. Simply running latexmk
in the root directory will automatically compile the source code the right
number of times. It will also run biber that generates the references from the
example references.bib file. You don’t have to use latexmk, but it’s very
convenient! The output file when using latexmk will be in a subfolder build
of the root directory.
Tip
The note template requires LuaLatex, which should be found in any default
LaTeX installations. latexmk is configured to use LuaLatex by default.
Integrate with Overleaf
Overleaf is a convenient web-based LaTeX authoring tool. It has GitHub integration 🎉!
You can then go to the Menu on the top right, and click on GitHub in the drawer menu to pull changes from GitHub, and to push changes that you made on Overleaf!
Danger
Overleaf is not particularly good at handling merge conflicts, so try not to make changes on both GitHub and Overleaf.
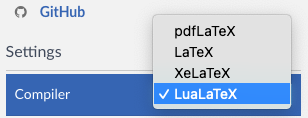
For the document to compile without errors on Overleaf, you will have to change the compiler to LuaLatex, by going to Menu in the top right, and changing the Compiler setting:
Template repository structure
The content of the template repository will look something like this:
whitepaper-template
├── main.tex
├── metadata.tex
├── abstract.tex
├── references.bib
├── latexmkrc
└── theme
├── acts.sty
└── logo_acts.pdf
main.texis the root source file for the document, and you can edit it to changed the content of the document.metadata.texandabstract.texcontain the document title, authors and abstract. Their content is consumed by the workflow described in Update the white paper overview.metadata.texcontains the two standard LaTeX commands:\title{A whitepaper about a topic} \author{First Author \and Second Author}
Note how the
\authordirective is given multiple authors separated by\and. The workflow below uses the literal\andto separate out different authors.abstract.texcontains the content of the abstract only, and is loaded into the abstract in themain.texdocument like:\begin{abstract} \input{abstract.tex} \end{abstract}
Warning
While LaTeX supports arbitrary content in the abstract, the index that lives in the documentation only supports basic math markup.
references.bibcontains an example reference in standard bibtex format, and is a good place to add any additional references that you want to cite in your document.latexmkrcconfigureslatexmk(see here)themecontains the overall theme of the document. You do not typically need to change anything in this folder.
Update the white paper overview
The white paper overview in this documentation here is
automatically generated using a registry file and a script, both of which are
located in the main ACTS repository under docs.
The registration file docs/white_papers.toml contains a list of all
known white papers, and also stores metadata information on the white paper. It looks something like:
[[white_papers]]
repository = "https://github.com/acts-project/whitepaper-template"
[white_papers.metadata]
authors = [ "First Author", "Second Author",]
title = "A whitepaper about a topic"
description = "This is a whitepaper example. It contains a number of example\npatterns, layouts etc.\nSimple math like $a + b = c$ or even $\\sqrt{s} = 14$ TeV is supported!\n\nQuisque ullamcorper placerat ipsum. Cras nibh. Morbi vel justo vitae lacus\ntincidunt ultrices. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. In hac\nhabitasse platea dictumst. Integer tempus convallis augue. Etiam facilisis. Nunc\nelementum fermentum wisi. Aenean placerat. Ut imperdiet, enim sed gravida\nsollicitudin, felis odio placerat quam, ac pulvinar elit purus eget enim. Nunc vitae\ntortor. Proin tempus nibh sit amet nisl. Vivamus quis tortor vitae risus porta\nvehicula."
[[white_papers]] indicates a white paper entry, while [white_papers.metadata] is a dictionary containing the metadata for that white paper.
Note
[white_papers.metadata] is auto-generated!
To add a new white paper, simply add a new section at the bottom of the file:
[[white_papers]]
repository = "https://github.com/acts-project/another-whitepaper"
slug = "another-whitepaper"
Note that slug should be lower case, not contain spaces, and be unique.
The script docs/white_papers.py is used to complete the metadata information
for the white papers. To run it, you need to install the dependencies in
docs/requirements.txt using pip.
Tip
It is strongly recommended to use a virtual environment for this purpose! For example, run
$ python -m venv venv
$ source venv/bin/activate
to create a local virtual environment, and then run the pip command above.
You also need the convert executable from
ImageMagick available on your $PATH. You can
then run
$ white_papers.py pull --github-token $GITHUB_TOKEN
which will for each white_paper listed in white_papers.toml
Download the most recent PDF of the document built by that repository’s CI
Make a PNG of the first page of that PDF to be displayed in the documentation
Download
metadata.texandabstract.texfrom the repository, and parse them to extract the title, authors and abstract content.
Important
Make sure to create a tag on GitHub before running this command! This is good for organizational purposes, but also allows directly linking to the PDF that is generated by the CI for that tag.
Afterwards, the white_papers.toml should now contain updated information from
all listed white papers. The white_papers.toml file is used to automatically
generate a white paper index, that is then used by the regular documentation
build, which you can read more about here.