API Reference
Classes
-
class AnnulusBounds : public Acts::DiscBounds
Class that implements a (potentially asymmetric) bounds with difference between surface bound center and surface coordinate center.
These bounds combine two different systems:
module system : radial bounds centred on the moduleOrigin
strip system : phi bounds centred on the stripOrigin
The measurement will be done in the strip system, with r/phi local coordinates.
Public Types
Public Functions
-
AnnulusBounds() = delete
-
AnnulusBounds(const AnnulusBounds &source) = default
-
AnnulusBounds(const std::array<double, eSize> &values) noexcept(false)
Constructor - from parameters array.
- Parameters:
values – The parameter array
-
inline AnnulusBounds(double minR, double maxR, double minPhiRel, double maxPhiRel, const Vector2 &moduleOrigin = {0, 0}, double avgPhi = 0) noexcept(false)
Default constructor from parameters.
Note
For
moriginyou need to actually calculate the cartesian offset- Parameters:
minR – inner radius, in module system
maxR – outer radius, in module system
minPhiRel – right angular edge, in strip system, rel to avgPhi
maxPhiRel – left angular edge, in strip system, rel to avgPhi
moduleOrigin – The origin offset between the two systems.
avgPhi – (Optional) internal rotation of this bounds object’s local frame
-
inline virtual double binningValuePhi() const final
Return a reference radius for binning.
-
inline virtual double binningValueR() const final
Return a reference radius for binning.
-
std::vector<Vector2> corners() const
This method returns the four corners of the bounds in polar coordinates Starting from the upper right (max R, pos locX) and proceeding clock-wise i.e.
(max R; pos locX), (min R; pos locX), (min R; neg loc X), (max R: neg locX)
-
inline virtual bool coversFullAzimuth() const final
Returns true for full phi coverage.
-
inline double get(BoundValues bValue) const
Access to the bound values.
- Parameters:
bValue – the class nested enum for the array access
-
virtual bool inside(const Vector2 &lposition, const BoundaryCheck &bcheck) const final
Inside check for the bounds object driven by the boundary check directive Each Bounds has a method inside, which checks if a LocalPosition is inside the bounds Inside can be called without/with tolerances.
- Parameters:
lposition – Local position (assumed to be in right surface frame)
bcheck – boundary check directive
- Returns:
boolean indicator for the success of this operation
-
inline virtual bool insideRadialBounds(double R, double tolerance = 0.) const final
Checks if this is inside the radial coverage given the a tolerance.
-
Vector2 moduleOrigin() const
Returns moduleOrigin, but rotated out, so
averagePhiis already considered.The module origin needs to consider the rotation introduced by
averagePhi- Returns:
The origin of the local frame
-
inline double phiMax() const
Returns the left angular edge of the module.
- Returns:
The left side angle
-
inline double phiMin() const
Returns the right angular edge of the module.
- Returns:
The right side angle
-
inline virtual double rMax() const final
This method returns outer radius.
-
inline virtual double rMin() const final
This method returns inner radius.
-
virtual std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &sl) const final
Outstream operator.
- Parameters:
sl – is the ostream to be dumped into
-
inline virtual SurfaceBounds::BoundsType type() const final
Return the bounds type - for persistency optimization.
- Returns:
is a BoundsType enum
-
inline virtual std::vector<double> values() const final
Return the bound values as dynamically sized vector.
- Returns:
this returns a copy of the internal values
-
virtual std::vector<Vector2> vertices(unsigned int lseg) const override
This method returns the xy coordinates of the four corners of the bounds in module coordinates (in x/y) Starting from the upper right (max R, pos locX) and proceeding clock-wise i.e.
(max R; pos locX), (min R; pos locX), (min R; neg loc X), (max R: neg locX)
Note
that that if
lseg> 0, the extrema points are given, which may slightly alter the number of segments returned- Parameters:
lseg – the number of segments used to approximate and eventually curved line
- Returns:
vector for vertices in 2D
-
class AnyCharge
Charge and momentum interpretation for arbitrarily charged particles.
Only a charge magnitude identical to zero is interpreted as representing a neutral particle. This avoids ambiguities that might arise from using an approximate comparison with an arbitrary epsilon.
Public Functions
-
inline constexpr AnyCharge(float absQ) noexcept
Construct with the magnitude of the input charge.
-
inline constexpr AnyCharge(SinglyCharged) noexcept
-
inline constexpr float absQ() const noexcept
-
inline constexpr float extractCharge(ActsScalar qOverP) const noexcept
-
inline constexpr ActsScalar extractMomentum(ActsScalar qOverP) const noexcept
-
inline constexpr ActsScalar qOverP(ActsScalar momentum, float signedQ) const noexcept
Friends
- inline friend constexpr friend bool operator== (AnyCharge lhs, AnyCharge rhs) noexcept
Compare for equality.
-
inline constexpr AnyCharge(float absQ) noexcept
-
template<int NComponents, int PolyDegree>
class AtlasBetheHeitlerApprox This class approximates the Bethe-Heitler distribution as a gaussian mixture.
To enable an approximation for continuous input variables, the weights, means and variances are internally parametrized as a Nth order polynomial.
Public Types
-
using Data = std::array<PolyData, NComponents>
Public Functions
-
inline constexpr AtlasBetheHeitlerApprox(const Data &lowData, const Data &highData, bool lowTransform, bool highTransform, double lowLimit = 0.1, double highLimit = 0.2)
Construct the Bethe-Heitler approximation description with two parameterizations, one for lower ranges, one for higher ranges.
Is it assumed that the lower limit of the high-x/x0 data is equal to the upper limit of the low-x/x0 data.
- Parameters:
lowData – data for the lower x/x0 range
highData – data for the higher x/x0 range
lowTransform – whether the low data need to be transformed
highTransform – whether the high data need to be transformed
lowLimit – the upper limit for the low data
highLimit – the upper limit for the high data
-
inline auto mixture(ActsScalar x) const
Generates the mixture from the polynomials and reweights them, so that the sum of all weights is 1.
- Parameters:
x – pathlength in terms of the radiation length
-
inline constexpr auto numComponents() const
Returns the number of components the returned mixture will have.
-
inline constexpr bool validXOverX0(ActsScalar x) const
Checks if an input is valid for the parameterization.
- Parameters:
x – pathlength in terms of the radiation length
Public Static Functions
-
static inline auto loadFromFiles(const std::string &low_parameters_path, const std::string &high_parameters_path, double lowLimit = 0.1, double highLimit = 0.2)
Loads a parameterization from a file according to the Atlas file description.
- Parameters:
low_parameters_path – Path to the foo.par file that stores the parameterization for low x/x0
high_parameters_path – Path to the foo.par file that stores the parameterization for high x/x0
lowLimit – the upper limit for the low x/x0-data
highLimit – the upper limit for the high x/x0-data
-
struct PolyData
Public Members
-
std::array<ActsScalar, PolyDegree + 1> meanCoeffs
-
std::array<ActsScalar, PolyDegree + 1> varCoeffs
-
std::array<ActsScalar, PolyDegree + 1> weightCoeffs
-
std::array<ActsScalar, PolyDegree + 1> meanCoeffs
-
using Data = std::array<PolyData, NComponents>
-
class AtlasStepper
the AtlasStepper implementation for the
Public Types
-
using BoundState = std::tuple<BoundTrackParameters, Jacobian, double>
-
using Covariance = BoundSquareMatrix
-
using Jacobian = BoundMatrix
Public Functions
-
inline double absoluteMomentum(const State &state) const
Absolute momentum accessor.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
inline Result<BoundState> boundState(State &state, const Surface &surface, bool transportCov = true, const FreeToBoundCorrection &freeToBoundCorrection = FreeToBoundCorrection(false)) const
Create and return the bound state at the current position.
- Parameters:
state – [in] State that will be presented as
BoundStatesurface – [in] The surface to which we bind the state
transportCov – [in] Flag steering covariance transport
freeToBoundCorrection – [in] Correction for non-linearity effect during transform from free to bound
- Returns:
A bound state:
the parameters at the surface
the stepwise jacobian towards it
and the path length (from start - for ordering)
-
inline double charge(const State &state) const
Charge access.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
inline CurvilinearState curvilinearState(State &state, bool transportCov = true) const
Create and return a curvilinear state at the current position.
- Parameters:
state – [in] State that will be presented as
CurvilinearStatetransportCov – [in] Flag steering covariance transport
- Returns:
A curvilinear state:
the curvilinear parameters at given position
the stepweise jacobian towards it
and the path length (from start - for ordering)
-
inline Result<Vector3> getField(State &state, const Vector3 &pos) const
Get the field for the stepping It checks first if the access is still within the Cell, and updates the cell if necessary, then it takes the field from the cell.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] is the stepper state associated with the track the magnetic field cell is used (and potentially updated)
pos – [in] is the field position
-
inline double getStepSize(const State &state, ConstrainedStep::Type stype) const
Get the step size.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
stype – [in] The step size type to be returned
-
inline State makeState(std::reference_wrapper<const GeometryContext> gctx, std::reference_wrapper<const MagneticFieldContext> mctx, const BoundTrackParameters &par, double ssize = std::numeric_limits<double>::max(), double stolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance) const
-
inline std::string outputStepSize(const State &state) const
Output the Step Size - single component.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
inline const ParticleHypothesis &particleHypothesis(const State &state) const
Particle hypothesis.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
If necessary fill additional members needed for curvilinearState.
Compute path length derivatives in case they have not been computed yet, which is the case if no step has been executed yet.
- Parameters:
prop_state – [inout] State that will be presented as
BoundStatenavigator – [in] the navigator of the propagation
- Returns:
true if nothing is missing after this call, false otherwise.
-
inline void releaseStepSize(State &state, ConstrainedStep::Type stype) const
Release the Step size.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
stype – [in] The step size type to be released
-
inline void resetState(State &state, const BoundVector &boundParams, const BoundSquareMatrix &cov, const Surface &surface, const double stepSize = std::numeric_limits<double>::max()) const
Resets the state.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] State of the stepper
boundParams – [in] Parameters in bound parametrisation
cov – [in] Covariance matrix
surface – [in] Reset state will be on this surface
stepSize – [in] Step size
-
inline void setIdentityJacobian(State &state) const
Method that reset the Jacobian to the Identity for when no bound state are available.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] State of the stepper
Perform the actual step on the state.
- Parameters:
state – is the provided stepper state (caller keeps thread locality)
-
inline void transportCovarianceToBound(State &state, const Surface &surface, const FreeToBoundCorrection& = FreeToBoundCorrection(false)) const
Method for on-demand transport of the covariance to a new curvilinear frame at current position, or direction of the state.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] State of the stepper
surface – [in] is the surface to which the covariance is forwarded to
-
inline void transportCovarianceToCurvilinear(State &state) const
Method for on-demand transport of the covariance to a new curvilinear frame at current position, or direction of the state.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] State of the stepper
-
inline void update(State &state, const FreeVector ¶meters, const BoundVector &boundParams, const Covariance &covariance, const Surface &surface) const
The state update method.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] The stepper state for
parameters – [in] The new free track parameters at start
boundParams – [in] Corresponding bound parameters
covariance – [in] The updated covariance matrix
surface – [in] The surface used to update the pVector
-
inline void update(State &state, const Vector3 &uposition, const Vector3 &udirection, double qop, double time) const
Method to update momentum, direction and p.
- Parameters:
state – The state object
uposition – the updated position
udirection – the updated direction
qop – the updated momentum value
time – the update time
-
template<typename object_intersection_t>
inline void updateStepSize(State &state, const object_intersection_t &oIntersection, Direction, bool release = true) const Update step size.
It checks the status to the reference surface & updates the step size accordingly
- Parameters:
state – [in,out] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
oIntersection – [in] The ObjectIntersection to layer, boundary, etc
release – [in] boolean to trigger step size release
-
inline void updateStepSize(State &state, double stepSize, ConstrainedStep::Type stype, bool release = true) const
Update step size - explicitly with a double.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
stepSize – [in] The step size value
stype – [in] The step size type to be set
release – [in] Do we release the step size?
-
inline Intersection3D::Status updateSurfaceStatus(State &state, const Surface &surface, std::uint8_t index, Direction navDir, const BoundaryCheck &bcheck, ActsScalar surfaceTolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance, const Logger &logger = getDummyLogger()) const
Update surface status.
This method intersect the provided surface and update the navigation step estimation accordingly (hence it changes the state). It also returns the status of the intersection to trigger onSurface in case the surface is reached.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
surface – [in] The surface provided
index – [in] The surface intersection index
navDir – [in] The navigation direction
bcheck – [in] The boundary check for this status update
surfaceTolerance – [in] Surface tolerance used for intersection
logger – [in] Logger instance to use
-
struct State
Nested State struct for the local caching.
Public Functions
-
State() = delete
Default constructor - deleted.
-
template<typename Parameters>
inline State(const GeometryContext &gctx, MagneticFieldProvider::Cache fieldCacheIn, const Parameters &pars, double ssize = std::numeric_limits<double>::max(), double stolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance) Constructor.
- Template Parameters:
Type – of TrackParameters
- Parameters:
gctx – [in] The geometry context tof this call
fieldCacheIn – [in] The magnetic field cache for this call
pars – [in] Input parameters
ssize – [in] the steps size limitation
stolerance – [in] is the stepping tolerance
Public Members
-
Covariance cov = Covariance::Zero()
-
const Covariance *covariance = nullptr
-
bool covTransport = false
-
bool debug = false
Debug output the string where debug messages are stored (optionally)
-
std::size_t debugMsgWidth = 50
-
std::size_t debugPfxWidth = 30
buffer & formatting for consistent output
-
std::string debugString = ""
-
MagneticFieldProvider::Cache fieldCache
It caches the current magnetic field cell and stays (and interpolates) within as long as this is valid.
See step() code for details.
-
std::reference_wrapper<const GeometryContext> geoContext
Cache the geometry context.
-
double jacobian[eBoundSize * eBoundSize] = {}
-
double maxPathLength = 0
-
bool mcondition = false
-
bool needgradient = false
-
bool newfield = true
-
double parameters[eBoundSize] = {0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.}
Storage pattern of pVector /dL0 /dL1 /dPhi /the /dCM /dT X ->P[0] dX / P[ 8] P[16] P[24] P[32] P[40] P[48] Y ->P[1] dY / P[ 9] P[17] P[25] P[33] P[41] P[49] Z ->P[2] dZ / P[10] P[18] P[26] P[34] P[42] P[50] T ->P[3] dT/ P[11] P[19] P[27] P[35] P[43] P[51] Ax ->P[4] dAx/ P[12] P[20] P[28] P[36] P[44] P[52] Ay ->P[5] dAy/ P[13] P[21] P[29] P[37] P[45] P[53] Az ->P[6] dAz/ P[14] P[22] P[30] P[38] P[46] P[54] CM ->P[7] dCM/ P[15] P[23] P[31] P[39] P[47] P[55] Cache: P[56] - P[59].
-
ParticleHypothesis particleHypothesis
-
double pathAccumulated = 0.
-
double previousStepSize = 0.
-
std::array<double, 60> pVector = {}
-
bool state_ready = false
-
double step = 0
-
ConstrainedStep stepSize
-
double tolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance
The tolerance for the stepping.
-
bool useJacobian = false
-
State() = delete
-
using BoundState = std::tuple<BoundTrackParameters, Jacobian, double>
-
class BinUtility
The BinUtility class that translated global and local position into a bins of a BinnedArray, most performant is equidistant binning without a transform, however, optionally a transform can be provided, e.g.
for binning on shifted object, the transform is usually shared with the geometric object the Array is defined on, for performance reasons, also the inverse transform is stored.
Public Functions
-
inline BinUtility()
Constructor for equidistant.
-
BinUtility(BinUtility &&sbu) = default
-
inline BinUtility(const BinningData &bData, const Transform3 &tForm = Transform3::Identity())
Constructor from BinningData directly.
- Parameters:
bData – is the provided binning data
tForm – is the (optional) transform
-
BinUtility(const BinUtility &sbu) = default
Copy constructor.
- Parameters:
sbu – is the source bin utility
-
inline BinUtility(const Transform3 &tForm)
Constructor with only a Transform3.
- Parameters:
tForm – is the local to global transform
-
inline BinUtility(std::size_t bins, float min, float max, BinningOption opt = open, BinningValue value = binX, const Transform3 &tForm = Transform3::Identity())
Constructor for equidistant.
- Parameters:
bins – is the number of bins
min – in the minimal value
max – is the maximal value
opt – is the binning option : open, closed
value – is the binninb value : binX, binY, binZ, etc.
tForm – is the (optional) transform
-
inline BinUtility(std::vector<float> &bValues, BinningOption opt = open, BinningValue value = binPhi, const Transform3 &tForm = Transform3::Identity())
Constructor for arbitrary.
- Parameters:
bValues – is the boundary values of the binning
opt – is the binning option : open, closed
value – is the binninb value : binX, binY, binZ, etc.
tForm – is the (optional) transform
-
~BinUtility() = default
Virtual Destructor.
-
inline std::size_t bin(const Vector2 &lposition, std::size_t ba = 0) const
Bin from a 2D vector (following local parameters defintitions)
no optional transform applied
USE WITH CARE !!
You need to make sure that the local position is actually in the binning frame of the BinUtility
- Parameters:
lposition – is the local position to be set
ba – is the bin dimension
- Returns:
bin calculated from local
-
inline std::size_t bin(const Vector3 &position, std::size_t ba = 0) const
Bin from a 3D vector (already in binning frame)
- Parameters:
position – is the 3D position to be evaluated
ba – is the bin dimension
- Returns:
is the bin value
-
inline const std::vector<BinningData> &binningData() const
Return the binning data vector.
-
inline BinningValue binningValue(std::size_t ba = 0) const
The type/value of the binning.
- Parameters:
ba – is the binaccessor
- Returns:
the binning value of the accessor entry
-
inline std::size_t bins() const
Return the total number of bins.
-
inline std::size_t bins(std::size_t ba) const
Number of bins.
- Parameters:
ba – is the binaccessor
- Returns:
std::size_t is the bins of the accessor entry
-
inline std::array<std::size_t, 3> binTriple(const Vector3 &position) const
Bin-triple fast access.
calculate the bin triple with one transform
- Parameters:
position – is the 3D position to be evaluated
- Returns:
is the bin value in 3D
-
inline std::size_t dimensions() const
First bin maximal value.
- Returns:
the dimension of the binning data
-
inline bool inside(const Vector3 &position) const
Check if bin is inside from Vector2 - optional transform applied.
- Parameters:
position – is the global position to be evaluated
- Returns:
is a boolean check
-
inline std::size_t max(std::size_t ba = 0) const
First bin maximal value.
- Parameters:
ba – is the binaccessor
- Returns:
std::size_t is the maximal bin of the accessor entry
-
inline int nextDirection(const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction, std::size_t ba = 0) const
Return the other direction for fast interlinking.
- Parameters:
position – is the global position for the next search
direction – is the global position for the next search
ba – is the bin accessor
- Returns:
the next bin
-
inline BinUtility &operator+=(const BinUtility &gbu)
Operator+= to make multidimensional BinUtility.
- Parameters:
gbu – is the additional BinUtility to be chosen
-
BinUtility &operator=(BinUtility&&) = default
-
inline BinUtility &operator=(const BinUtility &sbu)
Assignment operator.
- Parameters:
sbu – is the source bin utility
-
inline bool operator==(const BinUtility &other) const
Equality operator.
-
inline std::size_t serialize(const std::array<std::size_t, 3> &bin) const
Serialize the bin triple.
this creates a simple std::size_t from a triple object
- Parameters:
bin – is the bin to be serialized
-
inline std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &sl, const std::string &indent = "") const
Output Method for std::ostream, to be overloaded by child classes.
- Parameters:
sl – is the ostream to be dumped into
indent – the current indentation
- Returns:
the input stream
-
inline std::string toString(const std::string &indent = "") const
Output into a string.
- Parameters:
indent – the current indentation
- Returns:
a string with the stream information
-
inline const Transform3 &transform() const
Transform applied to global positions before lookup.
- Returns:
Shared pointer to transform
-
inline BinUtility()
-
class BinnedSurfaceMaterial : public Acts::ISurfaceMaterial
It extends the
ISurfaceMaterialbase class and is an array pf MaterialSlab.This is not memory optimised as every bin holds one material property object.
Public Functions
-
BinnedSurfaceMaterial() = delete
Default Constructor - deleted.
-
BinnedSurfaceMaterial(BinnedSurfaceMaterial &&bsm) = default
Copy Move Constructor.
- Parameters:
bsm – is the source object to be copied
-
BinnedSurfaceMaterial(const BinnedSurfaceMaterial &bsm) = default
Copy Constructor.
- Parameters:
bsm – is the source object to be copied
-
BinnedSurfaceMaterial(const BinUtility &binUtility, MaterialSlabMatrix fullProperties, double splitFactor = 0., MappingType mappingType = MappingType::Default)
Explicit constructor with only full MaterialSlab, for two-dimensional binning.
The split factors:
1. : oppositePre
0. : alongPre ===> 1 Dimensional array
- Parameters:
binUtility – defines the binning structure on the surface (copied)
fullProperties – is the vector of properties as recorded (moved)
splitFactor – is the pre/post splitting directive
mappingType – is the type of surface mapping associated to the surface
-
BinnedSurfaceMaterial(const BinUtility &binUtility, MaterialSlabVector fullProperties, double splitFactor = 0., MappingType mappingType = MappingType::Default)
Explicit constructor with only full MaterialSlab, for one-dimensional binning.
The split factors:
1. : oppositePre
0. : alongPre ===> 1 Dimensional array
- Parameters:
binUtility – defines the binning structure on the surface (copied)
fullProperties – is the vector of properties as recorded (moved)
splitFactor – is the pre/post splitting directive
mappingType – is the type of surface mapping associated to the surface
-
~BinnedSurfaceMaterial() override = default
Destructor.
-
inline const BinUtility &binUtility() const
Return the BinUtility.
-
inline const MaterialSlabMatrix &fullMaterial() const
Retrieve the entire material slab matrix.
-
virtual const MaterialSlab &materialSlab(const Vector2 &lp) const final
Return method for full material description of the Surface.
from local coordinate on the surface
- Parameters:
lp – is the local position used for the (eventual) lookup
- Returns:
const MaterialSlab
-
virtual const MaterialSlab &materialSlab(const Vector3 &gp) const final
Return method for full material description of the Surface.
from the global coordinates
- Parameters:
gp – is the global position used for the (eventual) lookup
- Returns:
const MaterialSlab
-
virtual BinnedSurfaceMaterial &operator*=(double scale) final
Scale operator.
- Parameters:
scale – is the scale factor for the full material
-
BinnedSurfaceMaterial &operator=(BinnedSurfaceMaterial &&bsm) = default
Assignment Move operator.
-
BinnedSurfaceMaterial &operator=(const BinnedSurfaceMaterial &bsm) = default
Assignment operator.
-
virtual std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &sl) const final
Output Method for std::ostream, to be overloaded by child classes.
-
BinnedSurfaceMaterial() = delete
-
class BinningData
This class holds all the data necessary for the bin calculation.
phi has a very particular behaviour:
there’s the change around +/- PI
it can be multiplicative or additive multiplicative : each major bin has the same sub structure i.e. first binnning
structure is equidistant additive : sub structure replaces one bin (and one bin only)
Public Functions
-
BinningData() = default
-
inline BinningData(BinningOption bOption, BinningValue bValue, const std::vector<float> &bBoundaries, std::unique_ptr<const BinningData> sBinData = nullptr)
Constructor for non-equidistant binning.
- Parameters:
bOption – is the binning option : open / closed
bValue – is the binning value : binX, binY, etc.
bBoundaries – are the bin boundaries
sBinData – is (optional) sub structure
-
inline BinningData(BinningOption bOption, BinningValue bValue, std::size_t bBins, float bMin, float bMax, std::unique_ptr<const BinningData> sBinData = nullptr, bool sBinAdditive = false)
Constructor for equidistant binning and optional sub structure can be multiplicative or additive.
- Parameters:
bOption – is the binning option : open, closed
bValue – is the binning value: binX, binY, etc.
bBins – is number of equidistant bins
bMin – is the minimum value
bMax – is the maximum value
sBinData – is (optional) sub structure
sBinAdditive – is the prescription for the sub structure
-
inline BinningData(BinningValue bValue, float bMin, float bMax)
Constructor for 0D binning.
- Parameters:
bValue – is the binning value: binX, binY, etc.
bMin – is the minimum value
bMax – is the maximum value
-
inline BinningData(const BinningData &bdata)
Copy constructor.
- Parameters:
bdata – is the source object
-
~BinningData() = default
-
inline std::size_t bins() const
Return the number of bins - including sub bins.
-
inline const std::vector<float> &boundaries() const
Return the boundaries - including sub boundaries.
- Returns:
vector of floats indicating the boundary values
-
inline float center(std::size_t bin) const
Get the center value of a bin.
- Parameters:
bin – is the bin for which the center value is requested
- Returns:
float value according to the bin center
-
inline float centerValue(std::size_t bin) const
access to the center value this uses the bin boundary vector, it also works with sub structure
- Parameters:
bin – is the bin for which the value is requested, if bin > nbins it is set to max
- Returns:
the center value of the bin is given
-
inline bool inside(const Vector2 &lposition) const
Check if bin is inside from Vector2.
- Parameters:
lposition – is the search position in global coordinated
- Returns:
boolean if this is inside() method is true
-
inline bool inside(const Vector3 &position) const
Check if bin is inside from Vector3.
- Parameters:
position – is the search position in global coordinated
- Returns:
boolean if this is inside() method is true
-
inline int nextDirection(const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &dir) const
Layer next direction is needed.
- Parameters:
position – is the start search position
dir – is the direction
- Returns:
integer that indicates which direction to move
-
inline BinningData &operator=(const BinningData &bdata)
Assignment operator.
- Parameters:
bdata – is the source object
-
inline bool operator==(const BinningData &bData) const
Equality operator.
- Parameters:
bData – is the binning data to be checked against
- Returns:
a boolean indicating if they are the same
-
inline std::size_t search(float value) const
Generic search - forwards to correct function pointer.
- Parameters:
value – is the searchvalue as float
- Returns:
bin according tot this
-
inline std::size_t searchGlobal(const Vector3 &position) const
Generic search from a 3D position — corresponds to global coordinate schema.
- Parameters:
position – is the search position in global coordinated
- Returns:
bin according tot this
-
inline std::size_t searchLocal(const Vector2 &lposition) const
Generic search from a 2D position — corresponds to local coordinate schema.
- Parameters:
lposition – is the search position in local coordinated
- Returns:
bin according tot this
-
inline std::size_t searchWithSubStructure(float value) const
Generic search with sub structure.
forwards to correct function pointer
- Parameters:
value – is the searchvalue as float
- Returns:
bin according tot this
-
inline std::string toString(const std::string &indent) const
String screen output method.
- Parameters:
indent – the current indentation
- Returns:
a string containing the screen information
-
inline float value(const Vector2 &lposition) const
Take the right float value.
- Parameters:
lposition – assumes the correct local position expression
- Returns:
float value according to the binning setup
-
inline float value(const Vector3 &position) const
Take the right float value.
- Parameters:
position – is the global position
- Returns:
float value according to the binning setup
-
inline float width(std::size_t bin) const
Get the width of a bin.
- Parameters:
bin – is the bin for which the width is requested
- Returns:
float value of width
Public Members
-
BinningValue binvalue = {}
binning value: binX, binY, binZ, binR …
-
float max = {}
maximum value
-
float min = {}
minimum value
-
BinningOption option = {}
binning option: open, closed
-
float step = {}
binning step
-
bool subBinningAdditive = {}
sub structure: additive or multipicative
-
std::unique_ptr<const BinningData> subBinningData
sub structure: describe some sub binning
-
BinningType type = {}
binning type: equidistant, arbitrary
-
bool zdim = {}
zero dimensional binning : direct access
-
class BoundaryCheck
The BoundaryCheck class provides boundary checks and distance calculations for aligned box-like and polygonal boundaries on local surfaces.
Different types of boundary checks are supported and are transparently selected when calling the
isInside(...)anddistance(...)methods:Hard checks w/o any tolerances
Tolerance-based checks in one or in both local coordinates
Chi2-based checks based on a covariance matrix. Non-vanishing correlations are correctly taken into account.
With a defined covariance matrix, the closest point and the distance are not defined along the usual Euclidean metric, but by the Mahalanobis distance induced by the covariance.
Public Types
Public Functions
-
inline explicit BoundaryCheck(bool check)
Construct either hard cut in both dimensions or no cut at all.
-
inline BoundaryCheck(bool checkLocal0, bool checkLocal1, double tolerance0 = 0, double tolerance1 = 0)
Construct a tolerance based check.
- Parameters:
checkLocal0 – Boolean directive to check coordinate 0
checkLocal1 – Boolean directive to check coordinate 1
tolerance0 – Tolerance along coordinate 0
tolerance1 – Tolerance along coordinate 1
-
inline BoundaryCheck(const SquareMatrix2 &localCovariance, double sigmaMax = 1)
Construct a chi2-based check.
- Parameters:
localCovariance – Coverance matrix in local coordinates
sigmaMax – Significance for the compatibility test
-
template<typename Vector2Container>
inline Acts::Vector2 computeClosestPointOnPolygon(const Acts::Vector2 &point, const Vector2Container &vertices) const
-
inline SquareMatrix2 covariance() const
-
inline double distance(const Vector2 &point, const Vector2 &lowerLeft, const Vector2 &upperRight) const
Calculate the signed, weighted, closest distance to an aligned box.
If a covariance is defined, the distance is the corresponding Mahalanobis distance. Otherwise, it is the Eucleadian distance.
- Parameters:
point – Test point
lowerLeft – Minimal vertex of the box
upperRight – Maximal vertex of the box
- Returns:
Negative value if inside, positive if outside
-
template<typename Vector2Container>
inline double distance(const Vector2 &point, const Vector2Container &vertices) const Calculate the signed, weighted, closest distance to a polygonal boundary.
If a covariance is defined, the distance is the corresponding Mahalanobis distance. Otherwise, it is the Eucleadian distance.
- Parameters:
point – Test point
vertices – Forward iterable container of convex polygon vertices. Calling
std::begin/std::endon the container must return an iterator where*itmust be convertible to anActs::Vector2.
- Returns:
Negative value if inside, positive if outside
-
inline bool isEnabled() const
-
inline bool isInside(const Vector2 &point, const Vector2 &lowerLeft, const Vector2 &upperRight) const
Check if the point is inside a box aligned with the local axes.
The check takes into account whether tolerances or covariances are defined for the boundary check.
- Parameters:
point – Test point
lowerLeft – Minimal vertex of the box
upperRight – Maximal vertex of the box
-
template<typename Vector2Container>
inline bool isInside(const Vector2 &point, const Vector2Container &vertices) const Check if the point is inside a polygon.
The check takes into account whether tolerances or covariances are defined for the boundary check.
- Parameters:
point – Test point
vertices – Forward iterable container of convex polygon vertices. Calling
std::begin/std::endon the container must return an iterator where*itmust be convertible to anActs::Vector2.
-
template<typename propagator_t, typename traj_t>
class CombinatorialKalmanFilter Combinatorial Kalman filter to find tracks.
The CombinatorialKalmanFilter contains an Actor and a Sequencer sub-class. The Sequencer has to be part of the Navigator of the Propagator in order to initialize and provide the measurement surfaces.
The Actor is part of the Propagation call and does the Kalman update and eventually the smoothing. Updater and Calibrator are given to the Actor for further use:
The Updater is the implemented kalman updater formalism, it runs via a visitor pattern through the measurements.
Measurements are not required to be ordered for the CombinatorialKalmanFilter, measurement ordering needs to be figured out by the navigation of the propagator.
The void components are provided mainly for unit testing.
- Template Parameters:
propagator_t – Type of the propagator
Public Functions
-
CombinatorialKalmanFilter() = delete
Default constructor is deleted.
-
inline CombinatorialKalmanFilter(propagator_t pPropagator, std::unique_ptr<const Logger> _logger = getDefaultLogger("CKF", Logging::INFO))
Constructor from arguments.
-
template<typename source_link_iterator_t, typename start_parameters_t, typename track_container_t, template<typename> class holder_t, typename parameters_t = BoundTrackParameters>
inline auto findTracks(const start_parameters_t &initialParameters, const CombinatorialKalmanFilterOptions<source_link_iterator_t, traj_t> &tfOptions, TrackContainer<track_container_t, traj_t, holder_t> &trackContainer) const -> Result<std::vector<typename std::decay_t<decltype(trackContainer)>::TrackProxy>> Combinatorial Kalman Filter implementation, calls the Kalman filter.
Note
The input measurements are given in the form of
SourceLinks. It’scalibrator_t'sjob to turn them into calibrated measurements used in the track finding.- Template Parameters:
source_link_iterator_t – Type of the source link iterator
start_parameters_container_t – Type of the initial parameters container
calibrator_t – Type of the source link calibrator
measurement_selector_t – Type of the measurement selector
track_container_t – Type of the track container backend
holder_t – Type defining track container backend ownership
parameters_t – Type of parameters used for local parameters
- Parameters:
initialParameters – The initial track parameters
tfOptions – CombinatorialKalmanFilterOptions steering the track finding
trackContainer – Input track container to use
- Returns:
a container of track finding result for all the initial track parameters
-
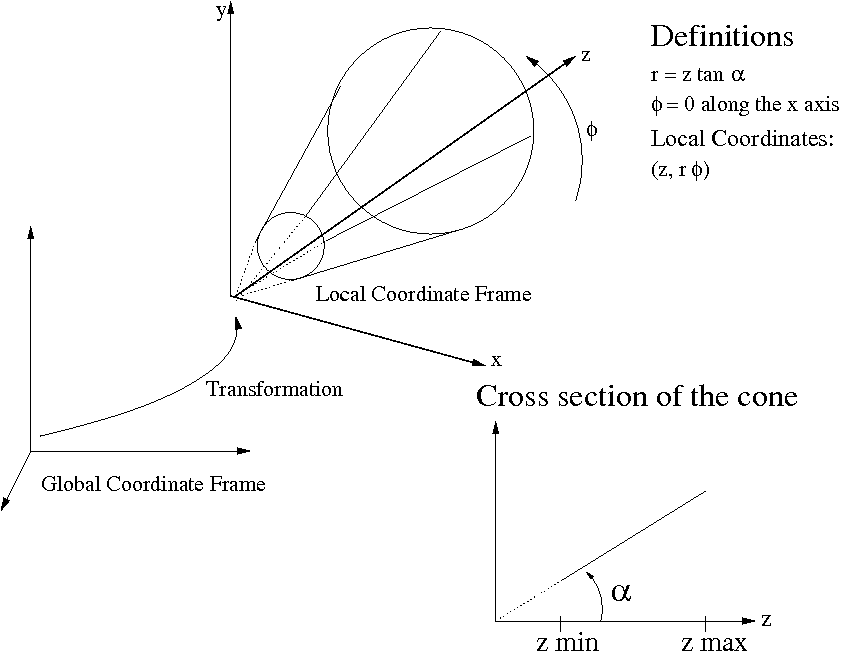
class ConeBounds : public Acts::SurfaceBounds
Bounds for a conical surface, the opening angle is stored in \( \tan(\alpha) \) and always positively defined.
The cone can open to both sides, steered by \( z_min \) and \( z_max \).
Public Types
Public Functions
-
ConeBounds() = delete
-
ConeBounds(const std::array<double, eSize> &values) noexcept(false)
Constructor - from parameters array.
- Parameters:
values – The parameter array
-
ConeBounds(double alpha, bool symm, double halfphi = M_PI, double avphi = 0.) noexcept(false)
Constructor - open cone with alpha, by default a full cone but optionally can make a conical section.
- Parameters:
alpha – is the opening angle of the cone
symm – is the boolean indicating if the cone is symmetric in +/- z
halfphi – is the half opening angle (default is pi)
avphi – is the phi value around which the bounds are opened (default=0)
-
ConeBounds(double alpha, double minz, double maxz, double halfphi = M_PI, double avphi = 0.) noexcept(false)
Constructor - open cone with alpha, minz and maxz, by default a full cone but can optionally make it a conical section.
- Parameters:
alpha – is the opening angle of the cone
minz – cone expanding from minimal z
maxz – cone expanding to maximal z
halfphi – is the half opening angle (default is pi)
avphi – is the phi value around which the bounds are opened (default=0)
-
~ConeBounds() override = default
-
inline double get(BoundValues bValue) const
Access to the bound values.
- Parameters:
bValue – the class nested enum for the array access
-
virtual bool inside(const Vector2 &lposition, const BoundaryCheck &bcheck = BoundaryCheck(true)) const final
inside method for local position
- Parameters:
lposition – is the local position to be checked
bcheck – is the boundary check directive
- Returns:
is a boolean indicating if the position is inside
-
inline double r(double z) const
Return the radius at a specific z values.
- Parameters:
z – is the z value for which r is requested
- Returns:
is the r value associated with z
-
inline double tanAlpha() const
Return tangent of alpha (pre-computed)
-
virtual std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &sl) const final
Output Method for std::ostream.
- Parameters:
sl – is the ostrea into which the dump is done
- Returns:
is the input object
-
virtual BoundsType type() const final
Return the bounds type - for persistency optimization.
- Returns:
is a BoundsType enum
-
inline virtual std::vector<double> values() const final
Return the bound values as dynamically sized vector.
- Returns:
this returns a copy of the internal values
-
ConeBounds() = delete
-
class ConeLayer : public virtual Acts::ConeSurface, public Acts::Layer
Class to describe a conical detector layer for tracking, it inhertis from both, Layer base class and ConeSurface class.
Public Functions
-
ConeLayer() = delete
-
~ConeLayer() override = default
-
virtual const ConeSurface &surfaceRepresentation() const override
Transforms the layer into a Surface representation for extrapolation.
-
virtual ConeSurface &surfaceRepresentation() override
Public Static Functions
Factory for shared layer.
- Parameters:
transform – is the 3D transform that positions the layer in 3D frame
cbounds – is the conical bound description
surfaceArray – is the array of sensitive surfaces
thickness – is the layer thickness along the normal axis
ad – is the approach descriptor for navigation towards the layer
laytyp – is the layer type
- Returns:
is a shared pointer to a layer
-
ConeLayer() = delete
-
class ConeSurface : public Acts::RegularSurface
Class for a conical surface in the Tracking geometry.
It inherits from Surface.
The ConeSurface is special since no corresponding Track parameters exist since they’re numerical instable at the tip of the cone. Propagations to a cone surface will be returned in curvilinear coordinates.
Subclassed by Acts::ConeLayer
Public Functions
-
ConeSurface() = delete
-
~ConeSurface() override = default
-
virtual AlignmentToPathMatrix alignmentToPathDerivative(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction) const final
Calculate the derivative of path length at the geometry constraint or point-of-closest-approach w.r.t.
alignment parameters of the surface (i.e. local frame origin in global 3D Cartesian coordinates and its rotation represented with extrinsic Euler angles)
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – global 3D position
direction – global 3D momentum direction
- Returns:
Derivative of path length w.r.t. the alignment parameters
-
virtual Vector3 binningPosition(const GeometryContext &gctx, BinningValue bValue) const final
The binning position method - is overloaded for r-type binning.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
bValue – defines the type of binning applied in the global frame
- Returns:
The return type is a vector for positioning in the global frame
-
virtual const ConeBounds &bounds() const final
This method returns the ConeBounds by reference.
-
Result<Vector2> globalToLocal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction, double tolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance) const final
Convert a global position to a local one this is the most generic interface, which is implemented by all surfaces.
Note
The
positionis required to be on-surface, which is indicated by theResultreturn value.- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – is the global position to be converted
direction – is the direction of the local position (ignored for
RegularSurface)tolerance – is the tolerance for the on-surface check
- Returns:
Result type containing local position by value
-
virtual Result<Vector2> globalToLocal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, double tolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance) const final
Global to local transformation.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – is the global position to be transformed
tolerance – optional tolerance within which a point is considered valid on surface
- Returns:
a Result<Vector2> which can be !ok() if the operation fails
-
Result<Vector2> globalToLocal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, double tolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance) const = 0
Convert a global position to a local one.
Note
The
positionis required to be on-surface, which is indicated by theResultreturn value.- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – is the global position to be converted
tolerance – is the tolerance for the on-surface check
- Returns:
Result type containing local position by value
-
virtual SurfaceMultiIntersection intersect(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction, const BoundaryCheck &bcheck = BoundaryCheck(false), double tolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance) const final
Straight line intersection schema from position/direction.
If possible returns both solutions for the cylinder
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – The position to start from
direction – The direction at start
bcheck – the Boundary Check
tolerance – the tolerance used for the intersection
- Returns:
SurfaceMultiIntersectionobject (contains intersection & surface)
-
virtual ActsMatrix<2, 3> localCartesianToBoundLocalDerivative(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position) const final
Calculate the derivative of bound track parameters local position w.r.t.
position in local 3D Cartesian coordinates
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – The position of the parameters in global
- Returns:
Derivative of bound local position w.r.t. position in local 3D cartesian coordinates
-
virtual Vector3 localToGlobal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector2 &lposition) const final
Local to global transformation.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lposition – is the local position to be transformed
- Returns:
The global position by value
-
Vector3 localToGlobal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector2 &lposition) const = 0
Local to global transformation.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lposition – local 2D position in specialized surface frame
- Returns:
The global position by value
-
Vector3 localToGlobal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector2 &lposition, const Vector3 &direction) const final
Local to global transformation.
This is the most generic interface, which is implemented by all surfaces.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lposition – local 2D position in specialized surface frame
direction – global 3D momentum direction (ignored for
RegularSurface)
- Returns:
The global position by value
-
virtual std::string name() const override
Return properly formatted class name for screen output.
-
virtual Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector2 &lposition) const final
Return method for surface normal information.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lposition – is the local position at normal vector request
- Returns:
Vector3 normal vector in global frame
-
Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector2 &lposition) const = 0
Calculate the normal vector of the surface This overload requires an on-surface local position.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lposition – is the local position where the normal vector is constructed
- Returns:
normal vector by value
-
Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &pos, const Vector3 &direction) const final
Calculate the normal vector of the surface This overload is fully generic, fulfills the Surface interface and accepts a global position and a direction.
For
RegularSurfacethis is equivalent to the normal overload, ignoring thedirection- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
pos – is the global position where the normal vector is constructed
direction – is the direction of the normal vector (ignored for
RegularSurface)
-
virtual Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position) const final
Return method for surface normal information.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – is the global position as normal vector base
- Returns:
Vector3 normal vector in global frame
-
Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position) const = 0
Calculate the normal vector of the surface This overload accepts a global position.
- Parameters:
position – is the global position where the normal vector is constructed
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
- Returns:
normal vector by value
-
ConeSurface &operator=(const ConeSurface &other)
Assignment operator.
- Parameters:
other – is the source surface for the assignment
-
virtual double pathCorrection(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction) const final
The pathCorrection for derived classes with thickness.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – is the global potion at the correction point
direction – is the momentum direction at the correction point
- Returns:
is the path correction due to incident angle
-
virtual Polyhedron polyhedronRepresentation(const GeometryContext &gctx, std::size_t lseg) const override
Return a Polyhedron for the surfaces.
Note
that a surface transform can invalidate the extrema in the transformed space
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lseg – Number of segments along curved lines, it represents the full 2*M_PI coverange, if lseg is set to 1 only the extrema are given
- Returns:
A list of vertices and a face/facett description of it
-
virtual RotationMatrix3 referenceFrame(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction) const final
Return the measurement frame - this is needed for alignment, in particular for StraightLine and Perigee Surface.
the default implementation is the RotationMatrix3 of the transform
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – is the global position where the measurement frame is constructed
direction – is the momentum direction used for the measurement frame construction
- Returns:
matrix that indicates the measurement frame
-
virtual Vector3 rotSymmetryAxis(const GeometryContext &gctx) const
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
-
virtual SurfaceType type() const override
Return the surface type.
-
ConeSurface() = delete
-
class ConeVolumeBounds : public Acts::VolumeBounds
Volume bound class for describing conical volumes either with cylindrical inlay or outer boundary, it also allows for a sectoral description.
Public Types
Public Functions
-
ConeVolumeBounds() = delete
-
ConeVolumeBounds(ActsScalar cylinderR, ActsScalar alpha, ActsScalar offsetZ, ActsScalar halflengthZ, ActsScalar averagePhi, ActsScalar halfPhiSector) noexcept(false)
Constructor - for general cylidner-cone setups.
Note
depending on cylinderR > coneR it is constructing a cone with cylindrical cutout or a cylinder with conical cutout
- Parameters:
cylinderR – The inner radius of the cylinder
alpha – The opening angle of the cone (0 if no cone)
offsetZ – The tip z position in of the cone, w.r.t center
halflengthZ – The minimum z value of the inner and outer cones
averagePhi – The phi orientation of the sector (defaulted to 0)
halfPhiSector – The opening angle phi sector
-
ConeVolumeBounds(ActsScalar innerAlpha, ActsScalar innerOffsetZ, ActsScalar outerAlpha, ActsScalar outerOffsetZ, ActsScalar halflengthZ, ActsScalar averagePhi, ActsScalar halfPhiSector) noexcept(false)
Constructor - for general cone-cone setups.
- Parameters:
innerAlpha – The opening angle of the inner cone (0 if no cone)
innerOffsetZ – The tip z position in of the inner cone, w.r.t center
outerAlpha – The opening angle of the outer cone (0 if no cone)
outerOffsetZ – The tip z position in of the outer cone, w.r.t center
halflengthZ – The minimum z value of the inner and outer cones
averagePhi – The phi orientation of the sector
halfPhiSector – The opening angle phi sector
-
ConeVolumeBounds(const ConeVolumeBounds &cobo) = default
-
inline ConeVolumeBounds(const std::array<ActsScalar, eSize> &values) noexcept(false)
Constructor - from a fixed size array.
- Parameters:
values – The bound values
-
~ConeVolumeBounds() override = default
-
virtual Volume::BoundingBox boundingBox(const Transform3 *trf = nullptr, const Vector3 &envelope = {0, 0, 0}, const Volume *entity = nullptr) const final
Construct bounding box for this shape.
- Parameters:
trf – Optional transform
envelope – Optional envelope to add / subtract from min/max
entity – Entity to associate this bounding box with
- Returns:
Constructed bounding box
-
inline ActsScalar get(BoundValues bValue) const
Access to the bound values.
- Parameters:
bValue – the class nested enum for the array access
-
ActsScalar innerRmax() const
-
ActsScalar innerRmin() const
-
ActsScalar innerTanAlpha() const
-
virtual bool inside(const Vector3 &pos, ActsScalar tol = 0.) const final
This method checks if position in the 3D volume frame is inside the cylinder.
- Parameters:
pos – is the position in volume frame to be checked
tol – is the absolute tolerance to be applied
-
ConeVolumeBounds &operator=(const ConeVolumeBounds &cobo) = default
-
virtual std::vector<OrientedSurface> orientedSurfaces(const Transform3 &transform = Transform3::Identity()) const final
Oriented surfaces, i.e.
the decomposed boundary surfaces and the according navigation direction into the volume given the normal vector on the surface
It will throw an exception if the orientation prescription is not adequate
- Parameters:
transform – is the 3D transform to be applied to the boundary surfaces to position them in 3D space
- Returns:
a vector of surfaces bounding this volume
-
ActsScalar outerRmax() const
-
ActsScalar outerRmin() const
-
ActsScalar outerTanAlpha() const
-
virtual std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &os) const final
Output Method for std::ostream.
- Parameters:
os – is ostream operator to be dumped into
-
inline virtual VolumeBounds::BoundsType type() const final
Return the bounds type - for persistency optimization.
- Returns:
is a BoundsType enum
-
virtual std::vector<ActsScalar> values() const final
Return the bound values as dynamically sized vector.
- Returns:
this returns a copy of the internal values
-
ConeVolumeBounds() = delete
-
class ConstantBField : public Acts::MagneticFieldProvider
This class implements a simple constant magnetic field.
The magnetic field value has to be set at creation time, but can be updated later on.
Public Functions
-
inline explicit ConstantBField(Vector3 B)
Construct constant magnetic field from field vector.
- Parameters:
B – [in] magnetic field vector in global coordinate system
-
inline virtual Result<Vector3> getField(const Vector3 &position, MagneticFieldProvider::Cache &cache) const override
Retrieve magnetic field value at a given location.
Requires a cache object created through makeCache().
Note
The
positionis ignored and only kept as argument to provide a consistent interface with other magnetic field services.- Parameters:
position – [in] global 3D position for the lookup
cache – [inout] Field provider specific cache object
- Returns:
magnetic field vector at given position
-
inline virtual Result<Vector3> getFieldGradient(const Vector3 &position, ActsMatrix<3, 3> &derivative, MagneticFieldProvider::Cache &cache) const override
Retrieve magnetic field value its its gradient.
Requires a cache object created through makeCache().
Note
The
positionis ignored and only kept as argument to provide a consistent interface with other magnetic field services.Note
currently the derivative is not calculated
- Parameters:
position – [in] global 3D position
derivative – [out] gradient of magnetic field vector as (3x3) matrix
cache – [inout] Field provider specific cache object
- Returns:
magnetic field vector
-
inline bool isInside(const Vector3&) const
check whether given 3D position is inside look-up domain
- Returns:
Always true for constant magnetic field
-
inline virtual Acts::MagneticFieldProvider::Cache makeCache(const Acts::MagneticFieldContext &mctx) const override
Make an opaque cache for the magnetic field.
Instructs the specific implementation to generate a
Cacheinstance for magnetic field lookup.- Parameters:
mctx – The magnetic field context to generate cache for
- Returns:
Cache The opaque cache object
-
struct Cache
Public Functions
-
inline Cache(const MagneticFieldContext&)
constructor with context
-
inline Cache(const MagneticFieldContext&)
-
inline explicit ConstantBField(Vector3 B)
-
class ConstrainedStep
A constrained step class for the steppers.
This class is symmetrical for forward and backward propagation. The sign of the propagation direction should not enter here but rather be applied the step is actually taken.
As simple as this class looks it hides a few very important details:
Overstepping handling. The step size sign will flip if we happened to pass our target.
Convergence handling. Smaller and smaller step sizes have to be used in order to converge on a target.
Because of the points mentioned above, the update function will always prefer negative step sizes. A side effect of this is that we will propagate in the opposite direction if the target is “behind us”.
The hierarchy is:
Overstepping resolution / backpropagation
Convergence
Step into the void with
std::numeric_limits<Scalar>max()
Public Types
-
using Scalar = ActsScalar
Public Functions
-
constexpr ConstrainedStep() = default
-
inline explicit constexpr ConstrainedStep(Scalar value)
constructor from Scalar
- Parameters:
value – is the user given initial value
-
inline constexpr void release(Type type)
release a certain constraint value
- Parameters:
type – is the constraint type to be released
-
inline constexpr void releaseAccuracy()
release accuracy
-
inline constexpr void setAccuracy(Scalar value)
set accuracy by one Scalar
this will set only the accuracy, as this is the most exposed to the Propagator
- Parameters:
value – is the new accuracy value
-
inline constexpr void setUser(Scalar value)
set user by one Scalar
- Parameters:
value – is the new user value
-
inline std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &os) const
-
inline std::string toString() const
-
inline constexpr void update(Scalar value, Type type, bool releaseStep = false)
Update the step size of a certain type.
Only navigation and target abortion step size updates may change the sign due to overstepping
- Parameters:
value – is the new value to be updated
type – is the constraint type
releaseStep – Allow step size to increase again
Public Members
-
std::size_t nStepTrials = std::numeric_limits<std::size_t>::max()
Number of iterations needed by the stepsize finder (e.g.
Runge-Kutta) of the stepper.
-
template<int N>
class ConvexPolygonBounds : public Acts::ConvexPolygonBoundsBase This is the actual implementation of the bounds.
It is templated on the number of vertices, but there is a specialization for dynamic number of vertices, where the underlying storage is then a vector.
- Template Parameters:
N – Number of vertices
Public Types
-
using value_array = std::array<double, eSize>
Type that’s used to store the vertices, in this case a fixed size array.
-
using vertex_array = std::array<Vector2, num_vertices>
Type that’s used to store the vertices, in this case a fixed size array.
Public Functions
-
ConvexPolygonBounds() = delete
-
ConvexPolygonBounds(const std::vector<Vector2> &vertices) noexcept(false)
Constructor from a vector of vertices, to facilitate construction.
This will throw if the vector size does not match
num_vertices. This will throw if the vertices do not form a convex polygon.- Parameters:
vertices – The list of vertices.
-
ConvexPolygonBounds(const value_array &values) noexcept(false)
Constructor from a fixed size array of parameters This will throw if the vertices do not form a convex polygon.
- Parameters:
values – The values to build up the vertices
-
ConvexPolygonBounds(const vertex_array &vertices) noexcept(false)
Constructor from a fixed size array of vertices.
This will throw if the vertices do not form a convex polygon.
- Parameters:
vertices – The vertices
-
~ConvexPolygonBounds() override = default
-
virtual const RectangleBounds &boundingBox() const final
Return a rectangle bounds object that encloses this polygon.
- Returns:
The rectangular bounds
-
virtual bool inside(const Vector2 &lposition, const BoundaryCheck &bcheck) const final
Return whether a local 2D point lies inside of the bounds defined by this object.
- Parameters:
lposition – The local position to check
bcheck – The
BoundaryCheckobject handling tolerances.
- Returns:
Whether the points is inside
-
virtual BoundsType type() const final
Return the bounds type - for persistency optimization.
- Returns:
is a BoundsType enum
-
class ConvexPolygonBoundsBase : public Acts::PlanarBounds
base class for convex polygon bounds
This class serves as a base class for the actual bounds class. The only deriving type is the templated
ConvexPolygonBounds.Subclassed by Acts::ConvexPolygonBounds< N >, Acts::ConvexPolygonBounds< PolygonDynamic >
Public Functions
-
virtual std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &sl) const final
Output Method for std::ostream.
- Parameters:
sl – is the ostream to be written into
-
virtual std::vector<double> values() const final
Return the bound values as dynamically sized vector.
- Returns:
this returns a copy of the internal values
-
virtual std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &sl) const final
-
class CuboidVolumeBounds : public Acts::VolumeBounds
Bounds for a cubical Volume, the orientedSurfaces(…) method creates a vector of 6 surfaces:
BoundarySurfaceFace [index]:
negativeFaceXY [0] : Rectangular Acts::PlaneSurface, parallel to \( xy \) plane at negative \( z \)
positiveFaceXY [1] : Rectangular Acts::PlaneSurface, parallel to \( xy \) plane at positive \( z \)
negativeFaceXY [2] : Rectangular Acts::PlaneSurface, attached to \( yz \) plane at negative \( x \)
positiveFaceXY [3] : Rectangular Acts::PlaneSurface, attached to \( yz \) plane at negative \( x \)
negativeFaceXY [4] : Rectangular Acts::PlaneSurface, parallel to \( zx \) plane at negative \( y \)
positiveFaceXY [5] : Rectangular Acts::PlaneSurface, parallel to \( zx \) plane at positive \( y \)
Public Types
Public Functions
-
CuboidVolumeBounds() = delete
-
CuboidVolumeBounds(ActsScalar halex, ActsScalar haley, ActsScalar halez) noexcept(false)
Constructor - the box boundaries.
- Parameters:
halex – is the half length of the cube in x
haley – is the half length of the cube in y
halez – is the half length of the cube in z
-
CuboidVolumeBounds(const CuboidVolumeBounds &bobo) = default
Copy Constructor.
- Parameters:
bobo – is the source volume bounds to be copied
-
CuboidVolumeBounds(const std::array<ActsScalar, eSize> &values)
Constructor - from a fixed size array.
- Parameters:
values – iw the bound values
-
~CuboidVolumeBounds() override = default
-
virtual ActsScalar binningBorder(BinningValue bValue) const final
Binning borders in ActsScalar.
- Parameters:
bValue – is the binning schema used
- Returns:
float offset to be used for the binning
-
virtual Volume::BoundingBox boundingBox(const Transform3 *trf = nullptr, const Vector3 &envelope = {0, 0, 0}, const Volume *entity = nullptr) const final
Construct bounding box for this shape.
- Parameters:
trf – Optional transform
envelope – Optional envelope to add / subtract from min/max
entity – Entity to associate this bounding box with
- Returns:
Constructed bounding box
-
inline virtual std::vector<Acts::BinningValue> canonicalBinning() const override
Get the canonical binning values, i.e.
the binning values for that fully describe the shape’s extent
- Returns:
vector of canonical binning values
-
inline ActsScalar get(BoundValues bValue) const
Access to the bound values.
- Parameters:
bValue – the class nested enum for the array access
-
virtual bool inside(const Vector3 &pos, ActsScalar tol = 0.) const override
This method checks if position in the 3D volume frame is inside the cylinder.
- Parameters:
pos – is the position in volume frame to be checked
tol – is the absolute tolerance to be applied
-
CuboidVolumeBounds &operator=(const CuboidVolumeBounds &bobo) = default
Assignment operator.
- Parameters:
bobo – is the source volume bounds to be assigned
-
virtual std::vector<OrientedSurface> orientedSurfaces(const Transform3 &transform = Transform3::Identity()) const override
Oriented surfaces, i.e.
the decomposed boundary surfaces and the according navigation direction into the volume given the normal vector on the surface
It will throw an exception if the orientation prescription is not adequate
- Parameters:
transform – is the 3D transform to be applied to the boundary surfaces to position them in 3D space
- Returns:
a vector of surfaces bounding this volume
-
void set(BoundValues bValue, ActsScalar value)
Set a bound value.
- Parameters:
bValue – the bound value identifier
value – the value to be set
-
void set(std::initializer_list<std::pair<BoundValues, ActsScalar>> keyValues)
Set a range of bound values.
- Parameters:
keyValues – the initializer list of key value pairs
-
virtual std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &os) const override
Output Method for std::ostream.
- Parameters:
os – is ostream operator to be dumped into
-
inline virtual VolumeBounds::BoundsType type() const final
Return the bounds type - for persistency optimization.
- Returns:
is a BoundsType enum
-
virtual std::vector<ActsScalar> values() const final
Return the bound values as dynamically sized vector.
- Returns:
this returns a copy of the internal values
-
class CutoutCylinderVolumeBounds : public Acts::VolumeBounds
Class which implements a cutout cylinder.
This shape is basically a cylinder, with another, smaller cylinder subtracted from the center. ——————— rmax | | | |———| | rmed | | | | —— —— rmin — hlZc — ——— hlZ —-—
Public Types
Public Functions
-
CutoutCylinderVolumeBounds() = delete
-
inline CutoutCylinderVolumeBounds(const std::array<double, eSize> &values) noexcept(false)
Constructor - from a fixed size array.
- Parameters:
values – The bound values
-
inline CutoutCylinderVolumeBounds(double rmin, double rmed, double rmax, double hlZ, double hlZc) noexcept(false)
Constructor from defining parameters.
- Parameters:
rmin – Minimum radius at the “choke points”
rmed – The medium radius (outer radius of the cutout)
rmax – The outer radius of the overall shape
hlZ – The longer halflength of the shape
hlZc – The cutout halflength of the shape
-
~CutoutCylinderVolumeBounds() override = default
-
virtual Volume::BoundingBox boundingBox(const Transform3 *trf = nullptr, const Vector3 &envelope = {0, 0, 0}, const Volume *entity = nullptr) const final
Construct bounding box for this shape.
- Parameters:
trf – Optional transform
envelope – Optional envelope to add / subtract from min/max
entity – Entity to associate this bounding box with
- Returns:
Constructed bounding box
-
inline virtual std::vector<Acts::BinningValue> canonicalBinning() const override
Get the canonical binning values, i.e.
the binning values for that fully describe the shape’s extent
- Returns:
vector of canonical binning values
-
inline double get(BoundValues bValue) const
Access to the bound values.
- Parameters:
bValue – the class nested enum for the array access
-
virtual bool inside(const Vector3 &gpos, double tol = 0) const override
Inside method to test whether a point is inside the shape.
- Parameters:
gpos – The point to test
tol – The tolerance to test with
- Returns:
Whether the point is inside or not.
-
virtual std::vector<OrientedSurface> orientedSurfaces(const Transform3 &transform = Transform3::Identity()) const override
Oriented surfaces, i.e.
the decomposed boundary surfaces and the according navigation direction into the volume given the normal vector on the surface
It will throw an exception if the orientation prescription is not adequate
- Parameters:
transform – is the 3D transform to be applied to the boundary surfaces to position them in 3D space
- Returns:
a vector of surfaces bounding this volume
-
virtual std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &sl) const override
Write information about this instance to an outstream.
- Parameters:
sl – The outstream
- Returns:
The outstream
-
inline virtual VolumeBounds::BoundsType type() const final
Return the bounds type - for persistency optimization.
- Returns:
is a BoundsType enum
-
inline virtual std::vector<double> values() const final
Return the bound values as dynamically sized vector.
- Returns:
this returns a copy of the internal values
-
CutoutCylinderVolumeBounds() = delete
-
class CylinderBounds : public Acts::SurfaceBounds
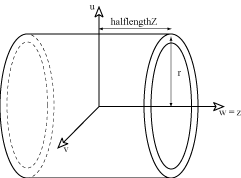
Bounds for a cylindrical Surface.
These bounds may be used for a CylinderSurface In case of bounds for a StraightLineSurface the radius determines the radius within a localPosition is regarded as inside bounds.
CylinderBounds also enhance the possibility of a cylinder segment with an opening angle \( 2\cdot\phi_{half}\) around an average \( \phi \) angle \( \phi_{ave} \).
CylinderBounds also supports beveled sides defined by an angle. Different angles can be defined on both sides of the cylinder. A positive angle is defined as “extruding” from the defined Zlength, while a negative angle is “intruding” on the Zlength.
- - +
\ | / \ | / \ | / \ | / |/______________|/ 2 * ZhalfLength
Public Types
Public Functions
-
CylinderBounds() = delete
-
inline CylinderBounds(const std::array<double, eSize> &values) noexcept(false)
Constructor - from fixed size array.
- Parameters:
values – The parameter values
-
inline CylinderBounds(double r, double halfZ, double halfPhi = M_PI, double avgPhi = 0., double bevelMinZ = 0., double bevelMaxZ = 0.) noexcept(false)
Constructor - full cylinder.
- Parameters:
r – The radius of the cylinder
halfZ – The half length in z
halfPhi – The half opening angle
avgPhi – (optional) The phi value from which the opening angle spans
bevelMinZ – (optional) The bevel on the negative z side
bevelMaxZ – (optional) The bevel on the positive z sid The bevel on the positive z side
-
~CylinderBounds() override = default
-
inline bool coversFullAzimuth() const
Returns true for full phi coverage.
-
std::vector<Vector3> createCircles(const Transform3 trans, std::size_t lseg) const
Create the bows/circles on either side of the cylinder.
- Parameters:
trans – is the global transform
lseg – are the numbero if phi segments
-
inline double get(BoundValues bValue) const
Access to the bound values.
- Parameters:
bValue – the class nested enum for the array access
-
virtual bool inside(const Vector2 &lposition, const BoundaryCheck &bcheck) const final
Inside check for the bounds object driven by the boundary check directive Each Bounds has a method inside, which checks if a LocalPosition is inside the bounds Inside can be called without/with tolerances.
- Parameters:
lposition – Local position (assumed to be in right surface frame)
bcheck – boundary check directive
- Returns:
boolean indicator for the success of this operation
-
bool inside3D(const Vector3 &position, const BoundaryCheck &bcheck = BoundaryCheck(true)) const
Specialized method for CylinderBounds that checks if a global position is within the cylinder cover.
- Parameters:
position – is the position in the cylinder frame
bcheck – is the boundary check directive
- Returns:
boolean indicator for operation success
-
virtual std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &sl) const final
Output Method for std::ostream.
-
virtual BoundsType type() const final
Return the bounds type - for persistency optimization.
- Returns:
is a BoundsType enum
-
inline virtual std::vector<double> values() const final
Return the bound values as dynamically sized vector.
- Returns:
this returns a copy of the internal values
-
class CylinderLayer : public Acts::CylinderSurface, public Acts::Layer
Class to describe a cylindrical detector layer for tracking, it inhertis from both, Layer base class and CylinderSurface class.
Public Functions
-
CylinderLayer() = delete
-
CylinderLayer(const CylinderLayer &cla) = delete
-
~CylinderLayer() override = default
-
CylinderLayer &operator=(const CylinderLayer&) = delete
-
virtual const CylinderSurface &surfaceRepresentation() const override
Transforms the layer into a Surface representation This is for positioning and extrapolation.
-
virtual CylinderSurface &surfaceRepresentation() override
Public Static Functions
Factory for shared Layer pointer create a shared, fully deployed CylinderLayer.
- Parameters:
transform – is the 3D transform that places the layer in 3D space
cbounds – are the cylindrical bounds of the layer
surfaceArray – is the Binned Array that holds the sensitive surfaces
thickness – is the layer thickness (along the normal)
ad – is the approach descriptor for approaching the layer
laytyp – is the layer type
- Returns:
The return object is a shared pointer to the layer.
-
CylinderLayer() = delete
-
class CylinderSurface : public Acts::RegularSurface
Class for a CylinderSurface in the TrackingGeometry.
It inherits from Surface.
The cylinder surface has a special role in the TrackingGeometry, since it builds the surfaces of all TrackingVolumes at container level for a cylindrical tracking geometry.
Subclassed by Acts::CylinderLayer
Public Functions
-
CylinderSurface() = delete
-
~CylinderSurface() override = default
-
virtual AlignmentToPathMatrix alignmentToPathDerivative(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction) const final
Calculate the derivative of path length at the geometry constraint or point-of-closest-approach w.r.t.
alignment parameters of the surface (i.e. local frame origin in global 3D Cartesian coordinates and its rotation represented with extrinsic Euler angles)
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – global 3D position
direction – global 3D momentum direction
- Returns:
Derivative of path length w.r.t. the alignment parameters
-
virtual Vector3 binningPosition(const GeometryContext &gctx, BinningValue bValue) const final
The binning position method - is overloaded for r-type binning.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
bValue – is the type of global binning to be done
- Returns:
is the global position to be used for binning
-
virtual const CylinderBounds &bounds() const final
This method returns the CylinderBounds by reference.
-
Result<Vector2> globalToLocal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction, double tolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance) const final
Convert a global position to a local one this is the most generic interface, which is implemented by all surfaces.
Note
The
positionis required to be on-surface, which is indicated by theResultreturn value.- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – is the global position to be converted
direction – is the direction of the local position (ignored for
RegularSurface)tolerance – is the tolerance for the on-surface check
- Returns:
Result type containing local position by value
-
virtual Result<Vector2> globalToLocal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, double tolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance) const final
Global to local transformation.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – is the global position to be transformed
tolerance – optional tolerance within which a point is considered valid on surface
- Returns:
a Result<Vector2> which can be !ok() if the operation fails
-
Result<Vector2> globalToLocal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, double tolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance) const = 0
Convert a global position to a local one.
Note
The
positionis required to be on-surface, which is indicated by theResultreturn value.- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – is the global position to be converted
tolerance – is the tolerance for the on-surface check
- Returns:
Result type containing local position by value
-
virtual SurfaceMultiIntersection intersect(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction, const BoundaryCheck &bcheck = BoundaryCheck(false), ActsScalar tolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance) const final
Straight line intersection schema from position/direction.
If possible returns both solutions for the cylinder
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – The position to start from
direction – The direction at start
bcheck – the Boundary Check
tolerance – the tolerance used for the intersection
- Returns:
SurfaceIntersection object (contains intersection & surface)
-
virtual ActsMatrix<2, 3> localCartesianToBoundLocalDerivative(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position) const final
Calculate the derivative of bound track parameters local position w.r.t.
position in local 3D Cartesian coordinates
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – The position of the parameters in global
- Returns:
Derivative of bound local position w.r.t. position in local 3D cartesian coordinates
-
virtual Vector3 localToGlobal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector2 &lposition) const final
Local to global transformation.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lposition – is the local position to be transformed
- Returns:
The global position by value
-
Vector3 localToGlobal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector2 &lposition) const = 0
Local to global transformation.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lposition – local 2D position in specialized surface frame
- Returns:
The global position by value
-
Vector3 localToGlobal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector2 &lposition, const Vector3 &direction) const final
Local to global transformation.
This is the most generic interface, which is implemented by all surfaces.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lposition – local 2D position in specialized surface frame
direction – global 3D momentum direction (ignored for
RegularSurface)
- Returns:
The global position by value
-
virtual std::string name() const override
Return method for properly formatted output string.
-
virtual Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector2 &lposition) const final
Return method for surface normal information.
Note
for a Cylinder a local position is always required for the normal vector
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lposition – is the local position for which the normal vector is requested
- Returns:
normal vector at the local position by value
-
Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector2 &lposition) const = 0
Calculate the normal vector of the surface This overload requires an on-surface local position.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lposition – is the local position where the normal vector is constructed
- Returns:
normal vector by value
-
Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &pos, const Vector3 &direction) const final
Calculate the normal vector of the surface This overload is fully generic, fulfills the Surface interface and accepts a global position and a direction.
For
RegularSurfacethis is equivalent to the normal overload, ignoring thedirection- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
pos – is the global position where the normal vector is constructed
direction – is the direction of the normal vector (ignored for
RegularSurface)
-
virtual Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position) const final
Return method for surface normal information.
Note
for a Cylinder a local position is always required for the normal vector
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – is the global position for which the normal vector is requested
- Returns:
normal vector at the global position by value
-
Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position) const = 0
Calculate the normal vector of the surface This overload accepts a global position.
- Parameters:
position – is the global position where the normal vector is constructed
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
- Returns:
normal vector by value
-
CylinderSurface &operator=(const CylinderSurface &other)
Assignment operator.
- Parameters:
other – is the source cylinder for the copy
-
virtual double pathCorrection(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction) const final
Path correction due to incident of the track.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – is the global position as a starting point
direction – is the global momentum direction at the starting point
- Returns:
is the correction factor due to incident
-
virtual Polyhedron polyhedronRepresentation(const GeometryContext &gctx, std::size_t lseg) const override
Return a Polyhedron for a cylinder.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lseg – Number of segments along curved lines, it represents the full 2*M_PI coverange, if lseg is set to 1 only the extrema are given
- Returns:
A list of vertices and a face/facett description of it
-
virtual RotationMatrix3 referenceFrame(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction) const final
Return the measurement frame - this is needed for alignment, in particular The measurement frame of a cylinder is the tangential plane at a given position.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – is the position where the measurement frame is defined
direction – is the momentum direction vector (ignored)
- Returns:
rotation matrix that defines the measurement frame
-
virtual Vector3 rotSymmetryAxis(const GeometryContext &gctx) const
Return method for the rotational symmetry axis.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
- Returns:
the z-Axis of transform
-
virtual SurfaceType type() const override
Return the surface type.
-
CylinderSurface() = delete
-
class CylinderVolumeBounds : public Acts::VolumeBounds
[0] and [1] at positive \( \phi \)
Bounds for a cylindrical Volume, the orientedSurfaces(..) method creates a vector of up to 6 surfaces:
case A) 3 Surfaces (full cylindrical tube): BoundarySurfaceFace [index]:
negativeFaceXY [0] : Acts::DiscSurface with \( r_{inner}=0 \), parallel to \( xy \) plane at negative \( z\)
positiveFaceXY [1] : Acts::DiscSurface with \( r_{inner}=0 \), parallel to \( xy \) plane at positive \( z\)
cylinderCover [2] : Acts::CylinderSurface confining the Acts::Volume
case B) 4 Surfaces (tube with inner and outer radius): BoundarySurfaceFace [index]:
negativeFaceXY [0] : Acts::DiscSurface with \( r_{inner}>0 \), parallel to \( xy \) plane at negative \( z\)
positiveFaceXY [1] : Acts::DiscSurface with \( r_{inner}>0 \), parallel to \( xy \) plane at positive \( z\)
tubeOuterCover [2] : Acts::CylinderSurface with \( r = r_{outer} \)
tubeInnerCover [3] : Acts::CylinderSurface with \( r = r_{inner} \)
case C) 6 Surfaces (sectoral tube with inner and outer radius): BoundarySurfaceFace [index]:
negativeFaceXY [0] : Acts::DiscSurface with \( r_{inner}>0\) and \( \phi < \pi \), parallel to \( xy \) plane at negative \(z\)
positiveFaceXY [1] : Acts::DiscSurface with \( r_{inner}>0 \) and \( \phi < \pi \), parallel to \( xy \) plane at positive \(z\)
tubeSectorOuterCover [2] : Acts::CylinderSurface with \( r = r_{outer}\)
tubeSectorInnerCover [3] : Acts::CylinderSurface with \( r = r_{inner} \)
tubeSectorNegativePhi [4] : Rectangular Acts::PlaneSurface attached to [0] and [1] at negative \( \phi \)
tubeSectorNegativePhi [5] :
Public Types
Public Functions
-
CylinderVolumeBounds() = delete
-
CylinderVolumeBounds(ActsScalar rmin, ActsScalar rmax, ActsScalar halfz, ActsScalar halfphi = M_PI, ActsScalar avgphi = 0., ActsScalar bevelMinZ = 0., ActsScalar bevelMaxZ = 0.)
Constructor.
- Parameters:
rmin – The inner radius of the cylinder
rmax – The outer radius of the cylinder
halfz – The half length in z
halfphi – The half lopening angle
avgphi – The average phi value
bevelMinZ – The bevel angle, in radians, for the negative side
bevelMaxZ – The bevel angle, in radians, for the positive side
-
CylinderVolumeBounds(const CylinderBounds &cBounds, ActsScalar thickness)
Constructor - extruded from cylinder bounds and thickness.
- Parameters:
cBounds – the cylinder bounds
thickness – of the extrusion
-
CylinderVolumeBounds(const CylinderVolumeBounds &cylbo) = default
Copy Constructor.
- Parameters:
cylbo – is the source cylinder volume bounds for the copy
-
CylinderVolumeBounds(const RadialBounds &rBounds, ActsScalar thickness)
Constructor - extruded from radial bounds and thickness.
- Parameters:
rBounds – the Radial bounds
thickness –
-
CylinderVolumeBounds(const std::array<ActsScalar, eSize> &values)
Constructor - from a fixed size array.
- Parameters:
values – The bound values
-
~CylinderVolumeBounds() override = default
-
virtual ActsScalar binningBorder(BinningValue bValue) const override
Binning borders in ActsScalar.
- Parameters:
bValue – is the type used for the binning
-
virtual Vector3 binningOffset(BinningValue bValue) const override
Binning offset - overloaded for some R-binning types.
- Parameters:
bValue – is the type used for the binning
-
virtual Volume::BoundingBox boundingBox(const Transform3 *trf = nullptr, const Vector3 &envelope = {0, 0, 0}, const Volume *entity = nullptr) const final
Construct bounding box for this shape.
- Parameters:
trf – Optional transform
envelope – Optional envelope to add / subtract from min/max
entity – Entity to associate this bounding box with
- Returns:
Constructed bounding box
-
inline virtual std::vector<Acts::BinningValue> canonicalBinning() const override
Get the canonical binning values, i.e.
the binning values for that fully describe the shape’s extent
- Returns:
vector of canonical binning values
-
inline ActsScalar get(BoundValues bValue) const
Access to the bound values.
- Parameters:
bValue – the class nested enum for the array access
-
virtual bool inside(const Vector3 &pos, ActsScalar tol = 0.) const override
This method checks if position in the 3D volume frame is inside the cylinder.
- Parameters:
pos – is a global position to be checked
tol – is the tolerance for the check
-
CylinderVolumeBounds &operator=(const CylinderVolumeBounds &cylbo) = default
-
virtual std::vector<OrientedSurface> orientedSurfaces(const Transform3 &transform = Transform3::Identity()) const override
Oriented surfaces, i.e.
the decomposed boundary surfaces and the according navigation direction into the volume given the normal vector on the surface
It will throw an exception if the orientation prescription is not adequate
- Parameters:
transform – is the 3D transform to be applied to the boundary surfaces to position them in 3D space
- Returns:
a vector of surfaces bounding this volume
-
void set(BoundValues bValue, ActsScalar value)
Set a bound value.
- Parameters:
bValue – the bound value identifier
value – the value to be set
-
void set(std::initializer_list<std::pair<BoundValues, ActsScalar>> keyValues)
Set a range of bound values.
- Parameters:
keyValues – the initializer list of key value pairs
-
virtual std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &os) const override
Output Method for std::ostream.
- Parameters:
os – is the output stream
-
inline virtual VolumeBounds::BoundsType type() const final
Return the bounds type - for persistency optimization.
- Returns:
is a BoundsType enum
-
virtual std::vector<ActsScalar> values() const final
Return the bound values as dynamically sized vector.
- Returns:
this returns a copy of the internal values
-
class CylinderVolumeBuilder : public Acts::ITrackingVolumeBuilder
A volume builder to be used for building a concentrical cylindrical volumes.
a) configured volume
b) wrapping around a cylindrical/disk layer config
All are optionally wrapped around a given volume which has to by a cylinder volume and which has to be center at z == 0
To receive the tracking volume it is possible to also hand over a triple of layers, which is a C++ tuple of three pointers to layer vectors (defined in the ITrackingVolumeBuilder). This functionality is needed for a possible translation of an geometry existing in another format. The first entry represents the layers of the negative endcap, the second the layers of the barrel and the third the layers of the positive endcap. If the one of these pointers is a nullptr no layers will be created for this volume
For the endcap region it is possible to check for a ring layout, in which case an attempt to split into individual ring volumes is done
Public Functions
-
CylinderVolumeBuilder(const Config &cvbConfig, std::unique_ptr<const Logger> logger = getDefaultLogger("CylinderVolumeBuilder", Logging::INFO))
Constructor.
- Parameters:
cvbConfig – [in] is the configuration struct to steer the builder
logger – [in] logging instance
-
~CylinderVolumeBuilder() override
Destructor.
-
VolumeConfig analyzeContent(const GeometryContext &gctx, const LayerVector &lVector, const MutableTrackingVolumeVector &mtvVector) const
Analyze the config to gather needed dimension.
- Parameters:
gctx – [in] the geometry context for this building
lVector – [in] is the vector of layers that are parsed
mtvVector – [in] Vector of mutable tracking volumes to analyze
- Returns:
a VolumeConfig representing this layer
-
inline Config getConfiguration() const
Get configuration method.
Return the configuration object.
- Returns:
a copy of the config object
-
void setConfiguration(const Config &cvbConfig)
Set configuration method.
- Parameters:
cvbConfig – [in] is the new configuration to be set
-
void setLogger(std::unique_ptr<const Logger> newLogger)
set logging instance
- Parameters:
newLogger – [in] is the logging instance to be set
CylinderVolumeBuilder main call method.
- Parameters:
gctx – [in] geometry context for which this cylinder volume is built
existingVolume – [in] is an (optional) volume to be included
externalBounds – [in] are (optional) external confinement constraints
- Returns:
a mutable pointer to a new TrackingVolume which includes the optionally provided existingVolume consistently for further processing
-
struct Config
Nested configuration struct for this CylinderVolumeBuilder.
Public Members
-
std::array<std::shared_ptr<const ISurfaceMaterial>, 6> boundaryMaterial{nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr}
—————–— MB (outer [1]) ————— | MB [2] NEC MB [3] | B | MB [4] PEC MB [5] | —————–— MB (inner [0]) —————
-
bool buildToRadiusZero = false
Build the volume to the beam line.
-
bool checkRingLayout = false
Check for endcap ring layout.
-
std::shared_ptr<const IConfinedTrackingVolumeBuilder> ctVolumeBuilder = nullptr
Builder to construct confined volumes within the volume.
-
std::shared_ptr<const ILayerBuilder> layerBuilder = nullptr
Builder to construct layers within the volume.
-
std::pair<double, double> layerEnvelopeR = {1. * UnitConstants::mm, 1. * UnitConstants::mm}
Additional envelope in R to create rMin, rMax.
-
double layerEnvelopeZ = 1. * UnitConstants::mm
the additional envelope in Z to create zMin, zMax
-
double ringTolerance = 0 * UnitConstants::mm
Tolerance for endcap ring association.
-
std::shared_ptr<const ITrackingVolumeHelper> trackingVolumeHelper = nullptr
The tracking volume helper for construction.
-
std::shared_ptr<const IVolumeMaterial> volumeMaterial = nullptr
The world material.
-
std::string volumeName = ""
The string based identification.
-
std::array<std::shared_ptr<const ISurfaceMaterial>, 6> boundaryMaterial{nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr}
-
class DD4hepDetectorElement : public Acts::TGeoDetectorElement
DetectorElement class implementation for DD4hep geometry.
DetectorElement plugin for DD4hep detector elements. DD4hep is based on TGeo shapes, therefore the DD4hepDetectorElement inherits from TGeoDetectorElement in order to perform the conversion.
The full geometrical information is provided by the TGeoDetectorElement. The DD4hepDetectorElement extends the TGeoDetectorElement by containing a segmentation for the readout.
Public Types
-
using ContextType = GeometryContext
Broadcast the context type.
-
using DD4hepVolumeID = dd4hep::DDSegmentation::VolumeID
-
using Store = std::map<std::string, std::vector<std::shared_ptr<DD4hepDetectorElement>>>
Define a string based story.
Public Functions
Constructor.
Example options are:
”XYZ” -> identical frame definition (default value)
”YZX” -> node y axis is tracking x axis, etc.
”XzY” -> negative node z axis is tracking y axis, etc.
Note
In the translation from a 3D geometry (TGeo) which only knows tubes to a 2D geometry (Tracking geometry) a distinction if the module should be described as a cylinder or a disc surface needs to be done. Since this information can not be taken just from the geometry description (both can be described as TGeoTubeSeg), one needs to set the flag ‘isDisc’ in case a volume with shape
TGeoTubeSegshould be translated to a disc surface. Per default it will be translated into a cylindrical surface.- Parameters:
scalor – is the scale factor for unit conversion if needed
isDisc – in case the sensitive detector module should be translated as disc (e.g. for endcaps) this flag should be set to true
material – Optional material of detector element
detElement – The DD4hep DetElement which should be associated to an ACTS surface
axes – is the axis orientation with respect to the tracking frame it is a string of the three characters x, y and z (standing for the three axes) There is a distinction between capital and lower case characters :
capital -> positive orientation of the axis
lower case -> negative orientation of the axis
-
~DD4hepDetectorElement() override = default
-
inline const dd4hep::DetElement &sourceElement() const
-
using ContextType = GeometryContext
-
template<typename, typename H = void, DelegateType = DelegateType::NonOwning>
class Delegate
-
class DetectorElementBase
Subclassed by Acts::Geant4DetectorElement, Acts::IdentifiedDetectorElement
Public Functions
-
DetectorElementBase() = default
-
virtual ~DetectorElementBase() = default
-
virtual double thickness() const = 0
Returns the thickness of the module.
- Returns:
double that indicates the thickness of the module
-
virtual const Transform3 &transform(const GeometryContext &gctx) const = 0
Return the transform for the Element proxy mechanism.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
-
DetectorElementBase() = default
-
class DiamondBounds : public Acts::PlanarBounds
Bounds for a double trapezoidal (“diamond”), planar Surface.
Public Types
Public Functions
-
DiamondBounds() = delete
-
inline DiamondBounds(const std::array<double, eSize> &values) noexcept(false)
Constructor - from fixed size array.
- Parameters:
values – The parameter values
-
inline DiamondBounds(double halfXnegY, double halfXzeroY, double halfXposY, double halfYneg, double halfYpos) noexcept(false)
Constructor for convex hexagon symmetric about the y axis.
- Parameters:
halfXnegY – is the halflength in x at minimal y
halfXzeroY – is the halflength in x at y = 0
halfXposY – is the halflength in x at maximal y
halfYneg – is the halflength into y < 0
halfYpos – is the halflength into y > 0
-
~DiamondBounds() override = default
-
virtual const RectangleBounds &boundingBox() const final
Bounding box parameters.
- Returns:
rectangle bounds for a bounding box
-
inline double get(BoundValues bValue) const
Access to the bound values.
- Parameters:
bValue – the class nested enum for the array access
-
virtual bool inside(const Vector2 &lposition, const BoundaryCheck &bcheck) const final
Inside check for the bounds object driven by the boundary check directive Each Bounds has a method inside, which checks if a LocalPosition is inside the bounds Inside can be called without/with tolerances.
- Parameters:
lposition – Local position (assumed to be in right surface frame)
bcheck – boundary check directive
- Returns:
boolean indicator for the success of this operation
-
virtual std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &sl) const final
Output Method for std::ostream.
- Parameters:
sl – is the ostream in which it is dumped
-
virtual BoundsType type() const final
Return the bounds type - for persistency optimization.
- Returns:
is a BoundsType enum
-
inline virtual std::vector<double> values() const final
Return the bound values as dynamically sized vector.
- Returns:
this returns a copy of the internal values
-
DiamondBounds() = delete
This is a fully guided navigator that progresses through a pre-given sequence of surfaces.
This can either be used as a validation tool, for truth tracking, or track refitting.
Public Types
The sequentially crossed surfaces.
Public Functions
Initialize call - start of propagation.
- Template Parameters:
propagator_state_t – The state type of the propagator
stepper_t – The type of stepper used for the propagation
- Parameters:
state – [inout] is the propagation state object
Navigator post step call.
- Template Parameters:
propagator_state_t – is the type of Propagatgor state
stepper_t – is the used type of the Stepper by the Propagator
- Parameters:
state – [inout] is the mutable propagator state object
stepper – [in] Stepper in use
Navigator pre step call.
- Template Parameters:
propagator_state_t – is the type of Propagatgor state
stepper_t – is the used type of the Stepper by the Propagator
- Parameters:
state – [inout] is the mutable propagator state object
stepper – [in] Stepper in use
Nested Actor struct, called Initializer.
This is needed for the initialization of the surface sequence.
Public Types
Public Functions
Defaulting the constructor.
Actor operator call.
- Template Parameters:
statet – Type of the full propagator state
stepper_t – Type of the stepper
navigator_t – Type of the navigator
- Parameters:
state – the entire propagator state
r – the result of this Actor
Public Members
The Surface sequence.
Actor result / state.
Public Members
Nested State struct.
It acts as an internal state which is created for every propagation/extrapolation step and keep thread-local navigation information
Public Members
Navigation state - external interface: the current surface.
Navigation state: the current volume.
Navigation state - external interface: a break has been detected.
Iterator the next surface.
Externally provided surfaces - expected to be ordered along the path.
Navigation state - starting layer.
Navigation state - external interface: the start surface.
Navigation state: the start volume.
Navigation state - target layer.
Navigation state - external interface: target is reached.
Navigation state - external interface: the target surface.
Navigation state: the target volume.
-
class Direction
The direction is always with respect to a given momentum, surface normal or other general axes.
Public Functions
-
inline constexpr Direction() = default
-
inline constexpr Direction(Value value)
-
inline constexpr std::size_t index() const
Convert dir to index [0,1] which allows to store direction dependent objects in std::array<T, 2u>
- Returns:
either 0 or 1
-
inline constexpr int sign() const
Turns the direction into a signed value.
- Returns:
a signed value
-
std::string toString() const
Public Static Functions
-
static inline constexpr Direction fromIndex(std::size_t index)
Convert and index [0,1] to a direction e.g.
for sorting in std::array<T, 2u>
- Parameters:
index – is the direction at input
-
static inline constexpr Direction fromScalar(ActsScalar scalar)
This turns a signed value into a direction.
Will assert on zero.
- Parameters:
scalar – is the signed value
- Returns:
a direction enum
-
static inline constexpr Direction fromScalarZeroAsPositive(ActsScalar scalar)
This turns a signed value into a direction and 0 will be handled as a positive direction.
Only use this when you are convinced that the 0 case is properly handled downstream.
- Parameters:
scalar – is the signed value
- Returns:
a direction enum
Public Static Attributes
-
static constexpr auto AlongNormal = Value::Positive
-
static constexpr auto Backward = Value::Negative
-
static constexpr auto Forward = Value::Positive
-
static constexpr auto Negative = Value::Negative
-
static constexpr auto OppositeNormal = Value::Negative
-
static constexpr auto Positive = Value::Positive
-
inline constexpr Direction() = default
-
class DiscBounds : public Acts::SurfaceBounds
common base class for all bounds that are in a r/phi frame
simply introduced to avoid wrong bound assignments to surfaces
Subclassed by Acts::AnnulusBounds, Acts::DiscTrapezoidBounds, Acts::RadialBounds
Public Functions
-
virtual double binningValuePhi() const = 0
Returns a refererance phi for binning.
-
virtual double binningValueR() const = 0
Returns a reference radius for binning.
-
virtual bool coversFullAzimuth() const = 0
Returns true for full phi coverage.
-
virtual bool insideRadialBounds(double R, double tolerance = 0.) const = 0
Checks if it’s inside the radius.
-
virtual double rMax() const = 0
Return method for outer Radius.
-
virtual double rMin() const = 0
Return method for inner Radius.
-
virtual std::vector<Vector2> vertices(unsigned int lseg) const = 0
Return the vertices.
Note
that the extremas are given, which may slightly alter the number of segments returned
- Parameters:
lseg – the number of segments used to approximate and eventually curved line, the number refers to full 2*PI
- Returns:
vector for vertices in 2D
-
class DiscLayer : public virtual Acts::DiscSurface, public Acts::Layer
Class to describe a disc-like detector layer for tracking, it inhertis from both, Layer base class and DiscSurface class.
Public Functions
-
DiscLayer() = delete
-
~DiscLayer() override = default
-
virtual const DiscSurface &surfaceRepresentation() const override
Transforms the layer into a Surface representation for extrapolation.
- Returns:
This method returns a surface reference
-
virtual DiscSurface &surfaceRepresentation() override
Public Static Functions
Factory constructor with DiscSurface components.
- Parameters:
transform – is the transform to place the layer in the 3D frame
dbounds – are the disc bounds that describe the layer dimensions
surfaceArray – is the array of sensitive surfaces
thickness – is the layer thickness (along the normal vector)
ad – is the approach descriptor that provides the approach surface
laytyp – is the layer type
- Returns:
a sharted pointer to the new layer
-
DiscLayer() = delete
-
class DiscSurface : public Acts::RegularSurface
Class for a disc surface (or a segment thereof)
The DiscSurface is defined by the local polar coordinates \( (r,phi) \).
The surface transform positions the disc such that the origin is at \( r=0 \), independent of the provided
DiscBounds. The normal vector of the disc (i.e., the local \(z\)-axis) is given by \( \vec e_{z} = \vec e_{r} \times\vec e_{phi} \).The disc surface The only surface type for which the covariance matrix is NOT given in the reference frame. A conversion from polar to cartesian coordinates needs to happen to transfer the local coordinates onto the cartesian reference frame coordinates.
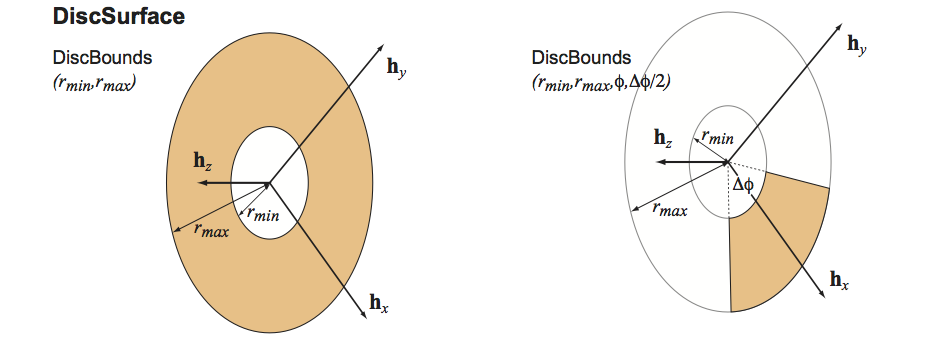
Subclassed by Acts::DiscLayer
Public Functions
-
DiscSurface() = delete
-
~DiscSurface() override = default
-
virtual Vector3 binningPosition(const GeometryContext &gctx, BinningValue bValue) const final
The binning position The position calculated for a certain binning type.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
bValue – The binning type to be used
- Returns:
position that can beused for this binning
-
virtual double binningPositionValue(const GeometryContext &gctx, BinningValue bValue) const final
Implement the binningValue.
Note
This calls the parent method except for binR
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
bValue – is the dobule in which you want to bin
- Returns:
float to be used for the binning schema
-
virtual const SurfaceBounds &bounds() const final
This method returns the bounds by reference.
-
virtual BoundToFreeMatrix boundToFreeJacobian(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction) const final
Calculate the jacobian from local to global which the surface knows best, hence the calculation is done here.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – global 3D position
direction – global 3D momentum direction
- Returns:
Jacobian from local to global
-
virtual FreeToBoundMatrix freeToBoundJacobian(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction) const final
Calculate the jacobian from global to local which the surface knows best, hence the calculation is done here.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – global 3D position
direction – global 3D momentum direction
- Returns:
Jacobian from global to local
-
Result<Vector2> globalToLocal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction, double tolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance) const final
Convert a global position to a local one this is the most generic interface, which is implemented by all surfaces.
Note
The
positionis required to be on-surface, which is indicated by theResultreturn value.- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – is the global position to be converted
direction – is the direction of the local position (ignored for
RegularSurface)tolerance – is the tolerance for the on-surface check
- Returns:
Result type containing local position by value
-
virtual Result<Vector2> globalToLocal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, double tolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance) const final
Global to local transformation.
Note
the direction is ignored for Disc surfaces in this calculateion
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – global 3D position - considered to be on surface but not inside bounds (check is done)
tolerance – optional tolerance within which a point is considered valid on surface
- Returns:
a Result<Vector2> which can be !ok() if the operation fails
-
Result<Vector2> globalToLocal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, double tolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance) const = 0
Convert a global position to a local one.
Note
The
positionis required to be on-surface, which is indicated by theResultreturn value.- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – is the global position to be converted
tolerance – is the tolerance for the on-surface check
- Returns:
Result type containing local position by value
-
Vector2 globalToLocalCartesian(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, double tol = 0.) const
Special method for DiscSurface : global<->local from cartesian coordinates.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – is a global cartesian 3D position
tol – The absolute tolerance parameter
- Returns:
value is a local polar
-
virtual SurfaceMultiIntersection intersect(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction, const BoundaryCheck &bcheck = BoundaryCheck(false), ActsScalar tolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance) const final
Straight line intersection schema.
Mathematical motivation:
the equation of the plane is given by: \( \vec n \cdot \vec x = \vec n \cdot \vec p,\) where \( \vec n = (n_{x}, n_{y}, n_{z})\) denotes the normal vector of the plane, \( \vec p = (p_{x}, p_{y}, p_{z})\) one specific point on the plane and \( \vec x = (x,y,z) \)
all possible points on the plane.
Given a line with:
\( \vec l(u) = \vec l_{1} + u \cdot \vec v \),
the solution for
\( u \) can be written: \( u = \frac{\vec n (\vec p - \vec l_{1})}{\vec n \vec v}\) If the denominator is 0 then the line lies:either in the plane
perpendicular to the normal of the plane
Note
expected to be normalized (no checking)
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – The global position as a starting point
direction – The global direction at the starting point
bcheck – The boundary check prescription
tolerance – the tolerance used for the intersection
- Returns:
The
SurfaceMultiIntersectionobject
-
virtual ActsMatrix<2, 3> localCartesianToBoundLocalDerivative(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position) const final
Calculate the derivative of bound track parameters local position w.r.t.
position in local 3D Cartesian coordinates
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – The position of the parameters in global
- Returns:
Derivative of bound local position w.r.t. position in local 3D cartesian coordinates
-
Vector3 localCartesianToGlobal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector2 &lposition) const
Special method for DiscSurface : local<->global transformation when provided cartesian coordinates.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lposition – is local 2D position in cartesian coordinates
- Returns:
value is a global cartesian 3D position
-
Vector2 localCartesianToPolar(const Vector2 &lcart) const
Special method for Disc surface : local<->local transformations polar <-> cartesian.
- Parameters:
lcart – is local 2D position in cartesian coordinates
- Returns:
value is a local position in polar coordinates
-
Vector2 localPolarToCartesian(const Vector2 &lpolar) const
Special method for DiscSurface : local<->local transformations polar <-> cartesian.
- Parameters:
lpolar – is a local position in polar coordinates
- Returns:
values is local 2D position in cartesian coordinates
-
Vector2 localPolarToLocalCartesian(const Vector2 &locpol) const
Special method for DiscSurface : local<->local transformations polar <-> cartesian.
- Parameters:
locpol – is a local position in polar coordinates
- Returns:
values is local 2D position in cartesian coordinates
-
virtual Vector3 localToGlobal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector2 &lposition) const final
Local to global transformation For planar surfaces the momentum direction is ignored in the local to global transformation.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lposition – local 2D position in specialized surface frame
- Returns:
global position by value
-
Vector3 localToGlobal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector2 &lposition) const = 0
Local to global transformation.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lposition – local 2D position in specialized surface frame
- Returns:
The global position by value
-
Vector3 localToGlobal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector2 &lposition, const Vector3 &direction) const final
Local to global transformation.
This is the most generic interface, which is implemented by all surfaces.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lposition – local 2D position in specialized surface frame
direction – global 3D momentum direction (ignored for
RegularSurface)
- Returns:
The global position by value
-
virtual std::string name() const override
Return properly formatted class name for screen output.
-
Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx) const
Get the normal vector, independent of the location.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
- Returns:
The normal vector
-
virtual Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector2 &lposition) const final
Normal vector return.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lposition – The local position is ignored
- Returns:
a Vector3 by value
-
Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector2 &lposition) const = 0
Calculate the normal vector of the surface This overload requires an on-surface local position.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lposition – is the local position where the normal vector is constructed
- Returns:
normal vector by value
-
Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &pos, const Vector3 &direction) const final
Calculate the normal vector of the surface This overload is fully generic, fulfills the Surface interface and accepts a global position and a direction.
For
RegularSurfacethis is equivalent to the normal overload, ignoring thedirection- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
pos – is the global position where the normal vector is constructed
direction – is the direction of the normal vector (ignored for
RegularSurface)
-
virtual Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position) const final
Get the normal vector of this surface at a given global position.
Note
The
positionis required to be on-surface.- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – is the global positiono (for DiscSurface this is ignored)
- Returns:
The normal vector
-
Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position) const = 0
Calculate the normal vector of the surface This overload accepts a global position.
- Parameters:
position – is the global position where the normal vector is constructed
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
- Returns:
normal vector by value
-
DiscSurface &operator=(const DiscSurface &other)
Assignment operator.
- Parameters:
other – The source sourface for the assignment
-
virtual double pathCorrection(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction) const final
Path correction due to incident of the track.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – The global position as a starting point
direction – The global momentum direction at the starting point
- Returns:
The correction factor due to incident
-
virtual Polyhedron polyhedronRepresentation(const GeometryContext &gctx, std::size_t lseg) const override
Return a Polyhedron for the surfaces.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lseg – Number of segments along curved lines, it represents the full 2*M_PI coverange, if lseg is set to 1 only the extrema are given
- Returns:
A list of vertices and a face/facett description of it
-
virtual SurfaceType type() const override
Return the surface type.
-
DiscSurface() = delete
-
class DiscTrapezoidBounds : public Acts::DiscBounds
Class to describe the bounds for a planar DiscSurface.
By providing an argument for hphisec, the bounds can be restricted to a phi-range around the center position.
Public Types
Public Functions
-
DiscTrapezoidBounds() = delete
-
inline DiscTrapezoidBounds(const std::array<double, eSize> &values) noexcept(false)
Constructor - from fixed size array.
- Parameters:
values – The parameter values
-
DiscTrapezoidBounds(double halfXminR, double halfXmaxR, double minR, double maxR, double avgPhi = M_PI_2, double stereo = 0.) noexcept(false)
Constructor for a symmetric Trapezoid giving min X length, max X length, Rmin and R max.
- Parameters:
halfXminR – half length in X at min radius
halfXmaxR – half length in X at maximum radius
minR – inner radius
maxR – outer radius
avgPhi – average phi value
stereo – optional stero angle applied
-
~DiscTrapezoidBounds() override = default
-
inline virtual double binningValuePhi() const final
Return a reference phi for binning.
-
inline virtual double binningValueR() const final
Return a reference radius for binning.
-
inline virtual bool coversFullAzimuth() const final
Returns true for full phi coverage - obviously false here.
-
inline double get(BoundValues bValue) const
Access to the bound values.
- Parameters:
bValue – the class nested enum for the array access
-
inline double halfLengthY() const
This method returns the half length in Y (this is Rmax -Rmin)
-
inline double halfPhiSector() const
This method returns the halfPhiSector which is covered by the disc.
-
virtual bool inside(const Vector2 &lposition, const BoundaryCheck &bcheck = BoundaryCheck(true)) const final
This method checks if the radius given in the LocalPosition is inside [rMin,rMax] if only tol0 is given and additional in the phi sector is tol1 is given.
- Parameters:
lposition – is the local position to be checked (in polar coordinates)
bcheck – is the boundary check directive
-
inline virtual bool insideRadialBounds(double R, double tolerance = 0.) const final
Checks if this is inside the radial coverage given the a tolerance.
-
inline double rCenter() const
This method returns the center radius.
-
inline virtual double rMax() const final
This method returns outer radius.
-
inline virtual double rMin() const final
This method returns inner radius.
-
inline double stereo() const
This method returns the stereo angle.
-
virtual std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &sl) const final
Output Method for std::ostream.
-
virtual SurfaceBounds::BoundsType type() const final
Return the bounds type - for persistency optimization.
- Returns:
is a BoundsType enum
-
inline virtual std::vector<double> values() const final
Return the bound values as dynamically sized vector.
- Returns:
this returns a copy of the internal values
-
virtual std::vector<Vector2> vertices(unsigned int lseg) const final
This method returns the xy coordinates of the four corners of the bounds in module coorindates (in xy)
Note
that the number of segments are ignored for this surface
- Parameters:
lseg – the number of segments used to approximate and eventually curved line
- Returns:
vector for vertices in 2D
-
DiscTrapezoidBounds() = delete
-
template<typename extensionlist_t = StepperExtensionList<DefaultExtension>, typename auctioneer_t = detail::VoidAuctioneer>
class EigenStepper Runge-Kutta-Nystroem stepper based on Eigen implementation for the following ODE:
r = (x,y,z) … global position T = (Ax,Ay,Az) … momentum direction (normalized)
dr/ds = T dT/ds = q/p * (T x B)
with s being the arc length of the track, q the charge of the particle, p the momentum magnitude and B the magnetic field
Public Types
-
using BoundState = std::tuple<BoundTrackParameters, Jacobian, double>
-
using Covariance = BoundSquareMatrix
-
using Jacobian = BoundMatrix
Jacobian, Covariance and State definitions.
Public Functions
Constructor requires knowledge of the detector’s magnetic field.
-
inline double absoluteMomentum(const State &state) const
Absolute momentum accessor.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
Result<BoundState> boundState(State &state, const Surface &surface, bool transportCov = true, const FreeToBoundCorrection &freeToBoundCorrection = FreeToBoundCorrection(false)) const
Create and return the bound state at the current position.
This transports (if necessary) the covariance to the surface and creates a bound state. It does not check if the transported state is at the surface, this needs to be guaranteed by the propagator
- Parameters:
state – [in] State that will be presented as
BoundStatesurface – [in] The surface to which we bind the state
transportCov – [in] Flag steering covariance transport
freeToBoundCorrection – [in] Correction for non-linearity effect during transform from free to bound
- Returns:
A bound state:
the parameters at the surface
the stepwise jacobian towards it (from last bound)
and the path length (from start - for ordering)
-
inline double charge(const State &state) const
Charge access.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
CurvilinearState curvilinearState(State &state, bool transportCov = true) const
Create and return a curvilinear state at the current position.
This transports (if necessary) the covariance to the current position and creates a curvilinear state.
- Parameters:
state – [in] State that will be presented as
CurvilinearStatetransportCov – [in] Flag steering covariance transport
- Returns:
A curvilinear state:
the curvilinear parameters at given position
the stepweise jacobian towards it (from last bound)
and the path length (from start - for ordering)
-
inline Vector3 direction(const State &state) const
Momentum direction accessor.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
inline Result<Vector3> getField(State &state, const Vector3 &pos) const
Get the field for the stepping, it checks first if the access is still within the Cell, and updates the cell if necessary.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] is the propagation state associated with the track the magnetic field cell is used (and potentially updated)
pos – [in] is the field position
-
inline double getStepSize(const State &state, ConstrainedStep::Type stype) const
Get the step size.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
stype – [in] The step size type to be returned
-
State makeState(std::reference_wrapper<const GeometryContext> gctx, std::reference_wrapper<const MagneticFieldContext> mctx, const BoundTrackParameters &par, double ssize = std::numeric_limits<double>::max()) const
-
inline Vector3 momentum(const State &state) const
Momentum accessor.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
inline std::string outputStepSize(const State &state) const
Output the Step Size - single component.
- Parameters:
state – [in,out] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
inline const ParticleHypothesis &particleHypothesis(const State &state) const
Particle hypothesis.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
inline Vector3 position(const State &state) const
Global particle position accessor.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
If necessary fill additional members needed for curvilinearState.
Compute path length derivatives in case they have not been computed yet, which is the case if no step has been executed yet.
- Parameters:
prop_state – [inout] State that will be presented as
BoundStatenavigator – [in] the navigator of the propagation
- Returns:
true if nothing is missing after this call, false otherwise.
-
inline double qOverP(const State &state) const
QoP direction accessor.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
inline void releaseStepSize(State &state, ConstrainedStep::Type stype) const
Release the Step size.
- Parameters:
state – [in,out] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
stype – [in] The step size type to be released
-
void resetState(State &state, const BoundVector &boundParams, const BoundSquareMatrix &cov, const Surface &surface, const double stepSize = std::numeric_limits<double>::max()) const
Resets the state.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] State of the stepper
boundParams – [in] Parameters in bound parametrisation
cov – [in] Covariance matrix
surface – [in] The reference surface of the bound parameters
stepSize – [in] Step size
-
void setIdentityJacobian(State &state) const
Method that reset the Jacobian to the Identity for when no bound state are available.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] State of the stepper
Perform a Runge-Kutta track parameter propagation step.
Note
The state contains the desired step size. It can be negative during backwards track propagation, and since we’re using an adaptive algorithm, it can be modified by the stepper class during propagation.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] the propagation state
navigator – [in] the navigator of the propagation
-
inline double time(const State &state) const
Time access.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
void transportCovarianceToBound(State &state, const Surface &surface, const FreeToBoundCorrection &freeToBoundCorrection = FreeToBoundCorrection(false)) const
Method for on-demand transport of the covariance to a new curvilinear frame at current position, or direction of the state.
Note
no check is done if the position is actually on the surface
- Template Parameters:
surface_t – the Surface type
- Parameters:
state – [inout] State of the stepper
surface – [in] is the surface to which the covariance is forwarded to
freeToBoundCorrection – [in] Correction for non-linearity effect during transform from free to bound
-
void transportCovarianceToCurvilinear(State &state) const
Method for on-demand transport of the covariance to a new curvilinear frame at current position, or direction of the state.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] State of the stepper
-
void update(State &state, const FreeVector &freeParams, const BoundVector &boundParams, const Covariance &covariance, const Surface &surface) const
Method to update a stepper state to the some parameters.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] State object that will be updated
freeParams – [in] Free parameters that will be written into
stateboundParams – [in] Corresponding bound parameters used to update jacToGlobal in
statecovariance – [in] The covariance that will be written into
statesurface – [in] The surface used to update the jacToGlobal
-
void update(State &state, const Vector3 &uposition, const Vector3 &udirection, double qOverP, double time) const
Method to update the stepper state.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] State object that will be updated
uposition – [in] the updated position
udirection – [in] the updated direction
qOverP – [in] the updated qOverP value
time – [in] the updated time value
-
template<typename object_intersection_t>
inline void updateStepSize(State &state, const object_intersection_t &oIntersection, Direction, bool release = true) const Update step size.
This method intersects the provided surface and update the navigation step estimation accordingly (hence it changes the state). It also returns the status of the intersection to trigger onSurface in case the surface is reached.
- Parameters:
state – [in,out] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
oIntersection – [in] The ObjectIntersection to layer, boundary, etc
release – [in] boolean to trigger step size release
-
inline void updateStepSize(State &state, double stepSize, ConstrainedStep::Type stype, bool release = true) const
Update step size - explicitly with a double.
- Parameters:
state – [in,out] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
stepSize – [in] The step size value
stype – [in] The step size type to be set
release – [in] Do we release the step size?
-
inline Intersection3D::Status updateSurfaceStatus(State &state, const Surface &surface, std::uint8_t index, Direction navDir, const BoundaryCheck &bcheck, ActsScalar surfaceTolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance, const Logger &logger = getDummyLogger()) const
Update surface status.
It checks the status to the reference surface & updates the step size accordingly
- Parameters:
state – [inout] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
surface – [in] The surface provided
index – [in] The surface intersection index
navDir – [in] The navigation direction
bcheck – [in] The boundary check for this status update
surfaceTolerance – [in] Surface tolerance used for intersection
logger – [in] A
Loggerinstance
-
struct State
State for track parameter propagation.
It contains the stepping information and is provided thread local by the propagator
Public Functions
-
State() = delete
-
inline explicit State(const GeometryContext &gctx, MagneticFieldProvider::Cache fieldCacheIn, const BoundTrackParameters &par, double ssize = std::numeric_limits<double>::max())
Constructor from the initial bound track parameters.
Note
the covariance matrix is copied when needed
- Parameters:
gctx – [in] is the context object for the geometry
fieldCacheIn – [in] is the cache object for the magnetic field
par – [in] The track parameters at start
ssize – [in] is the maximum step size
Public Members
-
auctioneer_t auctioneer
Auctioneer for choosing the extension.
-
Covariance cov = Covariance::Zero()
-
bool covTransport = false
Covariance matrix (and indicator) associated with the initial error on track parameters.
-
FreeVector derivative = FreeVector::Zero()
The propagation derivative.
-
extensionlist_t extension
List of algorithmic extensions.
-
MagneticFieldProvider::Cache fieldCache
This caches the current magnetic field cell and stays (and interpolates) within it as long as this is valid.
See step() code for details.
-
std::reference_wrapper<const GeometryContext> geoContext
The geometry context.
-
BoundToFreeMatrix jacToGlobal = BoundToFreeMatrix::Zero()
Jacobian from local to the global frame.
-
FreeMatrix jacTransport = FreeMatrix::Identity()
Pure transport jacobian part from runge kutta integration.
-
std::array<double, 4> kQoP = {}
k_i elements of the momenta
-
FreeVector pars = FreeVector::Zero()
Internal free vector parameters.
-
ParticleHypothesis particleHypothesis = ParticleHypothesis::pion()
Particle hypothesis.
-
double pathAccumulated = 0.
Accummulated path length state.
-
double previousStepSize = 0.
Last performed step (for overstep limit calculation)
-
struct Acts::EigenStepper::State::[anonymous] stepData
Storage of magnetic field and the sub steps during a RKN4 step.
-
ConstrainedStep stepSize
Adaptive step size of the runge-kutta integration.
-
State() = delete
-
using BoundState = std::tuple<BoundTrackParameters, Jacobian, double>
-
class EllipseBounds : public Acts::PlanarBounds
Class to describe the bounds for a planar ellispoid surface.
By providing an argument for hphisec, the bounds can be restricted to a phi-range around the center position.
Public Types
Public Functions
-
EllipseBounds() = delete
-
inline EllipseBounds(const std::array<double, eSize> &values) noexcept(false)
Constructor - from fixed size array.
- Parameters:
values – The parameter values
-
inline EllipseBounds(double innerRx, double innerRy, double outerRx, double outerRy, double halfPhi = M_PI, double averagePhi = 0.) noexcept(false)
Constructor for full of an ellipsoid ring.
- Parameters:
innerRx – The inner ellipse radius in x
innerRy – The inner ellipse radius in y
outerRx – The outer ellipse radius in x
outerRy – The outer ellipse radius in y
halfPhi – spanning phi sector (is set to pi as default)
averagePhi – average phi (is set to 0. as default)
-
~EllipseBounds() override = default
-
virtual const RectangleBounds &boundingBox() const final
Bounding box parameters.
- Returns:
rectangle bounds for a bounding box
-
inline double get(BoundValues bValue) const
Access to the bound values.
- Parameters:
bValue – the class nested enum for the array access
-
virtual bool inside(const Vector2 &lposition, const BoundaryCheck &bcheck) const final
This method checks if the point given in the local coordinates is between two ellipsoids if only tol0 is given and additional in the phi sector is tol1 is given.
- Parameters:
lposition – Local position (assumed to be in right surface frame)
bcheck – boundary check directive
- Returns:
boolean indicator for the success of this operation
-
virtual std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &sl) const final
Output Method for std::ostream.
-
virtual BoundsType type() const final
Return the bounds type - for persistency optimization.
- Returns:
is a BoundsType enum
-
inline virtual std::vector<double> values() const final
Return the bound values as dynamically sized vector.
- Returns:
this returns a copy of the internal values
-
virtual std::vector<Vector2> vertices(unsigned int lseg) const final
Return the vertices.
Note
the number of segments to may be altered by also providing the extremas in all direction
- Parameters:
lseg – the number of segments used to approximate and eventually curved line, here it refers to the full 2PI Ellipse
- Returns:
vector for vertices in 2D
-
EllipseBounds() = delete
-
class Detector : public std::enable_shared_from_this<Detector>
Public Functions
-
const DetectorVolumeUpdater &detectorVolumeFinder() const
Const access to the volume finder.
-
const DetectorVolume *findDetectorVolume(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position) const
Find a volume from a position.
Note
this creates internally a NavigationState object
- Parameters:
gctx – is the Geometry context of the call
position – is the position of the call
- Returns:
the volume pointer or nullptr (if outside)
-
const DetectorVolume *findDetectorVolume(const std::string &name) const
Find a volume by name.
- Parameters:
name – with which the volume is searched for
- Returns:
the volume pointer or nullptr (if not found)
Retrieve a
std::shared_ptrfor this surface (non-const version)Note
Will error if this was not created through the
makeSharedfactory since it needs access to the original reference. In C++14 this is undefined behavior (but most likely implemented as abad_weak_ptrexception), in C++17 it is defined as that exception.Note
Only call this if you need shared ownership of this object.
- Returns:
The shared pointer
Retrieve a
std::shared_ptrfor this surface (const version)Note
Will error if this was not created through the
makeSharedfactory since it needs access to the original reference. In C++14 this is undefined behavior, but most likely implemented as abad_weak_ptrexception, in C++17 it is defined as that exception.Note
Only call this if you need shared ownership of this object.
- Returns:
The shared pointer
-
const std::string &name() const
Return the name of the detector.
-
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<DetectorVolume>> &rootVolumePtrs()
Non-const access to the root volumes.
- Returns:
the root volume shared pointer
-
const std::vector<const DetectorVolume*> &rootVolumes() const
Const access to the root volumes.
- Returns:
a vector to const DetectorVolume raw pointers
-
const GeometryHierarchyMap<const Surface*> &sensitiveHierarchyMap() const
Const access to the hierarchy map of all sensitive surfaces.
- Returns:
the map which can be queried with GeometryID for ranges
Update the current volume of a given navigation state.
- Parameters:
gctx – is the Geometry context of the call
nState – [in, out] is the navigation state
-
void updateDetectorVolumeFinder(DetectorVolumeUpdater detectorVolumeUpdater)
Update the volume finder.
- Parameters:
detectorVolumeUpdater – the new volume finder
-
template<ACTS_CONCEPT visitor_t(MutableSurfaceVisitor)>
inline void visitMutableSurfaces(visitor_t &&visitor) Visit all reachable surfaces of the detector - non-const.
Note
if a context is needed for the visit, the vistitor has to provide it, e.g. as a private member
Note
due to the fact that this doesn’t run over root volumes, and due to the fact that portals can be shared between volumes, multiple visits may occur, duplicated addressing needs to be taken care of by the
- Template Parameters:
visitor_t – Type of the callable visitor
- Parameters:
visitor – will be handed to each root volume, eventually contained volumes within the root volumes are handled by the root volume
-
template<ACTS_CONCEPT visitor_t(MutableDetectorVolumeVisitor)>
inline void visitMutableVolumes(visitor_t &&visitor) Visit all reachable detector volumes of the detector - non-const.
Note
if a context is needed for the visit, the vistitor has to provide it, e.g. as a private member
Note
that due to non running over root volumes, multiple visits may occur, duplicated addressing needs to be taken care of by the visitor
- Template Parameters:
visitor_t – Type of the callable visitor
- Parameters:
visitor – will be handed to each root volume, eventually contained volumes within the root volumes are handled by the root volume
-
template<ACTS_CONCEPT visitor_t(SurfaceVisitor)>
inline void visitSurfaces(visitor_t &&visitor) const Visit all reachable surfaces of the detector.
Note
if a context is needed for the visit, the vistitor has to provide it, e.g. as a private member
Note
due to the fact that portals can be shared between volumes, multiple visits may occur, duplicated addressing needs to be taken care of by the visitor
- Template Parameters:
visitor_t – Type of the callable visitor
- Parameters:
visitor – will be handed to each root volume, eventually contained volumes within the root volumes are handled by the root volume
-
template<ACTS_CONCEPT visitor_t(DetectorVolumeVisitor)>
inline void visitVolumes(visitor_t &&visitor) const Visit all reachable detector volumes of the detector.
Note
if a context is needed for the visit, the vistitor has to provide it, e.g. as a private member
- Template Parameters:
visitor_t – Type of the callable visitor
- Parameters:
visitor – will be handed to each root volume, eventually contained volumes within the root volumes are handled by the root volume
-
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<DetectorVolume>> &volumePtrs()
Non-const access to the root volume.
- Returns:
the volumes shared pointer store
-
const std::vector<const DetectorVolume*> &volumes() const
Const access to sub volumes.
- Returns:
a vector to const DetectorVolume raw pointers
Public Static Functions
Factory for producing memory managed instances of Detector.
-
const DetectorVolumeUpdater &detectorVolumeFinder() const
-
class DetectorVolume : public std::enable_shared_from_this<DetectorVolume>
A detector volume description which can be:
Note
A detector volume holds non-const objects internally that are allowed to be modified as long as the geometry is not yet closed. Using this, material can be attached, and GeometryIdentifier can be set at construction time.
Note
The construction of DetectorVolumes is done via a dedicated factory, this is necessary as then the shared_ptr is non-weak and it can be registered in the portal generator for further geometry processing.
Note
Navigation is always done by plain pointers, while object ownership is done by shared/unique pointers.
Public Types
-
using BoundingBox = Acts::AxisAlignedBoundingBox<Acts::Experimental::DetectorVolume, Acts::ActsScalar, 3>
Public Functions
-
void assignDetector(const Detector &detector)
Assign Detector to this volume (for back navigation issues)
- Parameters:
detector – the parenting detector class
-
void assignGeometryId(const GeometryIdentifier &geoID)
Set the geometry identifier.
Note
no checking is done, it will overwrite any existing id
- Parameters:
geoID – is the geometry Id that is set to the object
This method allows to udate the navigation state updator module.
- Parameters:
surfaceCandidateUpdater – the new navigation state updator for surfaces
surfaces – the surfaces the new navigation state updator points to
volumes – the volumes the new navigation state updator points to
Assign the volume material description.
This method allows to load a material description during the detector geometry building, and assigning it (potentially multiple) times to detector volumes.
- Parameters:
material – Material description associated to this volumw
-
Vector3 center(const GeometryContext &gctx = GeometryContext()) const
Const access to the center.
Note
the geometry context is currently ignored, but is a placeholder for eventually misaligned volumes
- Parameters:
gctx – the geometry context
- Returns:
a contextually created center
-
void closePortals()
Final closing of portal, i.e. this sets the end of world.
-
const DetectorVolumeUpdater &detectorVolumeUpdater() const
Const access to the detector volume updator.
-
bool exclusivelyInside(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position) const
Check if a point is exclusively inside this volume i.e.
this point is not inside a subvolume.
- Parameters:
gctx – the geometry context
position – the position for the inside check
- Returns:
a bool to indicate inside/outside
-
Extent extent(const GeometryContext &gctx, std::size_t nseg = 1) const
The Extent for this volume.
- Parameters:
gctx – is the geometry context
nseg – is the number of segments to approximate
- Returns:
an Extent object
-
const GeometryIdentifier &geometryId() const
- Returns:
the geometry identifier
-
const BoundingBox &getBoundingBox() const
Retrieve a
std::shared_ptrfor this surface (non-const version)Note
Will error if this was not created through the
makeSharedfactory since it needs access to the original reference. In C++14 this is undefined behavior (but most likely implemented as abad_weak_ptrexception), in C++17 it is defined as that exception.Note
Only call this if you need shared ownership of this object.
- Returns:
The shared pointer
Retrieve a
std::shared_ptrfor this surface (const version)Note
Will error if this was not created through the
makeSharedfactory since it needs access to the original reference. In C++14 this is undefined behavior, but most likely implemented as abad_weak_ptrexception, in C++17 it is defined as that exception.Note
Only call this if you need shared ownership of this object.
- Returns:
The shared pointer
-
bool inside(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position) const
Check if a point is inside this volume.
Subvolumes will not be checked.
- Parameters:
gctx – the geometry context
position – the position for the inside check
- Returns:
a bool to indicate inside/outside
-
const std::string &name() const
- Returns:
the name of the volume
-
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<Portal>> &portalPtrs()
Non-const access to the portals.
- Returns:
the portal shared pointer store
-
const std::vector<const Portal*> &portals() const
Const access to the detector portals.
Note
an empty vector indicates a container volume that has not been properly connected
- Returns:
a vector to const Portal raw pointers
-
const SurfaceCandidatesUpdater &surfaceCandidatesUpdater() const
Const access to the navigation state updator.
-
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<Surface>> &surfacePtrs()
Non-const access to the surfaces.
- Returns:
the surfaces shared pointer store
-
const std::vector<const Surface*> &surfaces() const
Const access to the surfaces.
Note
an empty vector indicates either gap volume or container volume, a non-empty vector indicates a layer volume.
- Returns:
a vector to const Surface raw pointers
-
const Transform3 &transform(const GeometryContext &gctx = GeometryContext()) const
Const access to the transform.
Note
the geometry context is currently ignored, but is a placeholder for eventually misaligned volumes
- Parameters:
gctx – the geometry context
- Returns:
const reference to the contextual transform
Initialize/update the navigation status in this environment.
This method calls:
the local navigation delegate for candidate surfaces
the portal navigation delegate for candidate exit portals
set the current detector volume
- Parameters:
gctx – is the current geometry context
nState – [in,out] is the detector navigation state to be updated
Update a portal given a portal index.
Note
throws exception if portal index out of bounds
- Parameters:
portal – the portal to be updated
pIndex – the portal index
-
template<ACTS_CONCEPT visitor_t(MutableSurfaceVisitor)>
inline void visitMutableSurfaces(visitor_t &&visitor) Visit all reachable surfaces of the detector - non-const.
- Template Parameters:
visitor_t – Type of the callable visitor
- Parameters:
visitor – will be called for each found surface, it will be handed down to contained volumes and portals
-
template<ACTS_CONCEPT visitor_t(MutableDetectorVolumeVisitor)>
inline void visitMutableVolumes(visitor_t &&visitor) Visit all reachable detector volumes of the detector - non-const.
Note
if a context is needed for the visit, the vistitor has to provide it, e.g. as a private member
- Template Parameters:
visitor_t – Type of the callable visitor
- Parameters:
visitor – will be handed to each root volume, eventually contained volumes within the root volumes are handled by the root volume
-
template<ACTS_CONCEPT visitor_t(SurfaceVisitor)>
inline void visitSurfaces(visitor_t &&visitor) const Visit all reachable surfaces of the detector.
- Template Parameters:
visitor_t – Type of the callable visitor
- Parameters:
visitor – will be called for each found surface, it will be handed down to contained volumes and portals
-
template<ACTS_CONCEPT visitor_t(DetectorVolumeVisitor)>
inline void visitVolumes(visitor_t &&visitor) const Visit all reachable detector volumes of the detector.
Note
if a context is needed for the visit, the vistitor has to provide it, e.g. as a private member
- Template Parameters:
visitor_t – Type of the callable visitor
- Parameters:
visitor – will be handed to each root volume, eventually contained volumes within the root volumes are handled by the root volume
-
const VolumeBounds &volumeBounds() const
Const access to the volume bounds.
- Returns:
const reference to the volume bounds object
-
const IVolumeMaterial *volumeMaterial() const
Const access to the volume amterial.
-
std::shared_ptr<IVolumeMaterial> volumeMaterialPtr()
Non-const access to the voume material (for scaling, e.g.)
-
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<DetectorVolume>> &volumePtrs()
Non-const access to the volumes.
- Returns:
the volumes shared pointer store
-
const std::vector<const DetectorVolume*> &volumes() const
Const access to sub volumes.
Note
and empty vector indicates this is either a gap volume or a layer volume, in any case it means the volume is on navigation level and the portals need to be connected
- Returns:
a vector to const DetectorVolume raw pointers
Friends
- friend class DetectorVolumeFactory
-
template<typename internal_type>
struct ObjectStore Nested object store that holds the internal (non-const), reference counted objects and provides an external (const raw pointer) access.
- Template Parameters:
internal_type – is the internal storage representation, has to comply with std::shared_ptr semantics
Public Functions
-
ObjectStore() = default
-
inline ObjectStore(std::vector<internal_type> objects)
Store constructor.
- Parameters:
objects – are the ones copied into the internal store
Public Members
-
std::vector<const typename internal_type::element_type*> external = {}
The external storage vector, const raw pointer.
-
std::vector<internal_type> internal = {}
The internal storage vector.
-
using BoundingBox = Acts::AxisAlignedBoundingBox<Acts::Experimental::DetectorVolume, Acts::ActsScalar, 3>
-
class DetectorVolumeFactory
A detector volume factory which first constructs the detector volume and then constructs the portals.
This ensures that the std::shared_ptr holding the detector volume is not weak when assigning to the portals.
Note
Optional containment check is invoked by setting the number of segments nSeg to be greater than 0
Public Static Functions
Create a detector volume - from factory.
Create a detector volume - from factory.
-
class Portal
A portal description between the detector volumes.
It has a Surface representation for navigation and propagation and guides from one volume to the next.
The surface can carry material to allow mapping onto portal positions if required.
Public Types
-
using AttachedDetectorVolumes = std::array<std::vector<std::shared_ptr<DetectorVolume>>, 2u>
The vector of attached volumes forward/backward, this is useful in the geometry building.
-
using DetectorVolumeUpdaters = std::array<DetectorVolumeUpdater, 2u>
The volume links forward/backward with respect to the surface normal.
Public Functions
-
Portal() = delete
Constructor from surface w/o portal links.
- Parameters:
surface – is the representing surface
Update the volume link, w/o directive, i.e.
it relies that there’s only one remaining link to be set, throws an exception if that’s not the case
Note
this overwrites the existing link
- Parameters:
dVolumeUpdater – is the mangaged volume updator delegate
attachedVolumes – is the list of attached volumes for book keeping
Update the volume link.
Note
this overwrites the existing link
- Parameters:
dir – the direction of the link
dVolumeUpdater – is the mangaged volume updator delegate
attachedVolumes – is the list of attached volumes for book keeping
-
void assignGeometryId(const GeometryIdentifier &geometryId)
Set the geometry identifier (to the underlying surface)
- Parameters:
geometryId – the geometry identifier to be assigned
-
AttachedDetectorVolumes &attachedDetectorVolumes()
-
const DetectorVolumeUpdaters &detectorVolumeUpdaters() const
-
RegularSurface &surface()
Non-const access to the surface reference.
-
const RegularSurface &surface() const
Const access to the surface representation.
Update the current volume.
- Parameters:
gctx – is the Geometry context of this call
nState – [in,out] the navigation state for the volume to be updated
Public Static Functions
Fuse with another portal, this one is kept.
Note
this will combine the portal links from the both portals into a new one, it will throw an exception if the portals are not fusable
Note
if one portal carries material, it will be kept, however, if both portals carry material, an exception will be thrown and the portals are not fusable
Note
Both input portals become invalid, in that their update delegates and attached volumes are reset
- Parameters:
aPortal – is the first portal to fuse
bPortal – is the second portal to fuse
Friends
- friend class DetectorVolume
-
using AttachedDetectorVolumes = std::array<std::vector<std::shared_ptr<DetectorVolume>>, 2u>
-
class GainMatrixSmoother
Kalman trajectory smoother based on gain matrix formalism.
This implements not a single smoothing step, but the full backwards smoothing procedure for a filtered, forward trajectory using the stored linearization.
Public Types
Public Functions
-
Result<void> calculate(void *ts, void *prev_ts, const GetParameters &filtered, const GetCovariance &filteredCovariance, const GetParameters &smoothed, const GetParameters &predicted, const GetCovariance &predictedCovariance, const GetCovariance &smoothedCovariance, const GetCovariance &jacobian, const Logger &logger) const
-
template<typename traj_t>
inline Result<void> operator()(const GeometryContext&, traj_t &trajectory, std::size_t entryIndex, const Logger &logger = getDummyLogger()) const Run the Kalman smoothing for one trajectory.
- Parameters:
trajectory – [inout] The trajectory to be smoothed
entryIndex – [in] The index of state to start the smoothing
logger – [in] Where to write logging information to
-
Result<void> calculate(void *ts, void *prev_ts, const GetParameters &filtered, const GetCovariance &filteredCovariance, const GetParameters &smoothed, const GetParameters &predicted, const GetCovariance &predictedCovariance, const GetCovariance &smoothedCovariance, const GetCovariance &jacobian, const Logger &logger) const
-
class GainMatrixUpdater
Kalman update step using the gain matrix formalism.
Public Functions
-
template<typename traj_t>
inline Result<void> operator()(const GeometryContext&, typename traj_t::TrackStateProxy trackState, Direction direction = Direction::Forward, const Logger &logger = getDummyLogger()) const Run the Kalman update step for a single trajectory state.
- Template Parameters:
kMeasurementSizeMax –
- Parameters:
trackState – [inout] The track state
direction – [in] The navigation direction
logger – [in] Where to write logging information to
-
template<typename traj_t>
-
class Geant4DetectorElement : public Acts::DetectorElementBase
Detector element representative for Geant4 sensitive elements.
Public Types
-
using ContextType = GeometryContext
Broadcast the context type.
Public Functions
Constructor with arguments.
- Parameters:
surface – the surface representing this detector element
g4physVol – the physical volume representing this detector element
toGlobal – the global transformation before the volume
thickness – the thickness of this detector element
-
const G4VPhysicalVolume &g4PhysicalVolume() const
- Returns:
to the Geant4 physical volume
-
virtual const Surface &surface() const override
Return surface associated with this detector element.
-
virtual Surface &surface() override
Non-const access to surface associated with this detector element.
-
virtual ActsScalar thickness() const override
Return the thickness of this detector element.
-
virtual const Transform3 &transform(const GeometryContext &gctx) const override
Return local to global transform associated with this detector element.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
-
using ContextType = GeometryContext
-
class Geant4DetectorSurfaceFactory
A factory to convert Geant4 physical volumes into Geant4 detector elements.
Public Types
-
using Geant4SensitiveSurface = std::tuple<std::shared_ptr<Geant4DetectorElement>, std::shared_ptr<Surface>>
Public Functions
-
Geant4DetectorSurfaceFactory() = default
The Geant4 detector element factory.
-
void construct(Cache &cache, const G4Transform3D &g4ToGlobal, const G4VPhysicalVolume &g4PhysVol, const Options &option)
Construction method of the detector elements.
- Parameters:
cache – [in,out] into which the Elements are filled
g4ToGlobal – the transformation to global
g4PhysVol – the current physical volume
option – the factory creation option
-
struct Cache
Nested cache that records the conversion status.
Public Members
-
std::size_t convertedMaterials = 0
matching and conversion statistics: materials
-
std::size_t convertedSurfaces = 0
matching and conversion statistics: surfaces
-
std::size_t matchedG4Volumes = 0
matching and conversion statistics: volumes
-
std::vector<Geant4PassiveSurface> passiveSurfaces
The created non-const surfaces - for further processing,.
-
std::vector<Geant4SensitiveSurface> sensitiveSurfaces
The created detector elements - for the detector store.
-
std::size_t convertedMaterials = 0
-
struct Config
Nested configuration struct that holds global lifetime configuration.
-
struct Options
Nested option struct that allows per call changeable configuration.
Public Members
-
ActsScalar convertedMaterialThickness = -1
Converted material thickness (< 0 indicates keeping original thickness)
-
bool convertMaterial = true
Convert the material.
-
std::shared_ptr<IGeant4PhysicalVolumeSelector> passiveSurfaceSelector = nullptr
A selector for passive surfaces.
-
ActsScalar scaleConversion = 1.
Convert the length scale.
-
std::shared_ptr<IGeant4PhysicalVolumeSelector> sensitiveSurfaceSelector = nullptr
A selector for sensitive surfaces.
-
ActsScalar convertedMaterialThickness = -1
-
using Geant4SensitiveSurface = std::tuple<std::shared_ptr<Geant4DetectorElement>, std::shared_ptr<Surface>>
-
class GenericCuboidVolumeBounds : public Acts::VolumeBounds
Public Functions
-
GenericCuboidVolumeBounds() = delete
-
GenericCuboidVolumeBounds(const std::array<Acts::Vector3, 8> &vertices) noexcept(false)
Constructor from a set of vertices.
The ordering is considered to be:
the first 4 vertices are the “top” face
the second 4 vertices are the “bottom” face
both faces are given in counter clock wise order
- Parameters:
vertices – The set of input vertices
-
GenericCuboidVolumeBounds(const std::array<double, BoundValues::eSize> &values) noexcept(false)
Constructor from a fixed size array.
- Parameters:
values – The input values
-
~GenericCuboidVolumeBounds() override = default
-
virtual Volume::BoundingBox boundingBox(const Transform3 *trf = nullptr, const Vector3 &envelope = {0, 0, 0}, const Volume *entity = nullptr) const final
Construct bounding box for this shape.
- Parameters:
trf – Optional transform
envelope – Optional envelope to add / subtract from min/max
entity – Entity to associate this bounding box with
- Returns:
Constructed bounding box
-
inline virtual std::vector<Acts::BinningValue> canonicalBinning() const override
Get the canonical binning values, i.e.
the binning values for that fully describe the shape’s extent
- Returns:
vector of canonical binning values
-
void draw(IVisualization3D &helper, const Transform3 &transform = Transform3::Identity()) const
Draw this shape using a visualization helper.
- Parameters:
helper – The visualizatin helper
transform – Optional transformation matrix
-
virtual bool inside(const Vector3 &gpos, double tol = 0.) const override
Checking if position given in volume frame is inside.
- Parameters:
gpos – is the global position to be checked
tol – is the tolerance applied for the inside check
- Returns:
boolean indicating if the position is inside
-
virtual std::vector<OrientedSurface> orientedSurfaces(const Transform3 &transform = Transform3::Identity()) const override
Oriented surfaces, i.e.
the decomposed boundary surfaces and the according navigation direction into the volume given the normal vector on the surface
It will throw an exception if the orientation prescription is not adequate
- Parameters:
transform – is the 3D transform to be applied to the boundary surfaces to position them in 3D space
- Returns:
a vector of surfaces bounding this volume
-
virtual std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &sl) const override
- Parameters:
sl – is the output stream to be written into
-
inline virtual VolumeBounds::BoundsType type() const final
Return the bounds type - for persistency optimization.
- Returns:
is a BoundsType enum
-
virtual std::vector<double> values() const final
Return the bound values as dynamically sized vector.
- Returns:
this returns a copy of the internal values
-
GenericCuboidVolumeBounds() = delete
-
template<typename value_t>
class GeometryHierarchyMap Store values mapped into the geometry hierarchy.
The core functionality is to find an equivalent element, i.e. an identifier-value pair, for a given geometry identifier via
Trailing zero levels of stored geometry identifiers are used as broadcast values to refer to higher-level objects within the geometry, e.g. a geometry identifier with vanishing approach and sensitive index identifies a layer. An entry will all geometry identifier levels set to zero acts as the global default value.auto it = container.find(GeometryIdentifier(...)); if (it != container.end()) { ... }
The container also supports range-based iteration over all stored elements
and index-based access to stored elements and associated geometry identifiersfor (const auto& element : container) { ... }
Adding elements is potentially expensive as the internal lookup structure must be updated. In addition, modifying an element in-place could change its identifier which would also break the lookup. Thus, the container can not be modified after construction to prevent misuse.GeometryIdentifier id3 = container.idAt(3); const auto& element4 = container.valueAt(4);
Note
No guarantees are given for the element order when using range-based or index-based access. Any apparent ordering must be considered an implementation detail and might change.
- Template Parameters:
value_t – stored value type
Public Types
-
using InputElement = typename std::pair<GeometryIdentifier, value_t>
Combined geometry identifier and value element. Only used for input.
Public Functions
-
GeometryHierarchyMap() = default
-
GeometryHierarchyMap(const GeometryHierarchyMap&) = default
-
GeometryHierarchyMap(GeometryHierarchyMap&&) = default
-
inline GeometryHierarchyMap(std::initializer_list<InputElement> elements)
Construct the container from an initializer list.
- Parameters:
elements – input initializer list
-
inline GeometryHierarchyMap(std::vector<InputElement> elements)
Construct the container from the given elements.
- Parameters:
elements – input elements (must be unique with respect to identifier)
-
~GeometryHierarchyMap() = default
-
inline bool empty() const
Check if any elements are stored.
-
inline Iterator find(GeometryIdentifier id) const
Find the most specific value for a given geometry identifier.
This can be either from the element matching exactly to the given geometry id, if it exists, or from the element for the next available higher level within the geometry hierarchy.
- Parameters:
id – geometry identifier for which information is requested
- Return values:
iterator – to an existing value
<tt>.end()</tt> – iterator if no matching element exists
-
inline GeometryIdentifier idAt(Size index) const
Access the geometry identifier for the i-th element with bounds check.
- Throws:
std::out_of_range – for invalid indices
-
GeometryHierarchyMap &operator=(const GeometryHierarchyMap&) = default
-
GeometryHierarchyMap &operator=(GeometryHierarchyMap&&) = default
-
class GeometryIdentifier
Identifier for geometry nodes within the geometry hierarchy.
An identifier can be split into the following components. They define a hierarchy of objects starting from the high-level volumes:
Volume
Boundary surfaces (for a volume)
Layers (confined within a volume)
Approach surfaces (for a layer)
Sensitive surfaces (confined to a layer, also called modules)
Public Types
-
using Value = uint64_t
Public Functions
-
GeometryIdentifier() = default
Construct default GeometryIdentifier with all values set to zero.
-
GeometryIdentifier(const GeometryIdentifier&) = default
-
GeometryIdentifier(GeometryIdentifier&&) = default
-
~GeometryIdentifier() = default
-
inline constexpr Value extra() const
Return the extra identifier Usage can be experiment-specific, like tagging which kind of detector a surface object corresponds to, or which subsystem it belongs to.
-
GeometryIdentifier &operator=(const GeometryIdentifier&) = default
-
GeometryIdentifier &operator=(GeometryIdentifier&&) = default
-
inline constexpr GeometryIdentifier &setApproach(Value approach)
Set the approach identifier.
-
inline constexpr GeometryIdentifier &setBoundary(Value boundary)
Set the boundary identifier.
-
inline constexpr GeometryIdentifier &setExtra(Value extra)
Set the extra identifier.
-
inline constexpr GeometryIdentifier &setLayer(Value layer)
Set the layer identifier.
-
inline constexpr GeometryIdentifier &setPassive(Value approach)
Set the approach identifier - shared with Passive.
-
inline constexpr GeometryIdentifier &setSensitive(Value sensitive)
Set the sensitive identifier.
-
inline constexpr GeometryIdentifier &setVolume(Value volume)
Set the volume identifier.
-
class GeometryObject
Base class to provide GeometryIdentifier interface:
simple set and get
It also provides the binningPosition method for Geometry geometrical object to be binned in BinnedArrays
Subclassed by Acts::Layer, Acts::Surface, Acts::Volume
Public Functions
-
GeometryObject() = default
Defaulted constructor.
-
inline GeometryObject(const GeometryIdentifier &geometryId)
Constructor from a value.
- Parameters:
geometryId – the geometry identifier of the object
-
GeometryObject(const GeometryObject&) = default
Defaulted copy constructor.
-
inline void assignGeometryId(const GeometryIdentifier &geometryId)
Set the value.
- Parameters:
geometryId – the geometry identifier to be assigned
-
virtual Vector3 binningPosition(const GeometryContext &gctx, BinningValue bValue) const = 0
Force a binning position method.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
bValue – is the value in which you want to bin
- Returns:
vector 3D used for the binning schema
-
inline virtual double binningPositionValue(const GeometryContext &gctx, BinningValue bValue) const
Implement the binningValue.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
bValue – is the dobule in which you want to bin
- Returns:
float to be used for the binning schema
-
inline const GeometryIdentifier &geometryId() const
- Returns:
the geometry id by reference
-
inline GeometryObject &operator=(const GeometryObject &geometryId)
Assignment operator.
- Parameters:
geometryId – the source geometryId
-
template<typename T, class ...Axes>
class Grid class for describing a regular multi-dimensional grid
Class describing a multi-dimensional, regular grid which can store objects in its multi-dimensional bins. Bins are hyper-boxes and can be accessed either by global bin index, local bin indices or position.
Note
Tmust be default-constructible.- Template Parameters:
T – type of values stored inside the bins of the grid
Axes – parameter pack of axis types defining the grid
Public Types
-
using const_reference = const value_type&
constant reference type to values stored
-
using point_t = std::array<ActsScalar, DIM>
type for points in d-dimensional grid space
-
using reference = value_type&
reference type to values stored
Public Functions
-
inline Grid(const std::tuple<Axes...> &axes)
Constructor from const axis tuple, this will allow creating a grid with a different value type from a template grid object.
- Parameters:
axes –
-
Grid(std::tuple<Axes...> &axes) = delete
default constructor
- Parameters:
axes – [in] actual axis objects spanning the grid
-
inline reference at(std::size_t bin)
access value stored in bin with given global bin number
- Parameters:
bin – [in] global bin number
- Returns:
reference to value stored in bin containing the given point
-
inline const_reference at(std::size_t bin) const
access value stored in bin with given global bin number
- Parameters:
bin – [in] global bin number
- Returns:
const-reference to value stored in bin containing the given point
-
inline reference atLocalBins(const index_t &localBins)
access value stored in bin with given local bin numbers
- Parameters:
localBins – [in] local bin indices along each axis
- Returns:
reference to value stored in bin containing the given point
- Pre:
All local bin indices must be a valid index for the corresponding axis (including the under-/overflow bin for this axis).
-
inline const_reference atLocalBins(const index_t &localBins) const
access value stored in bin with given local bin numbers
- Parameters:
localBins – [in] local bin indices along each axis
- Returns:
const-reference to value stored in bin containing the given point
- Pre:
All local bin indices must be a valid index for the corresponding axis (including the under-/overflow bin for this axis).
-
template<class Point>
inline reference atPosition(const Point &point) access value stored in bin for a given point
Note
The look-up considers under-/overflow bins along each axis. Therefore, the look-up will never fail.
- Template Parameters:
Point – any type with point semantics supporting component access through
operator[]- Parameters:
point – [in] point used to look up the corresponding bin in the grid
- Returns:
reference to value stored in bin containing the given point
- Pre:
The given
Pointtype must represent a point in d (or higher) dimensions where d is dimensionality of the grid.
-
template<class Point>
inline const_reference atPosition(const Point &point) const access value stored in bin for a given point
Note
The look-up considers under-/overflow bins along each axis. Therefore, the look-up will never fail.
- Template Parameters:
Point – any type with point semantics supporting component access through
operator[]- Parameters:
point – [in] point used to look up the corresponding bin in the grid
- Returns:
const-reference to value stored in bin containing the given point
- Pre:
The given
Pointtype must represent a point in d (or higher) dimensions where d is dimensionality of the grid.
-
inline global_iterator_t begin() const
begin iterator for global bins
-
inline local_iterator_t begin(const std::array<std::vector<std::size_t>, DIM> &navigator) const
begin iterator for local bins
- Parameters:
navigator – is local navigator for the grid
-
inline std::array<ActsScalar, DIM> binCenter(const index_t &localBins) const
get center position of bin with given local bin numbers
- Parameters:
localBins – [in] local bin indices along each axis
- Returns:
center position of bin
- Pre:
All local bin indices must be a valid index for the corresponding axis (excluding the under-/overflow bins for each axis).
-
inline point_t binWidth() const
get bin width along each specific axis
- Returns:
array giving the bin width alonf all axes
-
template<class Point>
inline detail::GlobalNeighborHoodIndices<DIM> closestPointsIndices(const Point &position) const get global bin indices for closest points on grid
- Template Parameters:
Point – any type with point semantics supporting component access through
operator[]- Parameters:
position – [in] point of interest
- Returns:
Iterable thatemits the indices of bins whose lower-left corners are the closest points on the grid to the input.
- Pre:
The given
Pointtype must represent a point in d (or higher) dimensions where d is dimensionality of the grid. It must lie within the grid range (i.e. not within a under-/overflow bin).
-
template<typename converter_t>
inline Grid<typename converter_t::value_type, Axes...> convertGrid(converter_t &cVisitor) const Convenience function to convert the type of the grid to hold another object type.
This is designed to be most flexible with a converter object as a visitor. If needed, such a visitor could also use caching or other techniques to speed up the conversion.
- Template Parameters:
converter_t – the converter type
- Parameters:
cVisitor – the converter object as visitor
- Returns:
a new grid with the same axes and a different value type
-
template<typename U>
inline Grid<U, Axes...> convertType() const Convenience function to convert the type of the grid to hold another object type.
- Template Parameters:
U – the new grid value type
- Returns:
a new grid with the same axes and a different value type
-
inline global_iterator_t end() const
end iterator for global bins
-
inline local_iterator_t end(const std::array<std::vector<std::size_t>, DIM> &navigator) const
end iterator for local bins
- Parameters:
navigator – is local navigator for the grid
-
template<class Point>
inline std::size_t globalBinFromFromLowerLeftEdge(const Point &point) const determine global bin index of the bin with the lower left edge closest to the given point for each axis
Note
This could be a under-/overflow bin along one or more axes.
- Template Parameters:
Point – any type with point semantics supporting component access through
operator[]- Parameters:
point – [in] point to look up in the grid
- Returns:
global index for bin containing the given point
- Pre:
The given
Pointtype must represent a point in d (or higher) dimensions where d is dimensionality of the grid.
-
inline std::size_t globalBinFromLocalBins(const index_t &localBins) const
determine global bin index from local bin indices along each axis
- Parameters:
localBins – [in] local bin indices along each axis
- Returns:
global index for bin defined by the local bin indices
- Pre:
All local bin indices must be a valid index for the corresponding axis (including the under-/overflow bin for this axis).
-
template<class Point>
inline std::size_t globalBinFromPosition(const Point &point) const determine global index for bin containing the given point
Note
This could be a under-/overflow bin along one or more axes.
- Template Parameters:
Point – any type with point semantics supporting component access through
operator[]- Parameters:
point – [in] point to look up in the grid
- Returns:
global index for bin containing the given point
- Pre:
The given
Pointtype must represent a point in d (or higher) dimensions where d is dimensionality of the grid.
-
template<class Point, typename U = T, typename = std::enable_if_t<detail::can_interpolate<Point, std::array<ActsScalar, DIM>, std::array<ActsScalar, DIM>, U>::value>>
inline T interpolate(const Point &point) const interpolate grid values to given position
Note
This function is available only if the following conditions are fulfilled:
Given
UandVof value typeTas well as twoActsScalaraandb, then the following must be a valid expressiona * U + bVyielding an object which is (implicitly) convertible toT.Pointmust represent a d-dimensional position and support coordinate access usingoperator[] which should return aActsScalar(or a value which is implicitly convertible). Coordinate indices must start at 0.
Note
Bin values are interpreted as being the field values at the lower-left corner of the corresponding hyper-box.
- Template Parameters:
Point – type specifying geometric positions
U – dummy template parameter identical to
T
- Parameters:
point – [in] location to which to interpolate grid values. The position must be within the grid dimensions and not lie in an under-/overflow bin along any axis.
- Returns:
interpolated value at given position
- Pre:
The given
Pointtype must represent a point in d (or higher) dimensions where d is dimensionality of the grid.
-
template<class Point>
inline bool isInside(const Point &position) const check whether given point is inside grid limits
- Returns:
trueif \(\text{xmin_i} \le x_i < \text{xmax}_i \forall i=0, \dots, d-1\), otherwisefalse- Pre:
The given
Pointtype must represent a point in d (or higher) dimensions where d is dimensionality of the grid.- Post:
If
trueis returned, the global bin containing the given point is a valid bin, i.e. it is neither a underflow nor an overflow bin along any axis.
-
inline index_t localBinsFromGlobalBin(std::size_t bin) const
determine local bin index for each axis from global bin index
Note
Local bin indices can contain under-/overflow bins along the corresponding axis.
- Parameters:
bin – [in] global bin index
- Returns:
array with local bin indices along each axis (in same order as given
axesobject)
-
template<class Point>
inline index_t localBinsFromLowerLeftEdge(const Point &point) const determine local bin index of the bin with the lower left edge closest to the given point for each axis
Note
This could be a under-/overflow bin along one or more axes.
- Template Parameters:
Point – any type with point semantics supporting component access through
operator[]- Parameters:
point – [in] point to look up in the grid
- Returns:
array with local bin indices along each axis (in same order as given
axesobject)- Pre:
The given
Pointtype must represent a point in d (or higher) dimensions where d is dimensionality of the grid.
-
template<class Point>
inline index_t localBinsFromPosition(const Point &point) const determine local bin index for each axis from the given point
Note
This could be a under-/overflow bin along one or more axes.
- Template Parameters:
Point – any type with point semantics supporting component access through
operator[]- Parameters:
point – [in] point to look up in the grid
- Returns:
array with local bin indices along each axis (in same order as given
axesobject)- Pre:
The given
Pointtype must represent a point in d (or higher) dimensions where d is dimensionality of the grid.
-
inline point_t lowerLeftBinEdge(const index_t &localBins) const
retrieve lower-left bin edge from set of local bin indices
- Parameters:
localBins – [in] local bin indices along each axis
- Returns:
generalized lower-left bin edge position
- Pre:
localBinsmust only contain valid bin indices (excluding underflow bins).
-
inline point_t maxPosition() const
get the maximum value of all axes of one grid
- Returns:
array returning the maxima of all given axes
-
inline point_t minPosition() const
get the minimum value of all axes of one grid
- Returns:
array returning the minima of all given axes
-
inline detail::GlobalNeighborHoodIndices<DIM> neighborHoodIndices(const index_t &localBins, std::array<std::pair<int, int>, DIM> &sizePerAxis) const
get global bin indices for neighborhood
Note
Over-/underflow bins are included in the neighborhood.
Note
The
sizeparameter sets the range by how many units each local bin index is allowed to be varied. All local bin indices are varied independently, that is diagonal neighbors are included. Ignoring the truncation of the neighborhood size reaching beyond over-/underflow bins, the neighborhood is of size \(2 \times \text{size}+1\) along each dimension.- Parameters:
localBins – [in] center bin defined by local bin indices along each axis. If size is negative, center bin is not returned.
sizePerAxis – [in] size of neighborhood for each axis, how many adjacent bins along each axis are considered
- Returns:
set of global bin indices for all bins in neighborhood
-
inline detail::GlobalNeighborHoodIndices<DIM> neighborHoodIndices(const index_t &localBins, std::size_t size = 1u) const
get global bin indices for neighborhood
Note
Over-/underflow bins are included in the neighborhood.
Note
The
sizeparameter sets the range by how many units each local bin index is allowed to be varied. All local bin indices are varied independently, that is diagonal neighbors are included. Ignoring the truncation of the neighborhood size reaching beyond over-/underflow bins, the neighborhood is of size \(2 \times \text{size}+1\) along each dimension.- Parameters:
localBins – [in] center bin defined by local bin indices along each axis
size – [in] size of neighborhood determining how many adjacent bins along each axis are considered
- Returns:
set of global bin indices for all bins in neighborhood
-
inline index_t numLocalBins() const
get number of bins along each specific axis
Note
Not including under- and overflow bins
- Returns:
array giving the number of bins along all axes
-
inline void setExteriorBins(const value_type &value)
set all overflow and underflow bins to a certain value
- Parameters:
value – [in] value to be inserted in every overflow and underflow bin of the grid.
-
inline std::size_t size(bool fullCounter = true) const
total number of bins
Note
This number contains under-and overflow bins along all axes.
- Returns:
total number of bins in the grid
-
inline point_t upperRightBinEdge(const index_t &localBins) const
retrieve upper-right bin edge from set of local bin indices
- Parameters:
localBins – [in] local bin indices along each axis
- Returns:
generalized upper-right bin edge position
- Pre:
localBinsmust only contain valid bin indices (excluding overflow bins).
Public Static Functions
-
static inline constexpr std::size_t dimensions()
dimensionality of grid
- Returns:
number of axes spanning the grid
-
class HomogeneousSurfaceMaterial : public Acts::ISurfaceMaterial
It extends the ISurfaceMaterial virtual base class to describe a simple homogeneous material on a surface.
Public Functions
-
HomogeneousSurfaceMaterial() = default
Default Constructor - defaulted.
-
HomogeneousSurfaceMaterial(const HomogeneousSurfaceMaterial &hsm) = default
Copy Constructor.
- Parameters:
hsm – is the source material
-
HomogeneousSurfaceMaterial(const MaterialSlab &full, double splitFactor = 1., MappingType mappingType = MappingType::Default)
Explicit constructor.
- Parameters:
full – are the full material properties
splitFactor – is the split for pre/post update
mappingType – is the type of surface mapping associated to the surface
-
HomogeneousSurfaceMaterial(HomogeneousSurfaceMaterial &&hsm) = default
Copy Move Constructor.
- Parameters:
hsm – is the source material
-
~HomogeneousSurfaceMaterial() override = default
Destructor.
-
inline double factor(Direction pDir, MaterialUpdateStage mStage) const
The inherited methods - for scale access.
-
inline virtual const MaterialSlab &materialSlab(const Vector2 &lp) const final
Return method for full material description of the Surface.
from local coordinate on the surface
Note
the input parameter is ignored
- Parameters:
lp – is the local position used for the (eventual) lookup
- Returns:
const MaterialSlab
-
const MaterialSlab &materialSlab(const Vector2 &lp) const = 0
The inherited methods - for MaterialSlab access.
-
inline MaterialSlab materialSlab(const Vector2 &lp, Direction pDir, MaterialUpdateStage mStage) const
The inherited methods - for MaterialSlab access.
-
inline virtual const MaterialSlab &materialSlab(const Vector3 &gp) const final
Return method for full material description of the Surface.
from the global coordinates
Note
the input parameter is ignored
- Parameters:
gp – is the global position used for the (eventual) lookup
- Returns:
const MaterialSlab
-
const MaterialSlab &materialSlab(const Vector3 &gp) const = 0
The inherited methods - for MaterialSlab access.
-
inline MaterialSlab materialSlab(const Vector3 &gp, Direction pDir, MaterialUpdateStage mStage) const
The inherited methods - for MaterialSlab access.
-
virtual HomogeneousSurfaceMaterial &operator*=(double scale) final
Scale operator.
it is effectively a thickness scaling
- Parameters:
scale – is the scale factor
-
HomogeneousSurfaceMaterial &operator=(const HomogeneousSurfaceMaterial &hsm) = default
Assignment operator.
- Parameters:
hsm – is the source material
-
HomogeneousSurfaceMaterial &operator=(HomogeneousSurfaceMaterial &&hsm) = default
Assignment Move operator.
- Parameters:
hsm – is the source material
-
inline bool operator==(const HomogeneousSurfaceMaterial &hsm) const
Equality operator.
- Parameters:
hsm – is the source material
-
virtual std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &sl) const final
Output Method for std::ostream.
- Parameters:
sl – The outoput stream
-
HomogeneousSurfaceMaterial() = default
-
class IAxis
Common base class for all Axis instance.
This allows generice handling such as for inspection.
Public Functions
-
virtual std::vector<ActsScalar> getBinEdges() const = 0
Return a vector of bin edges.
- Returns:
Vector which contains the bin edges
-
virtual detail::AxisBoundaryType getBoundaryType() const = 0
returns the boundary type set in the template param
- Returns:
AxisBoundaryTypeof this axis
-
virtual ActsScalar getMax() const = 0
get maximum of binning range
- Returns:
maximum of binning range
-
virtual ActsScalar getMin() const = 0
get minimum of binning range
- Returns:
minimum of binning range
-
virtual std::size_t getNBins() const = 0
get total number of bins
- Returns:
total number of bins (excluding under-/overflow bins)
-
virtual bool isEquidistant() const = 0
returns whether the axis is equidistant
- Returns:
bool is equidistant
-
virtual bool isVariable() const = 0
returns whether the axis is variable
- Returns:
bool is variable
-
virtual std::vector<ActsScalar> getBinEdges() const = 0
-
class IGeant4PhysicalVolumeSelector
Interface class for selectors from physical volumes.
Subclassed by Acts::Geant4PhysicalVolumeSelectors::AllSelector, Acts::Geant4PhysicalVolumeSelectors::NameSelector, Acts::Geant4PhysicalVolumeSelectors::PositionSelector
-
class ISurfaceMaterial
Virtual base class of surface based material description.
MaterialSlab that are associated to a surface, extended by certain special representations (binned, homogeneous)
Subclassed by Acts::BinnedSurfaceMaterial, Acts::GridSurfaceMaterialT< grid_t, material_accessor_t >, Acts::HomogeneousSurfaceMaterial, Acts::ProtoSurfaceMaterialT< BinningType >
Public Functions
-
ISurfaceMaterial() = default
Constructor.
-
inline ISurfaceMaterial(double splitFactor)
Constructor.
- Parameters:
splitFactor – is the splitting ratio between pre/post update
-
inline ISurfaceMaterial(double splitFactor, Acts::MappingType mappingType)
Constructor.
- Parameters:
splitFactor – is the splitting ratio between pre/post update
mappingType – is the type of surface mapping associated to the surface
-
virtual ~ISurfaceMaterial() = default
Destructor.
-
inline double factor(Direction pDir, MaterialUpdateStage mStage) const
Update pre factor.
- Parameters:
pDir – is the positive direction through the surface
mStage – is the material update directive (onapproach, full, onleave)
-
inline MappingType mappingType() const
Return the type of surface material mapping.
-
virtual const MaterialSlab &materialSlab(const Vector2 &lp) const = 0
Return method for full material description of the Surface.
from local coordinate on the surface
- Parameters:
lp – is the local position used for the (eventual) lookup
- Returns:
const MaterialSlab
-
inline MaterialSlab materialSlab(const Vector2 &lp, Direction pDir, MaterialUpdateStage mStage) const
Return method for fully scaled material description of the Surface.
from local coordinate on the surface
- Parameters:
lp – is the local position used for the (eventual) lookup
pDir – is the positive direction through the surface
mStage – is the material update directive (onapproach, full, onleave)
- Returns:
MaterialSlab
-
virtual const MaterialSlab &materialSlab(const Vector3 &gp) const = 0
Return method for full material description of the Surface.
from the global coordinates
- Parameters:
gp – is the global position used for the (eventual) lookup
- Returns:
const MaterialSlab
-
inline MaterialSlab materialSlab(const Vector3 &gp, Direction pDir, MaterialUpdateStage mStage) const
Return method for full material description of the Surface.
from the global coordinates
- Parameters:
gp – is the global position used for the (eventual) lookup
pDir – is the positive direction through the surface
mStage – is the material update directive (onapproach, full, onleave)
- Returns:
MaterialSlab
-
virtual ISurfaceMaterial &operator*=(double scale) = 0
Scale operator.
- Parameters:
scale – is the scale factor applied
-
virtual std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &sl) const = 0
Output Method for std::ostream, to be overloaded by child classes.
Friends
-
inline friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &out, const ISurfaceMaterial &sm)
output stream operator
Prints information about this object to the output stream using the virtual ISurfaceMaterial::toStream method
- Returns:
modified output stream object
-
ISurfaceMaterial() = default
-
class IdentifiedDetectorElement : public Acts::DetectorElementBase
The identified detector element.
It adds the Identifier defnition and a forward declaration of the DigitizationModule to the detector elements
The identifier can be overwritten with by the use of the ACTS_CORE_IDENTIFIER_PLUGIN
Subclassed by Acts::TGeoDetectorElement
-
class InfiniteBounds : public Acts::SurfaceBounds
templated boundless extension to forward the interface Returns all inside checks to true and can templated for all bounds
Public Functions
-
InfiniteBounds() = default
-
~InfiniteBounds() override = default
-
inline virtual bool inside(const Vector2&, const BoundaryCheck&) const final
Method inside() returns true for any case.
ignores input parameters
- Returns:
always true
-
inline virtual std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &os) const final
Output Method for std::ostream.
-
inline virtual SurfaceBounds::BoundsType type() const final
Return the bounds type - for persistency optimization.
- Returns:
is a BoundsType enum
-
inline virtual std::vector<double> values() const final
Access method for bound values, this is a dynamically sized vector containing the parameters needed to describe these bounds.
- Returns:
of the stored values for this SurfaceBounds object
-
InfiniteBounds() = default
-
template<typename grid_t>
class InterpolatedBFieldMap : public Acts::InterpolatedMagneticField interpolate magnetic field value from field values on a given grid
This class implements a magnetic field service which is initialized by a field map defined by:
a list of field values on a regular grid in some n-Dimensional space,
a transformation of global 3D coordinates onto this n-Dimensional space.
a transformation of local n-Dimensional magnetic field coordinates into global (cartesian) 3D coordinates
The magnetic field value for a given global position is then determined by:
mapping the position onto the grid,
looking up the magnetic field values on the closest grid points,
doing a linear interpolation of these magnetic field values.
- Template Parameters:
grid_t – The Grid type which provides the field storage and interpolation
Public Functions
-
inline Result<Vector3> getField(const Vector3 &position) const
retrieve field at given position
- Parameters:
position – [in] global 3D position
- Returns:
magnetic field value at the given position
- Pre:
The given
positionmust lie within the range of the underlying magnetic field map.
-
inline virtual Result<Vector3> getField(const Vector3 &position, MagneticFieldProvider::Cache &cache) const final
Retrieve magnetic field value at a given location.
Requires a cache object created through makeCache().
- Parameters:
position – [in] global 3D position for the lookup
cache – [inout] Field provider specific cache object
- Returns:
magnetic field vector at given position
-
inline Result<FieldCell> getFieldCell(const Vector3 &position) const
retrieve field cell for given position
- Parameters:
position – [in] global 3D position
- Returns:
field cell containing the given global position
- Pre:
The given
positionmust lie within the range of the underlying magnetic field map.
-
inline virtual Result<Vector3> getFieldGradient(const Vector3 &position, ActsMatrix<3, 3> &derivative, MagneticFieldProvider::Cache &cache) const final
Retrieve magnetic field value its its gradient.
Requires a cache object created through makeCache().
Note
currently the derivative is not calculated
Note
Cache is not used currently
- Parameters:
position – [in] global 3D position
derivative – [out] gradient of magnetic field vector as (3x3) matrix
cache – [inout] Field provider specific cache object
- Returns:
magnetic field vector
-
inline virtual Vector3 getFieldUnchecked(const Vector3 &position) const final
Get a field value without checking if the lookup position is within the interpolation domain.
- Parameters:
position – The lookup position in 3D
- Returns:
The field value at
position
-
inline const Grid &getGrid() const
Get a const reference on the underlying grid structure.
- Returns:
grid reference
-
inline virtual std::vector<double> getMax() const final
get the maximum value of all axes of the field map
- Returns:
vector returning the maxima of all field map axes
-
inline virtual std::vector<double> getMin() const final
get the minimum value of all axes of the field map
- Returns:
vector returning the minima of all field map axes
-
inline virtual std::vector<std::size_t> getNBins() const final
get the number of bins for all axes of the field map
- Returns:
vector returning number of bins for all field map axes
-
inline virtual bool isInside(const Vector3 &position) const final
check whether given 3D position is inside look-up domain
- Parameters:
position – [in] global 3D position
- Returns:
trueif position is inside the defined look-up grid, otherwisefalse
-
inline bool isInsideLocal(const ActsVector<DIM_POS> &gridPosition) const
check whether given 3D position is inside look-up domain
- Parameters:
gridPosition – [in] local N-D position
- Returns:
trueif position is inside the defined look-up grid, otherwisefalse
-
inline virtual MagneticFieldProvider::Cache makeCache(const MagneticFieldContext &mctx) const final
Make an opaque cache for the magnetic field.
Instructs the specific implementation to generate a
Cacheinstance for magnetic field lookup.- Parameters:
mctx – The magnetic field context to generate cache for
- Returns:
Cache The opaque cache object
-
struct Cache
Public Functions
-
inline Cache(const MagneticFieldContext&)
Constructor with magnetic field context.
-
inline Cache(const MagneticFieldContext&)
-
struct Config
Config structure for the interpolated B field map.
Public Members
-
double scale = 1.
global B-field scaling factor
Note
Negative values for
scaleare accepted and will invert the direction of the magnetic field.
-
std::function<Vector3(const FieldType&, const Vector3&)> transformBField
calculating the global 3D coordinates (cartesian) of the magnetic field with the local n dimensional field and the global 3D position as input
- std::function< ActsVector< DIM_POS >const Vector3 &)> transformPos
mapping of global 3D coordinates (cartesian) onto grid space
-
double scale = 1.
-
struct FieldCell
struct representing smallest grid unit in magnetic field grid
This type encapsulate all required information to perform linear interpolation of magnetic field values within a confined 3D volume.
Public Functions
-
inline FieldCell(std::array<double, DIM_POS> lowerLeft, std::array<double, DIM_POS> upperRight, std::array<Vector3, N> fieldValues)
default constructor
- Parameters:
lowerLeft – [in] generalized lower-left corner of hyper box (containing the minima of the hyper box along each Dimension)
upperRight – [in] generalized upper-right corner of hyper box (containing the maxima of the hyper box along each Dimension)
fieldValues – [in] field values at the hyper box corners sorted in the canonical order defined in Acts::interpolate
-
inline Vector3 getField(const ActsVector<DIM_POS> &position) const
retrieve field at given position
- Parameters:
position – [in] global 3D position
- Returns:
magnetic field value at the given position
- Pre:
The given
positionmust lie within the current field cell.
-
inline bool isInside(const ActsVector<DIM_POS> &position) const
check whether given 3D position is inside this field cell
- Parameters:
position – [in] global 3D position
- Returns:
trueif position is inside the current field cell, otherwisefalse
-
inline FieldCell(std::array<double, DIM_POS> lowerLeft, std::array<double, DIM_POS> upperRight, std::array<Vector3, N> fieldValues)
-
class InterpolatedMagneticField : public Acts::MagneticFieldProvider
Subclassed by Acts::InterpolatedBFieldMap< grid_t >
Public Functions
-
virtual Vector3 getFieldUnchecked(const Vector3 &position) const = 0
Get a field value without checking if the lookup position is within the interpolation domain.
- Parameters:
position – The lookup position in 3D
- Returns:
The field value at
position
-
virtual std::vector<double> getMax() const = 0
get the maximum value of all axes of the field map
- Returns:
vector returning the maxima of all field map axes
-
virtual std::vector<double> getMin() const = 0
get the minimum value of all axes of the field map
- Returns:
vector returning the minima of all field map axes
-
virtual std::vector<std::size_t> getNBins() const = 0
get the number of bins for all axes of the field map
- Returns:
vector returning number of bins for all field map axes
-
virtual Vector3 getFieldUnchecked(const Vector3 &position) const = 0
-
class KDTreeTrackingGeometryBuilder : public Acts::ITrackingGeometryBuilder
A Tracking Geometry builder restricted to cylindrical geometries.
It takes some helper tools and a vector of surface objects, together with a ProtoDetector description that is used to query a KDTree for contained surfaces in structures defined by the proto volume.
Public Types
-
using SurfaceKDT = KDTree<2u, std::shared_ptr<Surface>, ActsScalar, std::array, 100>
Public Functions
-
KDTreeTrackingGeometryBuilder(const Config &cfg, std::unique_ptr<const Logger> logger = getDefaultLogger("KDTreeTrackingGeometryBuilder", Logging::INFO))
Constructor.
- Parameters:
cfg – [in] is the configuration struct for this builder
logger – [in] logging instance
-
virtual std::unique_ptr<const TrackingGeometry> trackingGeometry(const GeometryContext &gctx) const final
TrackingGeometry Interface method.
- Parameters:
gctx – geometry context of that building call
- Returns:
a unique pointer to a TrackingGeometry
-
struct Config
Nested Configuration for this TrackingGeometryBuilder.
Public Members
-
std::shared_ptr<const GeometryIdentifierHook> geometryIdentifierHook = std::make_shared<GeometryIdentifierHook>()
Optional geometry identifier hook to be used during closure.
-
std::string hierarchyIndent = " "
For screen output.
-
std::shared_ptr<const LayerCreator> layerCreator = nullptr
The layer creator - for sensitives.
-
ProtoDetector protoDetector
The proto tracking geometry description.
-
std::shared_ptr<const ITrackingVolumeHelper> trackingVolumeHelper = nullptr
The tracking volume helper for detector construction.
-
std::shared_ptr<const GeometryIdentifierHook> geometryIdentifierHook = std::make_shared<GeometryIdentifierHook>()
-
using SurfaceKDT = KDTree<2u, std::shared_ptr<Surface>, ActsScalar, std::array, 100>
-
template<typename propagator_t, typename traj_t>
class KalmanFitter Kalman fitter implementation.
The Kalman filter contains an Actor and a Sequencer sub-class. The Sequencer has to be part of the Navigator of the Propagator in order to initialize and provide the measurement surfaces.
The Actor is part of the Propagation call and does the Kalman update and eventually the smoothing. Updater, Smoother and Calibrator are given to the Actor for further use:
The Updater is the implemented kalman updater formalism, it runs via a visitor pattern through the measurements.
The Smoother is called at the end of the filtering by the Actor.
Measurements are not required to be ordered for the KalmanFilter, measurement ordering needs to be figured out by the navigation of the propagator.
The void components are provided mainly for unit testing.
- Template Parameters:
propagator_t – Type of the propagation class
Public Functions
-
inline KalmanFitter(propagator_t pPropagator, std::unique_ptr<const Logger> _logger = getDefaultLogger("KalmanFitter", Logging::INFO))
-
template<typename source_link_iterator_t, typename start_parameters_t, typename parameters_t = BoundTrackParameters, typename track_container_t, template<typename> class holder_t, bool _isdn = isDirectNavigator>
inline auto fit(source_link_iterator_t it, source_link_iterator_t end, const start_parameters_t &sParameters, const KalmanFitterOptions<traj_t> &kfOptions, const std::vector<const Surface*> &sSequence, TrackContainer<track_container_t, traj_t, holder_t> &trackContainer) const -> std::enable_if_t<_isdn, Result<typename TrackContainer<track_container_t, traj_t, holder_t>::TrackProxy>> Fit implementation of the forward filter, calls the the filter and smoother/reversed filter.
Note
The input measurements are given in the form of
SourceLinks. It’scalibrator_t'sjob to turn them into calibrated measurements used in the fit.- Template Parameters:
source_link_iterator_t – Iterator type used to pass source links
start_parameters_t – Type of the initial parameters
parameters_t – Type of parameters used for local parameters
track_container_t – Type of the track container backend
holder_t – Type defining track container backend ownership
- Parameters:
it – Begin iterator for the fittable uncalibrated measurements
end – End iterator for the fittable uncalibrated measurements
sParameters – The initial track parameters
kfOptions – KalmanOptions steering the fit
sSequence – surface sequence used to initialize a DirectNavigator
trackContainer – Input track container storage to append into
- Returns:
the output as an output track
-
template<typename source_link_iterator_t, typename start_parameters_t, typename parameters_t = BoundTrackParameters, typename track_container_t, template<typename> class holder_t, bool _isdn = isDirectNavigator>
inline auto fit(source_link_iterator_t it, source_link_iterator_t end, const start_parameters_t &sParameters, const KalmanFitterOptions<traj_t> &kfOptions, TrackContainer<track_container_t, traj_t, holder_t> &trackContainer) const -> std::enable_if_t<!_isdn, Result<typename TrackContainer<track_container_t, traj_t, holder_t>::TrackProxy>> Fit implementation of the forward filter, calls the the filter and smoother/reversed filter.
Note
The input measurements are given in the form of
SourceLinks. It’s the calibrators job to turn them into calibrated measurements used in the fit.- Template Parameters:
source_link_iterator_t – Iterator type used to pass source links
start_parameters_t – Type of the initial parameters
parameters_t – Type of parameters used for local parameters
track_container_t – Type of the track container backend
holder_t – Type defining track container backend ownership
- Parameters:
it – Begin iterator for the fittable uncalibrated measurements
end – End iterator for the fittable uncalibrated measurements
sParameters – The initial track parameters
kfOptions – KalmanOptions steering the fit
trackContainer – Input track container storage to append into
- Returns:
the output as an output track
-
class Layer : public virtual Acts::GeometryObject
Base Class for a Detector Layer in the Tracking Geometry.
An actual implemented Detector Layer inheriting from this base class has to inherit from a specific type of Surface as well. In addition, a Layer can carry:
A SurfaceArray of Surfaces holding the actual detector elements or subSurfaces. A pointer to the TrackingVolume (can only be set by such) An active/passive code : 0 - active 1 - passive [….] - other
The search type for compatible surfaces on a layer is [ the higher the number, the faster ]: ——— Layer internal ———————————————— -1 - provide all intersection tested without boundary check 0 - provide all intersection tested with boundary check 1 - provide overlap descriptor based without boundary check 2 - provide overlap descriptor based with boundary check
A layer can have substructure regarding:
m_ssRepresentingSurface -> always exists (1), can have material (2)
m_ssSensitiveSurfaces -> can or not exist (0,1), can have material (2)
m_ssApproachSurfaces -> can or not exist (0,1) cam have material (2)
Subclassed by Acts::ConeLayer, Acts::CylinderLayer, Acts::DiscLayer, Acts::NavigationLayer, Acts::PlaneLayer
Public Functions
-
Layer() = delete
Default Constructor - deleted.
-
virtual ~Layer() = default
Destructor.
-
ApproachDescriptor *approachDescriptor()
Non-const version of the approach descriptor.
-
const ApproachDescriptor *approachDescriptor() const
Return method for the approach descriptor, can be nullptr.
Decompose Layer into (compatible) surfaces.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – Position parameter for searching
direction – Direction of the parameters for searching
options – The navigation options
- Returns:
list of intersection of surfaces on the layer
-
virtual bool isOnLayer(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const BoundaryCheck &bcheck = BoundaryCheck(true)) const
geometrical isOnLayer() method
Note
using isOnSurface() with Layer specific tolerance
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – is the global position to be checked
bcheck – is the boundary check directive
- Returns:
boolean that indicates success of the operation
-
LayerType layerType() const
return the LayerType
-
const Layer *nextLayer(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction) const
Fast navigation to next layer.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – is the start position for the search
direction – is the direction for the search
- Returns:
the pointer to the next layer
-
Layer &operator=(const Layer &layer) = delete
Assignment operator - forbidden, layer assignment must not be ambiguous.
- Parameters:
layer – is the source layer for assignment
-
const Volume *representingVolume() const
Return the abstract volume that represents the layer.
- Returns:
the representing volume of the layer
-
virtual bool resolve(bool resolveSensitive, bool resolveMaterial, bool resolvePassive) const
Accept layer according to the following collection directives.
- Parameters:
resolveSensitive – is the prescription to find the sensitive surfaces
resolveMaterial – is the precription to find material surfaces
resolvePassive – is the prescription to find all passive surfaces
- Returns:
a boolean whether the layer is accepted for processing
-
template<typename options_t>
inline bool resolve(const options_t &options) const Accept layer according to the following collection directives.
- Template Parameters:
options_t – Type of the options for navigation
- Returns:
a boolean whether the layer is accepted for processing
-
SurfaceArray *surfaceArray()
Non-const version.
-
const SurfaceArray *surfaceArray() const
Return the entire SurfaceArray, returns a nullptr if no SurfaceArray.
Surface seen on approach for layers without sub structure, this is the surfaceRepresentation for layers with sub structure, this is the approachSurface.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – Position for searching
direction – Direction for searching
options – The navigation options
- Returns:
the Surface intersection of the approach surface
-
virtual const Surface &surfaceRepresentation() const = 0
Transforms the layer into a Surface representation for extrapolation.
Note
the layer can be hosting many surfaces, but this is the global one to which one can extrapolate
-
double thickness() const
Return the Thickness of the Layer this is by definition along the normal vector of the surfaceRepresentation.
-
const TrackingVolume *trackingVolume() const
Get the confining TrackingVolume.
- Returns:
the pointer to the enclosing volume
-
class LineBounds : public Acts::SurfaceBounds
Bounds for a LineSurface.
Public Functions
-
LineBounds() = delete
-
inline LineBounds(const std::array<double, eSize> &values) noexcept(false)
Constructor - from fixed size array.
- Parameters:
values – The parameter values
-
inline LineBounds(double r, double halfZ) noexcept(false)
Constructor.
- Parameters:
r – is the radius of the cylinder, default = 0.
halfZ – is the half length in z, default = 0.
-
~LineBounds() override = default
-
inline double get(BoundValues bValue) const
Access to the bound values.
- Parameters:
bValue – the class nested enum for the array access
-
virtual bool inside(const Vector2 &lposition, const BoundaryCheck &bcheck) const final
Inside check for the bounds object driven by the boundary check directive Each Bounds has a method inside, which checks if a LocalPosition is inside the bounds Inside can be called without/with tolerances.
- Parameters:
lposition – Local position (assumed to be in right surface frame)
bcheck – boundary check directive
- Returns:
boolean indicator for the success of this operation
-
virtual std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &sl) const final
Output Method for std::ostream.
- Parameters:
sl – is the ostream to be dumped into
-
virtual BoundsType type() const final
Return the bounds type - for persistency optimization.
- Returns:
is a BoundsType enum
-
inline virtual std::vector<double> values() const final
Return the bound values as dynamically sized vector.
- Returns:
this returns a copy of the internal values
-
LineBounds() = delete
-
class LineSurface : public Acts::Surface
Base class for a linear surfaces in the TrackingGeometry to describe dirft tube, straw like detectors or the Perigee It inherits from Surface.
Note
It leaves the type() method virtual, so it can not be instantiated
Subclassed by Acts::PerigeeSurface, Acts::StrawSurface
Public Functions
-
LineSurface() = delete
-
~LineSurface() override = default
-
virtual AlignmentToPathMatrix alignmentToPathDerivative(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction) const final
Calculate the derivative of path length at the geometry constraint or point-of-closest-approach w.r.t.
alignment parameters of the surface (i.e. local frame origin in global 3D Cartesian coordinates and its rotation represented with extrinsic Euler angles)
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – global 3D position
direction – global 3D momentum direction
- Returns:
Derivative of path length w.r.t. the alignment parameters
-
virtual Vector3 binningPosition(const GeometryContext &gctx, BinningValue bValue) const final
The binning position is the position calculated for a certain binning type.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
bValue – is the binning type to be used
- Returns:
position that can beused for this binning
-
virtual const SurfaceBounds &bounds() const final
This method returns the bounds of the surface by reference.
-
virtual BoundToFreeMatrix boundToFreeJacobian(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction) const final
Calculate the jacobian from local to global which the surface knows best, hence the calculation is done here.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – global 3D position
direction – global 3D momentum direction
- Returns:
Jacobian from local to global
-
virtual FreeToPathMatrix freeToPathDerivative(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction) const final
Calculate the derivative of path length at the geometry constraint or point-of-closest-approach w.r.t.
free parameters
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – global 3D position
direction – global 3D momentum direction
- Returns:
Derivative of path length w.r.t. free parameters
-
virtual Result<Vector2> globalToLocal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction, double tolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance) const final
Specified for
LineSurface: global to local method without dynamic memory allocation.This method is the true global -> local transformation. It makes use of
globalToLocaland indicates the sign of theActs::eBoundLoc0by the given momentum direction.The calculation of the sign of the radius (or \( d_0 \)) can be done as follows: May \( \vec d = \vec m - \vec c \) denote the difference between the center of the line and the global position of the measurement/predicted state. Then, \( \vec d \) lies in the so-called measurement plane. The latter is determined by the two orthogonal vectors \( \vec{\texttt{measY}} = \vec{e}_z \) and \( \vec{\texttt{measX}} = \vec{\texttt{measY}} \times \frac{\vec{p}}{|\vec{p}|} \).
The sign of the radius (or \( d_{0} \) ) is then defined by the projection of \( \vec{d} \) on \( \vec{measX} \):\( sign = -sign(\vec{d} \cdot \vec{measX}) \)
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – global 3D position - considered to be on surface but not inside bounds (check is done)
direction – global 3D momentum direction (optionally ignored)
tolerance – (unused)
- Returns:
A
Result<Vector2>, which is set to!ok()if thepositionis not the point of closest approach to the line surface.
-
virtual SurfaceMultiIntersection intersect(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction, const BoundaryCheck &bcheck = BoundaryCheck(false), ActsScalar tolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance) const final
Calculate the straight-line intersection with the line surface.
Mathematical motivation:
Given two lines in parameteric form:
\( \vec l_{a}(u) = \vec m_a + u \cdot \vec e_{a} \)
\( \vec l_{b}(\mu) = \vec m_b + \mu \cdot \vec e_{b} \)
The vector between any two points on the two lines is given by:
\( \vec s(u, \mu) = \vec l_{b} - l_{a} = \vec m_{ab} + \mu \cdot \vec e_{b} - u \cdot \vec e_{a} \),
where \( \vec m_{ab} = \vec m_{b} - \vec m_{a} \).
\( \vec s(u_0, \mu_0) \) denotes the vector between the two closest points
\( \vec l_{a,0} = l_{a}(u_0) \) and \( \vec l_{b,0} = l_{b}(\mu_0) \)
and is perpendicular to both, \( \vec e_{a} \) and \( \vec e_{b} \).
This results in a system of two linear equations:
(i) \( 0 = \vec s(u_0, \mu_0) \cdot \vec e_a = \vec m_{ab} \cdot \vec e_a + \mu_0 \vec e_a \cdot \vec e_b - u_0 \)
(ii) \( 0 = \vec s(u_0, \mu_0) \cdot \vec e_b = \vec m_{ab} \cdot \vec e_b + \mu_0 - u_0 \vec e_b \cdot \vec e_a \)
Solving (i) and (ii) for \( u \) and \( \mu_0 \) yields:
\( u_0 = \frac{(\vec m_{ab} \cdot \vec e_a)-(\vec m_{ab} \cdot \vec e_b)(\vec e_a \cdot \vec e_b)}{1-(\vec e_a \cdot \vec e_b)^2} \)
\( \mu_0 = - \frac{(\vec m_{ab} \cdot \vec e_b)-(\vec m_{ab} \cdot \vec e_a)(\vec e_a \cdot \vec e_b)}{1-(\vec e_a \cdot \vec e_b)^2} \)
The function checks if \( u_0 \simeq 0\) to check if the current
positionis at the point of closest approach, i.e. the intersection point, in which case it will return anonSuraceintersection result. Otherwise, the path length frompositionto the point of closest approach ( \( u_0 \)) is returned in areachableintersection.Note
expected to be normalized
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – The global position as a starting point
direction – The global direction at the starting point
bcheck – The boundary check directive for the estimate
tolerance – the tolerance used for the intersection
- Returns:
is the intersection object
-
Vector3 lineDirection(const GeometryContext &gctx) const
-
virtual ActsMatrix<2, 3> localCartesianToBoundLocalDerivative(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position) const final
Calculate the derivative of bound track parameters local position w.r.t.
position in local 3D Cartesian coordinates
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – The position of the parameters in global
- Returns:
Derivative of bound local position w.r.t. position in local 3D cartesian coordinates
-
virtual Vector3 localToGlobal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector2 &lposition, const Vector3 &direction) const final
Local to global transformation.
Note
for line surfaces the momentum direction is used in order to interpret the drift radius
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lposition – is the local position to be transformed
direction – is the global momentum direction (used to sign the closest approach)
- Returns:
global position by value
-
virtual std::string name() const override
Return properly formatted class name for screen output.
-
virtual Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &pos, const Vector3 &direction) const override
Return the surface normal at a given
positionanddirection.This method is fully generic, and valid for all surface types.
Note
For some surface types, the
directionis ignored, but it is not safe to pass in a zero vector!- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
pos – The position at which to calculate the normal
direction – The direction at which to calculate the normal
- Returns:
The normal vector at the given position and direction
-
LineSurface &operator=(const LineSurface &other)
Assignment operator.
- Parameters:
other – is the source surface dor copying
-
virtual double pathCorrection(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction) const override
the pathCorrection for derived classes with thickness is by definition 1 for LineSurfaces
Note
input parameters are ignored
Note
there’s no material associated to the line surface
-
virtual RotationMatrix3 referenceFrame(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction) const final
Return the measurement frame - this is needed for alignment, in particular.
for StraightLine and Perigee Surface
the default implementation is the RotationMatrix3 of the transform
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – is the global position where the measurement frame is constructed
direction – is the momentum direction used for the measurement frame construction
- Returns:
is a rotation matrix that indicates the measurement frame
-
LineSurface() = delete
-
class Logger
class for printing debug output
This class provides the user interface for printing debug messages with different levels of severity.
Public Functions
-
inline Logger(std::unique_ptr<Logging::OutputPrintPolicy> pPrint, std::unique_ptr<Logging::OutputFilterPolicy> pFilter)
construct from output print and filter policy
- Parameters:
pPrint – [in] policy for printing debug messages
pFilter – [in] policy for filtering debug messages
-
inline std::unique_ptr<Logger> clone(const std::optional<std::string> &_name = std::nullopt, const std::optional<Logging::Level> &_level = std::nullopt) const
Make a copy of this logger, optionally changing the name or the level.
- Parameters:
_name – the optional new name
_level – the optional new level
-
inline std::unique_ptr<Logger> clone(Logging::Level _level) const
Make a copy of the logger, with a new level.
Convenience function for if you only want to change the level but not the name.
- Parameters:
_level – the new level
- Returns:
the new logger
-
inline std::unique_ptr<Logger> cloneWithSuffix(const std::string &suffix, std::optional<Logging::Level> _level = std::nullopt) const
Make a copy of the logger, with a suffix added to the end of it’s name.
You can also optionally supply a new level
- Parameters:
suffix – the suffix to add to the end of the name
_level – the optional new level
-
inline bool doPrint(const Logging::Level &lvl) const
decide whether a message with a given debug level has to be printed
- Parameters:
lvl – [in] debug level of debug message
- Returns:
trueif debug message should be printed, otherwisefalse
-
inline const Logging::OutputFilterPolicy &filterPolicy() const
Return the filter policy for this logger.
- Returns:
the filter policy
-
inline Logging::Level level() const
Return the level of the filter policy of this logger.
- Returns:
the level
-
inline void log(const Logging::Level &lvl, const std::string &input) const
log a debug message
- Parameters:
lvl – [in] debug level of debug message
input – [in] text of debug message
-
inline const std::string &name() const
Return the name of the print policy of this logger.
- Returns:
the name
-
inline const Logger &operator()() const
Helper function so a logger reference can be used as is with the logging macros.
-
inline const Logging::OutputPrintPolicy &printPolicy() const
Return the print policy for this logger.
- Returns:
the print policy
-
inline Logger(std::unique_ptr<Logging::OutputPrintPolicy> pPrint, std::unique_ptr<Logging::OutputFilterPolicy> pFilter)
-
class DefaultFilterPolicy : public Acts::Logging::OutputFilterPolicy
default filter policy for debug messages
All debug messages with a debug level equal or larger to the specified threshold level are processed.
Public Functions
-
inline explicit DefaultFilterPolicy(Level lvl)
constructor
- Parameters:
lvl – [in] threshold debug level
-
~DefaultFilterPolicy() override = default
virtual default destructor
-
inline virtual std::unique_ptr<OutputFilterPolicy> clone(Level level) const override
Make a copy of this filter policy with a new level.
- Parameters:
level – the new level
- Returns:
the new copy
-
inline explicit DefaultFilterPolicy(Level lvl)
-
class DefaultPrintPolicy : public Acts::Logging::OutputPrintPolicy
default print policy for debug messages
This class allows to print debug messages without further modifications to a specified output stream.
Public Functions
-
inline explicit DefaultPrintPolicy(std::ostream *out = &std::cout)
constructor
- Parameters:
out – [in] pointer to output stream object
- Pre:
outis non-zero
-
inline virtual std::unique_ptr<OutputPrintPolicy> clone(const std::string&) const override
Make a copy of this print policy with a new name.
- Returns:
the copy
-
inline virtual void flush(const Level &lvl, const std::string &input) final
flush the debug message to the destination stream
- Parameters:
lvl – [in] debug level of debug message
input – [in] text of debug message
-
inline virtual const std::string &name() const override
Fulfill
OutputPrintPolicyinterface.This policy doesn’t actually have a name, so the assumption is that somewhere in the decorator hierarchy, there is something that returns a name without delegating to a wrappee, before reaching this overload.
Note
This method will throw an exception
- Returns:
the name, but it never returns
-
inline explicit DefaultPrintPolicy(std::ostream *out = &std::cout)
-
class LevelOutputDecorator : public Acts::Logging::OutputDecorator
decorate debug message with its debug level
The debug message is complemented with its debug level.
Public Functions
-
inline explicit LevelOutputDecorator(std::unique_ptr<OutputPrintPolicy> wrappee)
constructor
- Parameters:
wrappee – [in] output print policy object to be wrapped
-
inline virtual std::unique_ptr<OutputPrintPolicy> clone(const std::string &name) const override
Make a copy of this print policy with a new name.
- Parameters:
name – the new name
- Returns:
the copy
-
inline virtual void flush(const Level &lvl, const std::string &input) override
flush the debug message to the destination stream
This function prepends the debug level to the debug message and then delegates the flushing of the whole message to its wrapped object.
- Parameters:
lvl – [in] debug level of debug message
input – [in] text of debug message
-
inline explicit LevelOutputDecorator(std::unique_ptr<OutputPrintPolicy> wrappee)
-
class NamedOutputDecorator : public Acts::Logging::OutputDecorator
decorate debug message with a name
The debug message is complemented with a name.
Public Functions
-
inline NamedOutputDecorator(std::unique_ptr<OutputPrintPolicy> wrappee, const std::string &name, unsigned int maxWidth = 15)
constructor
- Parameters:
wrappee – [in] output print policy object to be wrapped
name – [in] name to be added to debug message
maxWidth – [in] maximum width of field used for name
-
inline virtual std::unique_ptr<OutputPrintPolicy> clone(const std::string &name) const override
Make a copy of this print policy with a new name.
- Parameters:
name – the new name
- Returns:
the copy
-
inline virtual void flush(const Level &lvl, const std::string &input) override
flush the debug message to the destination stream
This function prepends the given name to the debug message and then delegates the flushing of the whole message to its wrapped object.
- Parameters:
lvl – [in] debug level of debug message
input – [in] text of debug message
-
inline virtual const std::string &name() const override
Get this named output decorators name.
- Returns:
the name
-
inline NamedOutputDecorator(std::unique_ptr<OutputPrintPolicy> wrappee, const std::string &name, unsigned int maxWidth = 15)
-
class OutputDecorator : public Acts::Logging::OutputPrintPolicy
base class for decorating the debug output
Derived classes may augment the debug message with additional information. Chaining different decorators is possible to customize the output to your needs.
Subclassed by Acts::Logging::LevelOutputDecorator, Acts::Logging::NamedOutputDecorator, Acts::Logging::ThreadOutputDecorator, Acts::Logging::TimedOutputDecorator
Public Functions
-
inline explicit OutputDecorator(std::unique_ptr<OutputPrintPolicy> wrappee)
constructor wrapping actual output print policy
- Parameters:
wrappee – [in] output print policy object which is wrapped by this decorator object
-
inline virtual void flush(const Level &lvl, const std::string &input) override
flush the debug message to the destination stream
This function delegates the flushing of the debug message to its wrapped object.
- Parameters:
lvl – [in] debug level of debug message
input – [in] text of debug message
-
inline virtual const std::string &name() const override
Return the name of the output decorator (forwards to wrappee)
- Returns:
the name
-
inline explicit OutputDecorator(std::unique_ptr<OutputPrintPolicy> wrappee)
-
class OutputFilterPolicy
abstract base class for filtering debug output
Implementations of this interface need to define whether a debug message with a certain debug level is processed or filtered out.
Subclassed by Acts::Logging::DefaultFilterPolicy
Public Functions
-
virtual ~OutputFilterPolicy() = default
virtual default destructor
-
virtual std::unique_ptr<OutputFilterPolicy> clone(Level level) const = 0
Make a copy of this filter policy with a new level.
- Parameters:
level – the new level
- Returns:
the new copy
-
virtual ~OutputFilterPolicy() = default
-
class OutputPrintPolicy
abstract base class for printing debug output
Implementations of this interface need to define how and where to print debug messages (e.g. to a file, to a stream into a database etc).
Subclassed by Acts::Logging::DefaultPrintPolicy, Acts::Logging::OutputDecorator
Public Functions
-
virtual ~OutputPrintPolicy() = default
virtual default destructor
-
virtual std::unique_ptr<OutputPrintPolicy> clone(const std::string &name) const = 0
Make a copy of this print policy with a new name.
- Parameters:
name – the new name
- Returns:
the copy
-
virtual void flush(const Level &lvl, const std::string &input) = 0
handle output of debug message
- Parameters:
lvl – [in] debug output level of message
input – [in] text of debug message
-
virtual const std::string &name() const = 0
Return the name of the print policy.
- Returns:
the name
-
virtual ~OutputPrintPolicy() = default
-
class ThreadOutputDecorator : public Acts::Logging::OutputDecorator
decorate debug message with a thread ID
The debug message is complemented with a thread ID.
Public Functions
-
inline explicit ThreadOutputDecorator(std::unique_ptr<OutputPrintPolicy> wrappee)
constructor
- Parameters:
wrappee – [in] output print policy object to be wrapped
-
inline virtual std::unique_ptr<OutputPrintPolicy> clone(const std::string &name) const override
Make a copy of this print policy with a new name.
- Parameters:
name – the new name
- Returns:
the copy
-
inline virtual void flush(const Level &lvl, const std::string &input) override
flush the debug message to the destination stream
This function prepends the thread ID to the debug message and then delegates the flushing of the whole message to its wrapped object.
- Parameters:
lvl – [in] debug level of debug message
input – [in] text of debug message
-
inline explicit ThreadOutputDecorator(std::unique_ptr<OutputPrintPolicy> wrappee)
-
class ThresholdFailure : public std::runtime_error
Custom exception class so threshold failures can be caught.
-
class TimedOutputDecorator : public Acts::Logging::OutputDecorator
decorate debug message with a time stamp
The debug message is complemented with a time stamp.
Public Functions
-
inline TimedOutputDecorator(std::unique_ptr<OutputPrintPolicy> wrappee, const std::string &format = "%X")
constructor
- Parameters:
wrappee – [in] output print policy object to be wrapped
format – [in] format of time stamp (see std::strftime)
-
inline virtual std::unique_ptr<OutputPrintPolicy> clone(const std::string &name) const override
Make a copy of this print policy with a new name.
- Parameters:
name – the new name
- Returns:
the copy
-
inline virtual void flush(const Level &lvl, const std::string &input) override
flush the debug message to the destination stream
This function prepends a time stamp to the debug message and then delegates the flushing of the whole message to its wrapped object.
- Parameters:
lvl – [in] debug level of debug message
input – [in] text of debug message
-
inline TimedOutputDecorator(std::unique_ptr<OutputPrintPolicy> wrappee, const std::string &format = "%X")
-
class MagneticFieldProvider
Base class for all magnetic field providers.
Subclassed by Acts::ConstantBField, Acts::DD4hepFieldAdapter, Acts::InterpolatedMagneticField, Acts::NullBField, Acts::SolenoidBField
Public Types
-
using Cache = Acts::AnyBase<sizeof(char) * 512>
Opaque cache type that can store arbitrary implementation specific cache data.
Examples are an interpolation cell, or an experiment specific conditions data handle.
Public Functions
-
inline virtual ~MagneticFieldProvider()
-
virtual Result<Vector3> getField(const Vector3 &position, Cache &cache) const = 0
Retrieve magnetic field value at a given location.
Requires a cache object created through makeCache().
- Parameters:
position – [in] global 3D position for the lookup
cache – [inout] Field provider specific cache object
- Returns:
magnetic field vector at given position
-
virtual Result<Vector3> getFieldGradient(const Vector3 &position, ActsMatrix<3, 3> &derivative, Cache &cache) const = 0
Retrieve magnetic field value its its gradient.
Requires a cache object created through makeCache().
- Parameters:
position – [in] global 3D position
derivative – [out] gradient of magnetic field vector as (3x3) matrix
cache – [inout] Field provider specific cache object
- Returns:
magnetic field vector
-
virtual Cache makeCache(const MagneticFieldContext &mctx) const = 0
Make an opaque cache for the magnetic field.
Instructs the specific implementation to generate a
Cacheinstance for magnetic field lookup.- Parameters:
mctx – The magnetic field context to generate cache for
- Returns:
Cache The opaque cache object
-
using Cache = Acts::AnyBase<sizeof(char) * 512>
-
class Material
Public Types
-
using ParametersVector = Eigen::Matrix<float, 5, 1>
Public Functions
-
Material() = default
Construct a vacuum representation.
-
Material(const ParametersVector ¶meters)
Construct from an encoded parameters vector.
-
~Material() = default
-
inline constexpr float Ar() const
Return the relative atomic mass.
-
inline constexpr float L0() const
Return the nuclear interaction length. Infinity in case of vacuum.
-
float massDensity() const
Return the mass density.
-
float meanExcitationEnergy() const
Return the mean electron excitation energy.
-
inline constexpr float molarDensity() const
Return the molar density.
-
inline constexpr float molarElectronDensity() const
Return the molar electron density.
-
inline constexpr operator bool() const
Check if the material is valid, i.e. it is not vacuum.
-
ParametersVector parameters() const
Encode the properties into an opaque parameters vector.
-
inline constexpr float X0() const
Return the radition length. Infinity in case of vacuum.
-
inline constexpr float Z() const
Return the nuclear charge number.
Public Static Functions
-
static Material fromMassDensity(float x0, float l0, float ar, float z, float massRho)
Construct from material parameters using the mass density.
Warning
Due to the choice of native mass units, using the mass density can lead to numerical problems. Typical mass densities lead to computations with values differing by 20+ orders of magnitude.
- Parameters:
x0 – is the radiation length
l0 – is the nuclear interaction length
ar – is the relative atomic mass
z – is the nuclear charge number
massRho – is the mass density
-
static Material fromMolarDensity(float x0, float l0, float ar, float z, float molarRho)
Construct from material parameters using the molar density.
- Parameters:
x0 – is the radiation length
l0 – is the nuclear interaction length
ar – is the relative atomic mass
z – is the nuclear charge number
molarRho – is the molar density
-
using ParametersVector = Eigen::Matrix<float, 5, 1>
-
class MaterialSlab
Material description for an object with defined thickness.
This is intended to describe concrete surface materials.
See also
Material for a description of the available parameters.
Public Functions
-
MaterialSlab() = default
Construct vacuum without thickness.
-
MaterialSlab(const Material &material, float thickness)
Construct from material description.
- Parameters:
material – is the material description
thickness – is the thickness of the material
-
MaterialSlab(const MaterialSlab&) = default
-
MaterialSlab(float thickness)
Construct vacuum with thickness.
-
MaterialSlab(MaterialSlab&&) = default
-
~MaterialSlab() = default
-
inline constexpr operator bool() const
Check if the material is valid, i.e. it is finite and not vacuum.
-
MaterialSlab &operator=(const MaterialSlab&) = default
-
MaterialSlab &operator=(MaterialSlab&&) = default
-
void scaleThickness(float scale)
Scale the material thickness by the given factor.
-
inline constexpr float thickness() const
Return the thickness.
-
inline constexpr float thicknessInL0() const
Return the nuclear interaction length fraction.
-
inline constexpr float thicknessInX0() const
Return the radiation length fraction.
Public Static Functions
-
static MaterialSlab averageLayers(const MaterialSlab &layerA, const MaterialSlab &layerB)
Combine material properties of two layers by averaging them.
- Parameters:
layerA – Input layer A to average over.
layerB – Input layer B to average over.
- Returns:
The resulting object has the combined thickness of all layers but just one set of appropriately averaged material constants.
-
static MaterialSlab averageLayers(const std::vector<MaterialSlab> &layers)
Combine material properties of multiple layers by averaging them.
- Parameters:
layers – Input layers to average over.
- Returns:
The resulting object has the combined thickness of all layers but just one set of appropriately averaged material constants.
-
MaterialSlab() = default
-
template<typename indices_t, std::size_t kSize>
class Measurement A measurement of a fixed-size subspace of the full parameters.
The measurement intentionally does not store a pointer/reference to the reference object in the geometry hierarchy, i.e. the surface or volume. The reference object can already be identified via the geometry identifier provided by the source link. Since a measurement must be anchored within the geometry hierarchy, all measurement surfaces and volumes must provide valid geometry identifiers. In all use-cases, e.g. Kalman filtering, a pointer/reference to the reference object is available before the measurement is accessed; e.g. the propagator provides the surface pointer during navigation, which is then used to lookup possible measurements.
The pointed-to geometry object would differ depending on the parameter type. This means either, that there needs to be an additional variable type or that a pointer to a base object is stored (requiring a
dynamic_castlater on). Both variants add additional complications. Since the geometry object is not required anyway (as discussed above), not storing it removes all these complications altogether.- Template Parameters:
indices_t – Parameter index type, determines the full parameter space
kSize – Size of the parameter subset.
Public Types
-
using CovarianceMatrix = ActsSquareMatrix<kSize>
Matrix type for the measurement covariance.
-
using ExpansionMatrix = ActsMatrix<kFullSize, kSize>
-
using FullParametersVector = ActsVector<kFullSize>
Vector type containing all parameters in the same space.
-
using ParametersVector = ActsVector<kSize>
Vector type containing for measured parameter values.
-
using ProjectionMatrix = ActsMatrix<kSize, kFullSize>
-
using Scalar = ActsScalar
Public Functions
-
Measurement() = delete
A measurement can only be constructed with valid parameters.
-
Measurement(const Measurement&) = default
-
Measurement(Measurement&&) = default
-
template<typename parameters_t, typename covariance_t>
inline Measurement(SourceLink source, const std::array<indices_t, kSize> &indices, const Eigen::MatrixBase<parameters_t> ¶ms, const Eigen::MatrixBase<covariance_t> &cov) Construct from source link, subset indices, and measured data.
Note
The indices must be ordered and must describe/match the content of parameters and covariance.
- Template Parameters:
parameters_t – Input parameters vector type
covariance_t – Input covariance matrix type
- Parameters:
source – The link that connects to the underlying detector readout
indices – Which parameters are measured
params – Measured parameters values
cov – Measured parameters covariance
-
~Measurement() = default
-
inline const CovarianceMatrix &covariance() const
Measured parameters covariance.
-
inline ExpansionMatrix expander() const
Expansion matrix from the measured subspace into the full space.
This is equivalent to the transpose of the projection matrix only in the case of a trivial projection matrix. While this is the case here, it is still recommended to use the expansion matrix directly in cases where it is explicitly used.
-
inline std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os) const
-
Measurement &operator=(const Measurement&) = default
-
Measurement &operator=(Measurement&&) = default
-
inline const ParametersVector ¶meters() const
Measured parameters values.
-
inline ProjectionMatrix projector() const
Projection matrix from the full space into the measured subspace.
-
inline ParametersVector residuals(const FullParametersVector &reference) const
Compute residuals in the measured subspace.
This computes the difference
measured - referencetaking into account the allowed parameter ranges. Only the reference values in the measured subspace are used for the computation.- Parameters:
reference – Reference parameters in the full space.
-
inline const SourceLink &sourceLink() const
Source link that connects to the underlying detector readout.
Public Static Functions
-
static inline constexpr std::size_t size()
Number of measured parameters.
-
class MeasurementSelector
Measurement selection struct selecting those measurements compatible with the given track parameter against provided criteria on one surface.
The selection criteria could be allowed maximum chi2 and allowed maximum number of measurements on one surface
If there is no compatible measurement, the measurement with the minimum chi2 will be selected and the status will be tagged as an outlier
Public Types
-
using Config = Acts::GeometryHierarchyMap<MeasurementSelectorCuts>
Geometry-dependent cut configuration.
Different components on the geometry can require different cut settings. The configuration must either contain explicit settings for all geometry components that are used or contain a global default.
Public Functions
-
MeasurementSelector()
Default constructor.
This will use the default configuration for the cuts.
-
explicit MeasurementSelector(Config config)
Constructor with config.
- Parameters:
config – a config instance
-
explicit MeasurementSelector(const MeasurementSelectorCuts &cuts)
Constructor with cuts.
- Parameters:
cuts – The cuts to use
-
template<typename traj_t>
Result<std::pair<typename std::vector<typename traj_t::TrackStateProxy>::iterator, typename std::vector<typename traj_t::TrackStateProxy>::iterator>> select(std::vector<typename traj_t::TrackStateProxy> &candidates, bool &isOutlier, const Logger &logger) const Function that select the measurements compatible with the given track parameter on a surface.
- Parameters:
candidates – The track state candidates which already contain predicted parameters
isOutlier – The indicator for outlier or not
logger – The logger wrapper
- Returns:
Pair of iterators into candidates marking the range of selected candidates
-
using Config = Acts::GeometryHierarchyMap<MeasurementSelectorCuts>
-
template<typename extensionlist_t = StepperExtensionList<DefaultExtension>, typename component_reducer_t = WeightedComponentReducerLoop, typename auctioneer_t = detail::VoidAuctioneer>
class MultiEigenStepperLoop : public Acts::EigenStepper<StepperExtensionList<DefaultExtension>, detail::VoidAuctioneer> Stepper based on the EigenStepper, but handles Multi-Component Tracks (e.g., for the GSF).
Internally, this only manages a vector of EigenStepper::States. This simplifies implementation, but has several drawbacks:
There are certain redundancies between the global State and the component states
The components do not share a single magnetic-field-cache
- Template Parameters:
extensionlist_t – See EigenStepper for details
component_reducer_t – How to map the multi-component state to a single component
auctioneer_t – See EigenStepper for details
small_vector_size – A size-hint how much memory should be allocated by the small vector
Public Types
-
using BoundState = std::tuple<MultiComponentBoundTrackParameters, Jacobian, ActsScalar>
Define an own bound state.
-
using ComponentProxy = detail::LoopComponentProxy<typename State::Component, MultiEigenStepperLoop>
A proxy struct which allows access to a single component of the multi-component state.
It has the semantics of a mutable reference, i.e. it requires a mutable reference of the single-component state it represents
-
using ConstComponentProxy = detail::LoopComponentProxyBase<const typename State::Component, MultiEigenStepperLoop>
A proxy struct which allows access to a single component of the multi-component state.
It has the semantics of a const reference, i.e. it requires a const reference of the single-component state it represents
-
using Covariance = BoundSquareMatrix
-
using CurvilinearState = std::tuple<MultiComponentCurvilinearTrackParameters, Jacobian, ActsScalar>
Define an own curvilinear state.
-
using Jacobian = BoundMatrix
Jacobian, Covariance and State definitions.
-
using Reducer = component_reducer_t
The reducer type.
-
using SingleState = typename SingleStepper::State
Typedef to the State of the single component Stepper.
-
using SingleStepper = EigenStepper<extensionlist_t, auctioneer_t>
Typedef to the Single-Component Eigen Stepper.
Public Functions
Constructor from a magnetic field and a optionally provided Logger.
-
inline double absoluteMomentum(const State &state) const
Absolute momentum accessor.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
inline Result<ComponentProxy> addComponent(State &state, const BoundTrackParameters &pars, double weight) const
Add a component to the Multistepper.
Note
: It is not ensured that the weights are normalized afterwards
Note
This function makes no garantuees about how new components are initialized, it is up to the caller to ensure that all components are valid in the end.
Note
The returned component-proxy is only garantueed to be valid until the component number is again modified
- Parameters:
state – [inout] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
pars – [in] Parameters of the component to add
weight – [in] Weight of the component to add
-
Result<BoundState> boundState(State &state, const Surface &surface, bool transportCov = true, const FreeToBoundCorrection &freeToBoundCorrection = FreeToBoundCorrection(false)) const
Create and return the bound state at the current position.
This transports (if necessary) the covariance to the surface and creates a bound state. It does not check if the transported state is at the surface, this needs to be guaranteed by the propagator.
Note
This is done by combining the gaussian mixture on the specified surface. If the conversion to bound states of some components fails, these components are ignored unless all components fail. In this case an error code is returned.
- Parameters:
state – [in] State that will be presented as
BoundStatesurface – [in] The surface to which we bind the state
transportCov – [in] Flag steering covariance transport
freeToBoundCorrection – [in] Flag steering non-linear correction during global to local correction
- Returns:
A bound state:
the parameters at the surface
the stepwise jacobian towards it (from last bound)
and the path length (from start - for ordering)
-
inline double charge(const State &state) const
Charge access.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
inline void clearComponents(State &state) const
Reset the number of components.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
inline auto componentIterable(State &state) const
Creates an iterable which can be plugged into a range-based for-loop to iterate over components.
Note
Use a for-loop with by-value semantics, since the Iterable returns a proxy internally holding a reference
-
inline auto constComponentIterable(const State &state) const
Creates an constant iterable which can be plugged into a range-based for-loop to iterate over components.
Note
Use a for-loop with by-value semantics, since the Iterable returns a proxy internally holding a reference
-
CurvilinearState curvilinearState(State &state, bool transportCov = true) const
Create and return a curvilinear state at the current position.
This transports (if necessary) the covariance to the current position and creates a curvilinear state.
Note
This is done as a simple average over the free representation and covariance of the components.
- Parameters:
state – [in] State that will be presented as
CurvilinearStatetransportCov – [in] Flag steering covariance transport
- Returns:
A curvilinear state:
the curvilinear parameters at given position
the stepweise jacobian towards it (from last bound)
and the path length (from start - for ordering)
-
inline Vector3 direction(const State &state) const
Momentum direction accessor.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
inline Result<Vector3> getField(State &state, const Vector3 &pos) const
Get the field for the stepping, it checks first if the access is still within the Cell, and updates the cell if necessary.
Note
This uses the cache of the first component stored in the state
- Parameters:
state – [inout] is the propagation state associated with the track the magnetic field cell is used (and potentially updated)
pos – [in] is the field position
-
inline double getStepSize(const State &state, ConstrainedStep::Type stype) const
Get the step size.
Note
This returns the smallest step size of all components. It uses std::abs for comparison to handle backward propagation and negative step sizes correctly.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
stype – [in] The step size type to be returned
-
inline State makeState(std::reference_wrapper<const GeometryContext> gctx, std::reference_wrapper<const MagneticFieldContext> mctx, const MultiComponentBoundTrackParameters &par, double ssize = std::numeric_limits<double>::max()) const
Construct and initialize a state.
-
inline Vector3 momentum(const State &state) const
Momentum accessor.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
inline std::size_t numberComponents(const State &state) const
Get the number of components.
- Parameters:
state – [in,out] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
inline std::string outputStepSize(const State &state) const
Output the Step Size of all components into one std::string.
- Parameters:
state – [in,out] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
inline double overstepLimit(const State &state) const
Overstep limit.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
inline ParticleHypothesis particleHypothesis(const State &state) const
Particle hypothesis.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
inline Vector3 position(const State &state) const
Global particle position accessor.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
If necessary fill additional members needed for curvilinearState.
Compute path length derivatives in case they have not been computed yet, which is the case if no step has been executed yet.
- Parameters:
prop_state – [inout] State that will be presented as
BoundStatenavigator – [in] the navigator of the propagation
- Returns:
true if nothing is missing after this call, false otherwise.
-
inline double qOverP(const State &state) const
QoP access.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
inline void releaseStepSize(State &state, ConstrainedStep::Type stype) const
Release the step-size for all components.
- Parameters:
state – [in,out] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
stype – [in] The step size type to be released
-
inline void removeMissedComponents(State &state) const
Remove missed components from the component state.
- Parameters:
state – [in,out] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
inline void resetState(State &state, const BoundVector &boundParams, const BoundSquareMatrix &cov, const Surface &surface, const double stepSize = std::numeric_limits<double>::max()) const
Resets the state.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] State of the stepper
boundParams – [in] Parameters in bound parametrisation
cov – [in] Covariance matrix
surface – [in] The reference surface of the bound parameters
stepSize – [in] Step size
-
inline void reweightComponents(State &state) const
Reweight the components.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
Perform a Runge-Kutta track parameter propagation step.
The state contains the desired step size. It can be negative during backwards track propagation, and since we’re using an adaptive algorithm, it can be modified by the stepper class during propagation.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] is the propagation state associated with the track parameters that are being propagated.
navigator – [in] is the navigator of the propagation
-
inline double time(const State &state) const
Time access.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
inline void transportCovarianceToBound(State &state, const Surface &surface, const FreeToBoundCorrection &freeToBoundCorrection = FreeToBoundCorrection(false)) const
Method for on-demand transport of the covariance to a new curvilinear frame at current position, or direction of the state.
Note
no check is done if the position is actually on the surface
- Template Parameters:
surface_t – the Surface type
- Parameters:
state – [inout] State of the stepper
surface – [in] is the surface to which the covariance is forwarded
freeToBoundCorrection – [in] Flag steering non-linear correction during global to local correction to
-
inline void transportCovarianceToCurvilinear(State &state) const
Method for on-demand transport of the covariance to a new curvilinear frame at current position, or direction of the state.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] State of the stepper
-
template<typename object_intersection_t>
inline void updateStepSize(State &state, const object_intersection_t &oIntersection, Direction direction, bool release = true) const Update step size.
This method intersects the provided surface and update the navigation step estimation accordingly (hence it changes the state). It also returns the status of the intersection to trigger onSurface in case the surface is reached.
- Parameters:
state – [in,out] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
oIntersection – [in] The ObjectIntersection to layer, boundary, etc
direction – [in] The propagation direction
release – [in] boolean to trigger step size release
-
inline void updateStepSize(State &state, double stepSize, ConstrainedStep::Type stype, bool release = true) const
Update step size - explicitly with a double.
- Parameters:
state – [in,out] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
stepSize – [in] The step size value
stype – [in] The step size type to be set
release – [in] Do we release the step size?
-
inline Intersection3D::Status updateSurfaceStatus(State &state, const Surface &surface, std::uint8_t index, Direction navDir, const BoundaryCheck &bcheck, ActsScalar surfaceTolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance, const Logger &logger = getDummyLogger()) const
Update surface status.
It checks the status to the reference surface & updates the step size accordingly
- Parameters:
state – [inout] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
surface – [in] The surface provided
index – [in] The surface intersection index
navDir – [in] The navigation direction
bcheck – [in] The boundary check for this status update
surfaceTolerance – [in] Surface tolerance used for intersection
logger – [in] A
Loggerinstance
Public Static Attributes
-
static constexpr int maxComponents = std::numeric_limits<int>::max()
How many components can this stepper manage?
-
struct State
Public Functions
-
State() = delete
No default constructor is provided.
Constructor from the initial bound track parameters.
Note
the covariance matrix is copied when needed
- Parameters:
gctx – [in] is the context object for the geometry
mctx – [in] is the context object for the magnetic field
bfield – [in] the shared magnetic filed provider
multipars – [in] The track multi-component track-parameters at start
ssize – [in] is the maximum step size
Public Members
-
bool covTransport = false
-
std::reference_wrapper<const GeometryContext> geoContext
geoContext
-
std::reference_wrapper<const MagneticFieldContext> magContext
MagneticFieldContext.
-
ParticleHypothesis particleHypothesis = ParticleHypothesis::pion()
Particle hypothesis.
-
double pathAccumulated = 0.
-
std::optional<std::size_t> stepCounterAfterFirstComponentOnSurface
Step-limit counter which limits the number of steps when one component reached a surface.
-
std::size_t steps = 0
-
struct Component
The struct that stores the individual components.
-
State() = delete
-
template<typename derived_t>
class MultiTrajectory Store a trajectory of track states with multiple components.
This container supports both simple, sequential trajectories as well as combinatorial or multi-component trajectories. Each point can store a parent point such that the trajectory forms a directed, acyclic graph of sub-trajectories. From a set of endpoints, all possible sub-components can be easily identified. Some functionality is provided to simplify iterating over specific sub-components.
MultiTrajectory track state (proxy) access and manipulation
These methods allow accessing track states, i.e. adding or retrieving a track state proxy that points at a specific track state in the container.
-
inline ConstTrackStateProxy getTrackState(IndexType istate) const
Access a read-only point on the trajectory by index.
Note
Only available if the MultiTrajectory is not read-only
- Parameters:
istate – The index to access
- Returns:
Read only proxy to the stored track state
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline TrackStateProxy getTrackState(IndexType istate) Access a writable point on the trajectory by index.
Note
Only available if the MultiTrajectory is not read-only
- Parameters:
istate – The index to access
- Returns:
Read-write proxy to the stored track state
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline IndexType addTrackState(TrackStatePropMask mask = TrackStatePropMask::All, IndexType iprevious = kInvalid) Add a track state without providing explicit information.
Which components of the track state are initialized/allocated can be controlled via
maskNote
Only available if the MultiTrajectory is not read-only
- Parameters:
mask – The bitmask that instructs which components to allocate and which to leave invalid
iprevious – index of the previous state, kInvalid if first
- Returns:
Index of the newly added track state
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline TrackStateProxy makeTrackState(TrackStatePropMask mask = TrackStatePropMask::All, IndexType iprevious = kInvalid) Add a track state to the container and return a track state proxy to it This effectively calls
addTrackStateandgetTrackState.Note
Only available if the track state container is not read-only
- Returns:
a track state proxy to the newly added track state
MultiTrajectory track state iteration
-
template<typename F>
void visitBackwards(IndexType iendpoint, F &&callable) const Visit all previous states starting at a given endpoint.
- Parameters:
iendpoint – index of the last state
callable – non-modifying functor to be called with each point
-
template<typename F, bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline void applyBackwards(IndexType iendpoint, F &&callable) Apply a function to all previous states starting at a given endpoint.
Note
Only available if the MultiTrajectory is not read-only
Warning
If the trajectory contains multiple components with common points, this can have an impact on the other components.
- Parameters:
iendpoint – index of the last state
callable – modifying functor to be called with each point
-
inline auto reverseTrackStateRange(IndexType iendpoint) const
Range for the track states from
iendpointto the trajectory start.Note
Const version
- Parameters:
iendpoint – Trajectory entry point to start from
- Returns:
Iterator pair to iterate over
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline auto reverseTrackStateRange(IndexType iendpoint) Range for the track states from
iendpointto the trajectory start, i.e from the outside in.Note
Only available if the MultiTrajectory is not read-only
Note
Mutable version
- Parameters:
iendpoint – Trajectory entry point to start from
- Returns:
Iterator pair to iterate over
-
inline auto forwardTrackStateRange(IndexType istartpoint) const
Range for the track states from
istartpointto the trajectory end, i.e from inside out.Note
Const version
- Parameters:
istartpoint – Trajectory state index for the innermost track state to start from
- Returns:
Iterator pair to iterate over
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline auto forwardTrackStateRange(IndexType istartpoint) Range for the track states from
istartpointto the trajectory end, i.e from inside out.Note
Only available if the MultiTrajectory is not read-only
- Parameters:
istartpoint – Trajectory state index for the innermost track state to start from
- Returns:
Iterator pair to iterate over
MultiTrajectory column management
MultiTrajectory can manage a set of common static columns, and dynamic columns that can be added at runtime.
This set of methods allows you to manage the dynamic columns.
-
template<typename T, bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline void addColumn(const std::string &key) Add a column to the
MultiTrajectory.Note
This takes a string argument rather than a hashed string to maintain compatibility with backends.
Note
Only available if the MultiTrajectory is not read-only
- Template Parameters:
T – Type of the column values to add
-
inline bool hasColumn(HashedString key) const
Check if a column with a key
keyexists.- Parameters:
key – Key to check for a column with
- Returns:
True if the column exists, false if not.
Public Types
-
using ConstTrackStateProxy = Acts::TrackStateProxy<Derived, MeasurementSizeMax, true>
Alias for the const version of a track state proxy, with the same backends as this container.
-
using IndexType = typename TrackStateProxy::IndexType
The index type of the track state container.
-
using TrackStateProxy = Acts::TrackStateProxy<Derived, MeasurementSizeMax, false>
Alias for the mutable version of a track state proxy, with the same backends as this container.
Public Functions
Public Static Attributes
-
static constexpr IndexType kInvalid = TrackStateProxy::kInvalid
Sentinel value that indicates an invalid index.
-
inline ConstTrackStateProxy getTrackState(IndexType istate) const
Class to be used for gaps in Volumes as a navigational link.
Navigation Layers have a surface representation, but should usually never be propagated to.
Public Functions
Default Constructor - deleted.
Copy Constructor - deleted.
Destructor.
The binning position method.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
bValue – is the value for which the binning position is requested
as default the center is given, but may be overloaded
- Returns:
The return vector can be used for binning in a TrackingVolume
Geometric isOnLayer() method using isOnSurface() with Layer specific tolerance.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
gp – is the global position for the check
bcheck – is the boundary check directive
- Returns:
boolean that indicates if the position is on surface
Assignment operator - deleted.
Accept layer according to the following collection directives.
Note
navigation layers are never accepted
- Parameters:
resolveSensitive – is the prescription to find the sensitive surfaces
resolveMaterial – is the precription to find material surfaces
resolvePassive – is the prescription to find all passive surfaces
- Returns:
a boolean whether the layer is accepted for processing
Transforms the layer into a Surface representation for extrapolation In general, extrapolation to a surface should be avoided.
Public Static Functions
Factory Constructor - the surface representation is given by pointer (ownership passed)
- Parameters:
sRepresentation – is the representation for extrapolation
thickness – is the thickness for the binning
Steers the propagation through the geometry by adjusting the step size and providing the next surface to be targeted.
The Navigator is part of the propagation and responsible for steering the step size in order to encounter all the relevant surfaces which are intersected by the trajectory.
The current navigation stage is cached in the state struct and updated when necessary. If any surface in the extrapolation flow is hit, it is set to the navigation state, such that other actors can deal with it.
The current target surface is referenced by an index which points into the navigation candidates. The navigation candidates are ordered by the path length to the surface. If a surface is hit, the
state.navigation.currentSurfacepointer is set. This actors to observe that we are on a surface.Public Types
The navigation stage.
Values:
Public Functions
Constructor with configuration object.
- Parameters:
cfg – The navigator configuration
_logger – a logger instance
Initialize call - start of navigation.
- Template Parameters:
propagator_state_t – The state type of the propagator
stepper_t – The type of stepper used for the propagation
- Parameters:
state – [inout] is the propagation state object
stepper – [in] Stepper in use
Navigator post step call.
(a) It initializes the Navigation stream if start volume is not yet defined:
initialize the volume
establish the start layer and start volume
set the current surface to the start surface
(b) It establishes the currentSurface status during the propagation flow, currentSurface can be
surfaces still to be handled within a layer
layers still to be handled within a volume
boundaries still to be handled to exit a volume
- Template Parameters:
propagator_state_t – is the type of Propagatgor state
stepper_t – is the used type of the Stepper by the Propagator
- Parameters:
state – [inout] is the mutable propagator state object
stepper – [in] Stepper in use
Navigator pre step call.
Call options (a) there are still surfaces to be resolved: handle those (b) there no surfaces but still layers to be resolved, handle those (c) there are no surfaces nor layers to be resolved, handle boundary
- Template Parameters:
propagator_state_t – is the type of Propagatgor state
stepper_t – is the used type of the Stepper by the Propagator
- Parameters:
state – [inout] is the mutable propagator state object
stepper – [in] Stepper in use
Public Members
stop at every material surface (whether it is passive or not)
stop at every surface regardless what it is
stop at every sensitive surface (whether it has material or not)
Tracking Geometry for this Navigator.
Nested State struct.
It acts as an internal state which is created for every propagation and meant to keep thread-local navigation information.
Public Functions
Public Members
Navigation state - external state: the current surface.
Navigation state: the current volume.
Externally provided surfaces - these are tried to be hit.
Force intersection with boundaries.
Indicator that the last VolumeHierarchy surface was reached skip the next layer targeting to the next boundary/volume.
the vector of boundary surfaces to work through
the current boundary index of the navigation state
Navigation state : a break has been detected.
the current layer index of the navigation state
the vector of navigation layers to work through
the current surface index of the navigation state
the vector of navigation surfaces to work through
Navigation state: the start layer.
Indicator for start layer treatment.
Navigation state: the start surface.
Navigation state: the start volume.
Navigation state: the target layer.
Indicator if the target is reached.
Navigation state: the target surface.
Navigation state: the target volume.
Navigation state: the world volume.
-
class NeutralParticleHypothesis : public Acts::GenericParticleHypothesis<Neutral>
Specialized particle hypothesis for neutral particles.
Note
This serves as a factory for common neutral particles.
Public Functions
-
template<typename other_charge_t>
inline constexpr NeutralParticleHypothesis(const GenericParticleHypothesis<other_charge_t> &other)
-
inline NeutralParticleHypothesis(PdgParticle absPdg)
-
inline constexpr NeutralParticleHypothesis(PdgParticle absPdg, float mass)
Public Static Functions
-
static inline NeutralParticleHypothesis geantino()
-
static inline NeutralParticleHypothesis photon()
-
static inline NeutralParticleHypothesis pion0()
-
template<typename other_charge_t>
-
class NonNeutralCharge
Charge and momentum interpretation for arbitrarily charged but not neutral particles.
Public Functions
-
inline constexpr NonNeutralCharge(float absQ) noexcept
Construct with the magnitude of the input charge.
-
inline constexpr NonNeutralCharge(SinglyCharged) noexcept
-
inline constexpr float absQ() const noexcept
-
inline constexpr float extractCharge(ActsScalar qOverP) const noexcept
-
inline constexpr ActsScalar extractMomentum(ActsScalar qOverP) const noexcept
-
inline constexpr ActsScalar qOverP(ActsScalar momentum, float signedQ) const noexcept
Friends
- inline friend constexpr friend bool operator== (NonNeutralCharge lhs, NonNeutralCharge rhs) noexcept
Compare for equality.
-
inline constexpr NonNeutralCharge(float absQ) noexcept
-
class NonNeutralChargedParticleHypothesis : public Acts::GenericParticleHypothesis<NonNeutralCharge>
Specialized particle hypothesis for non-neutral particles.
Note
This serves as a factory for common non-neutral particles.
Public Functions
-
template<typename other_charge_t>
inline constexpr NonNeutralChargedParticleHypothesis(const GenericParticleHypothesis<other_charge_t> &other)
-
inline NonNeutralChargedParticleHypothesis(PdgParticle absPdg)
-
inline constexpr NonNeutralChargedParticleHypothesis(PdgParticle absPdg, float mass, NonNeutralCharge chargeType)
Public Static Functions
-
static inline NonNeutralChargedParticleHypothesis chargedGeantino()
-
static inline NonNeutralChargedParticleHypothesis chargedGeantino(float absQ)
-
static inline NonNeutralChargedParticleHypothesis electron()
-
static inline NonNeutralChargedParticleHypothesis kaon()
-
static inline NonNeutralChargedParticleHypothesis muon()
-
static inline NonNeutralChargedParticleHypothesis pion()
-
static inline NonNeutralChargedParticleHypothesis pionLike(float absQ)
-
static inline NonNeutralChargedParticleHypothesis proton()
-
template<typename other_charge_t>
-
class NullBField : public Acts::MagneticFieldProvider
Null bfield which returns 0 always.
Public Functions
-
NullBField() = default
Default constructor.
-
inline virtual Result<Vector3> getField(const Vector3 &position, MagneticFieldProvider::Cache &cache) const override
Retrieve magnetic field value at a given location.
Requires a cache object created through makeCache().
Note
The
positionis ignored and only kept as argument to provide a consistent interface with other magnetic field services.- Parameters:
position – [in] global 3D position for the lookup
cache – [inout] Field provider specific cache object
- Returns:
magnetic field vector at given position
-
inline virtual Result<Vector3> getFieldGradient(const Vector3 &position, ActsMatrix<3, 3> &derivative, MagneticFieldProvider::Cache &cache) const override
Retrieve magnetic field value its its gradient.
Requires a cache object created through makeCache().
Note
The
positionis ignored and only kept as argument to provide a consistent interface with other magnetic field services.Note
currently the derivative is not calculated
- Parameters:
position – [in] global 3D position
derivative – [out] gradient of magnetic field vector as (3x3) matrix
cache – [inout] Field provider specific cache object
- Returns:
magnetic field vector
-
inline bool isInside(const Vector3&) const
check whether given 3D position is inside look-up domain
Note
The method will always return true for the null B-Field
- Returns:
trueif position is inside the defined look-up grid, otherwisefalse
-
inline virtual Acts::MagneticFieldProvider::Cache makeCache(const Acts::MagneticFieldContext &mctx) const override
Make an opaque cache for the magnetic field.
Instructs the specific implementation to generate a
Cacheinstance for magnetic field lookup.- Parameters:
mctx – The magnetic field context to generate cache for
- Returns:
Cache The opaque cache object
-
struct Cache
Public Functions
-
inline Cache(const MagneticFieldContext&)
constructor with context
-
inline Cache(const MagneticFieldContext&)
-
NullBField() = default
-
class ParticleHypothesis : public Acts::GenericParticleHypothesis<AnyCharge>
Specialized particle hypothesis for any kind of charged particles.
Note
This serves as a factory for common particles with any kind of charge.
Public Functions
-
template<typename other_charge_t>
inline constexpr ParticleHypothesis(const GenericParticleHypothesis<other_charge_t> &other)
-
inline ParticleHypothesis(PdgParticle absPdg)
Public Static Functions
-
static inline ParticleHypothesis chargedGeantino()
-
static inline ParticleHypothesis chargedGeantino(float absQ)
-
static inline ParticleHypothesis electron()
-
static inline ParticleHypothesis geantino()
-
static inline ParticleHypothesis kaon()
-
static inline ParticleHypothesis muon()
-
static inline ParticleHypothesis photon()
-
static inline ParticleHypothesis pion()
-
static inline ParticleHypothesis pion0()
-
static inline ParticleHypothesis pionLike(float absQ)
-
static inline ParticleHypothesis proton()
-
template<typename other_charge_t>
-
class PerigeeSurface : public Acts::LineSurface
Class describing the Line to which the Perigee refers to.
The Surface axis is fixed to be the z-axis of the Tracking frame. It inherits from StraingLineSurface.

Public Functions
-
PerigeeSurface() = delete
Default Constructor - deleted.
-
~PerigeeSurface() override = default
Destructor - defaulted.
-
virtual std::string name() const final
Return properly formatted class name for screen output */.
-
PerigeeSurface &operator=(const PerigeeSurface &other)
Assignment operator.
- Parameters:
other – is the source surface to be assigned
-
virtual Polyhedron polyhedronRepresentation(const GeometryContext &gctx, std::size_t lseg) const final
Return a Polyhedron for the surfaces.
Note
ignored
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lseg – is ignored for a perigee
- Returns:
A list of vertices and a face/facett description of it
-
virtual std::ostream &toStream(const GeometryContext &gctx, std::ostream &sl) const final
Output Method for std::ostream.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
sl – is the ostream to be dumped into
- Returns:
ostreamn object which was streamed into
-
virtual SurfaceType type() const final
Return the surface type.
-
PerigeeSurface() = delete
-
class PlanarBounds : public Acts::SurfaceBounds
common base class for all bounds that are in a local x/y cartesian frame
simply introduced to avoid wrong bound assignments to surfaces
Subclassed by Acts::ConvexPolygonBoundsBase, Acts::DiamondBounds, Acts::EllipseBounds, Acts::RectangleBounds, Acts::TrapezoidBounds
Public Functions
-
virtual const RectangleBounds &boundingBox() const = 0
Bounding box parameters.
- Returns:
rectangle bounds for a bounding box
-
virtual std::vector<Vector2> vertices(unsigned int lseg = 1) const = 0
Return the vertices.
Note
that the extremas are given, which may slightly alter the number of segments returned
- Parameters:
lseg – the number of segments used to approximate and eventually curved line
- Returns:
vector for vertices in 2D
-
class PlaneLayer : public virtual Acts::PlaneSurface, public Acts::Layer
Class to describe a planar detector layer for tracking, it inhertis from both, Layer base class and PlaneSurface class.
Public Functions
-
PlaneLayer() = delete
-
PlaneLayer(const PlaneLayer &pla) = delete
-
~PlaneLayer() override = default
-
PlaneLayer &operator=(const PlaneLayer&) = delete
-
virtual const PlaneSurface &surfaceRepresentation() const override
Transforms the layer into a Surface representation for extrapolation.
- Returns:
returns a reference to a PlaneSurface
-
virtual PlaneSurface &surfaceRepresentation() override
Public Static Functions
Factory for a shared plane layer.
- Parameters:
transform – which places the layer in the global frame
pbounds – the planar bounds that define the layer dimensions
surfaceArray – is the surface array that holds the sensitive surfaces
thickness – is the thickness of the layer (normal direction to plane)
ad – is the approach descriptor for describing the approach surface
laytyp – is the layer type
- Returns:
shared pointer to a PlaneLayer
-
PlaneLayer() = delete
-
class PlaneSurface : public Acts::RegularSurface
Class for a planaer in the TrackingGeometry.
The PlaneSurface extends the Surface class with the possibility to convert local to global positions (vice versa).
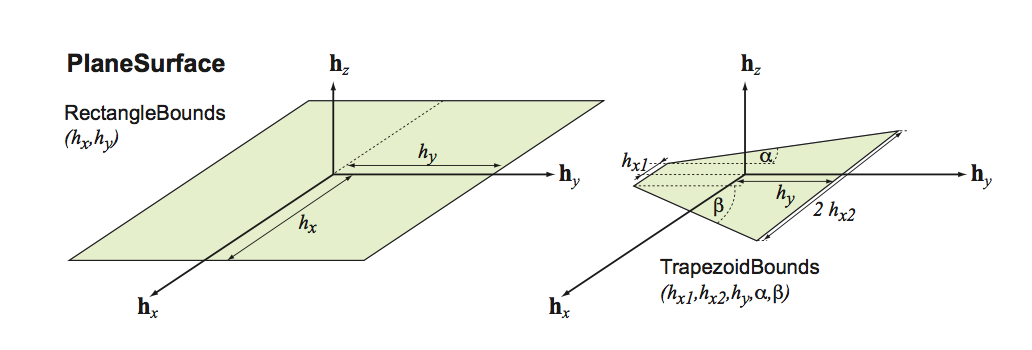
Subclassed by Acts::PlaneLayer
Public Functions
-
PlaneSurface() = delete
-
~PlaneSurface() override = default
-
virtual Vector3 binningPosition(const GeometryContext &gctx, BinningValue bValue) const final
The binning position is the position calculated for a certain binning type.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
bValue – is the binning type to be used
- Returns:
position that can beused for this binning
-
virtual const SurfaceBounds &bounds() const override
Return method for bounds object of this surfrace.
-
Result<Vector2> globalToLocal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction, double tolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance) const final
Convert a global position to a local one this is the most generic interface, which is implemented by all surfaces.
Note
The
positionis required to be on-surface, which is indicated by theResultreturn value.- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – is the global position to be converted
direction – is the direction of the local position (ignored for
RegularSurface)tolerance – is the tolerance for the on-surface check
- Returns:
Result type containing local position by value
-
virtual Result<Vector2> globalToLocal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, double tolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance) const override
Global to local transformation.
Note
For planar surfaces the momentum direction is ignored in the global to local transformation
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – global 3D position - considered to be on surface but not inside bounds (check is done)
tolerance – optional tolerance within which a point is considered valid on surface
- Returns:
a Result<Vector2> which can be !ok() if the operation fails
-
Result<Vector2> globalToLocal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, double tolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance) const = 0
Convert a global position to a local one.
Note
The
positionis required to be on-surface, which is indicated by theResultreturn value.- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – is the global position to be converted
tolerance – is the tolerance for the on-surface check
- Returns:
Result type containing local position by value
-
virtual SurfaceMultiIntersection intersect(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction, const BoundaryCheck &bcheck = BoundaryCheck(false), ActsScalar tolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance) const final
Straight line intersection.
mathematical motivation:
the equation of the plane is given by: \( \vec n \cdot \vec x = \vec n \cdot \vec p,\) where \( \vec n = (n_{x}, n_{y}, n_{z})\) denotes the normal vector of the plane, \( \vec p = (p_{x}, p_{y}, p_{z})\) one specific point on the plane and \( \vec x = (x,y,z) \) all possible points on the plane.
Given a line with:\( \vec l(u) = \vec l_{1} + u \cdot \vec v \)
,
the solution for
\( u \) can be written: \( u = \frac{\vec n (\vec p - \vec l_{1})}{\vec n \vec v}\) If the denominator is 0 then the line lies:either in the plane
perpendicular to the normal of the plane
Note
expected to be normalized)
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – The start position of the intersection attempt
direction – The direction of the intersection attempt, (
bcheck – The boundary check directive
tolerance – the tolerance used for the intersection
- Returns:
the
SurfaceMultiIntersectionobject
-
virtual ActsMatrix<2, 3> localCartesianToBoundLocalDerivative(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position) const final
Calculate the derivative of bound track parameters local position w.r.t.
position in local 3D Cartesian coordinates
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – The position of the parameters in global
- Returns:
Derivative of bound local position w.r.t. position in local 3D cartesian coordinates
-
virtual Vector3 localToGlobal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector2 &lposition) const override
Local to global transformation.
Note
For planar surfaces the momentum direction is ignored in the local to global transformation
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lposition – local 2D position in specialized surface frame
- Returns:
the global position by value
-
Vector3 localToGlobal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector2 &lposition) const = 0
Local to global transformation.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lposition – local 2D position in specialized surface frame
- Returns:
The global position by value
-
Vector3 localToGlobal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector2 &lposition, const Vector3 &direction) const final
Local to global transformation.
This is the most generic interface, which is implemented by all surfaces.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lposition – local 2D position in specialized surface frame
direction – global 3D momentum direction (ignored for
RegularSurface)
- Returns:
The global position by value
-
virtual std::string name() const override
Return properly formatted class name for screen output.
-
Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx) const
Get the normal vector, independent of the location.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
- Returns:
The normal vector
-
virtual Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector2 &lposition) const final
Get the normal vector of this surface at a given local position.
return a Vector3 by value
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lposition – is the local position is ignored
-
Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector2 &lposition) const = 0
Calculate the normal vector of the surface This overload requires an on-surface local position.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lposition – is the local position where the normal vector is constructed
- Returns:
normal vector by value
-
Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &pos, const Vector3 &direction) const final
Calculate the normal vector of the surface This overload is fully generic, fulfills the Surface interface and accepts a global position and a direction.
For
RegularSurfacethis is equivalent to the normal overload, ignoring thedirection- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
pos – is the global position where the normal vector is constructed
direction – is the direction of the normal vector (ignored for
RegularSurface)
-
virtual Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position) const final
Get the normal vector of this surface at a given global position.
Note
The
positionis required to be on-surface.- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – is the global positiono (for PlaneSurface this is ignored)
- Returns:
The normal vector
-
Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position) const = 0
Calculate the normal vector of the surface This overload accepts a global position.
- Parameters:
position – is the global position where the normal vector is constructed
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
- Returns:
normal vector by value
-
PlaneSurface &operator=(const PlaneSurface &other)
Assignment operator.
- Parameters:
other – The source PlaneSurface for assignment
-
virtual double pathCorrection(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction) const final
Method that calculates the correction due to incident angle.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – global 3D position (ignored for PlaneSurface)
direction – global 3D momentum direction (ignored for PlaneSurface)
- Returns:
a double representing the scaling factor
-
virtual Polyhedron polyhedronRepresentation(const GeometryContext &gctx, std::size_t lseg) const override
Return a Polyhedron for the surfaces.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lseg – Number of segments along curved lines, it represents the full 2*M_PI coverange, if lseg is set to 1 only the extrema are given
- Returns:
A list of vertices and a face/facett description of it
-
virtual SurfaceType type() const override
Return the surface type.
-
PlaneSurface() = delete
-
template<typename stepper_t, typename navigator_t = VoidNavigator>
class Propagator : public std::conditional_t<SupportsBoundParameters_v<stepper_t, VoidNavigator>, detail::BasePropagatorHelper<Propagator<stepper_t, VoidNavigator>>, detail::PropagatorStub> Propagator for particles (optionally in a magnetic field)
The Propagator works with a state objects given at function call This state object contains the thread local state objects
Navigator::state_type for object navigation and screen output
Stepper::state_type state for the actual transport caching (pos,dir,field)
This Propagator class serves as high-level steering code for propagating track parameters. The actual implementation of the propagation has to be implemented in the stepper_t object, which has to provide the following:
a function for performing a single propagation step
a type mapping for: initial track parameter type -> type of final track parameters
a type mapping for: (initial track parameter type and destination surface type) -> type of final track parameters
a type mapping for: initial track parameter type -> type of internal state object
a type mapping for: (initial track parameter type and destination surface type) -> type of internal state object
- Template Parameters:
stepper_t – Type of stepper implementation of the propagation
naviagor_t – Type of the navigator (optional)
Public Types
-
template<typename parameters_t, typename action_list_t>
using action_list_t_result_t = typename result_type_helper<parameters_t, action_list_t>::type Short-hand type definition for propagation result derived from an action list.
- Template Parameters:
parameters_t – Type of the final track parameters
action_list_t – List of propagation action types
-
template<typename propagator_options_t, typename action_list_t>
using action_list_t_state_t = typename state_type_helper<propagator_options_t, action_list_t>::type Short-hand type definition for propagation state derived from an action list.
- Template Parameters:
action_list_t – List of propagation action types
Type of the navigator in use for public scope.
Typedef the navigator state.
Public Functions
Constructor from implementation object.
- Parameters:
stepper – The stepper implementation is moved to a private member
navigator – The navigator implementation, moved to a private member
_logger – a logger instance
-
template<typename propagator_state_t, typename propagator_options_t>
Result<action_list_t_result_t<StepperCurvilinearTrackParameters, typename propagator_options_t::action_list_type>> makeResult(propagator_state_t state, Result<void> result, const propagator_options_t &options, bool makeCurvilinear) const
-
template<typename propagator_state_t, typename propagator_options_t>
Result<action_list_t_result_t<StepperBoundTrackParameters, typename propagator_options_t::action_list_type>> makeResult(propagator_state_t state, Result<void> result, const Surface &target, const propagator_options_t &options) const
-
template<typename parameters_t, typename propagator_options_t, typename path_aborter_t = PathLimitReached>
auto makeState(const parameters_t &start, const propagator_options_t &options) const
-
template<typename parameters_t, typename propagator_options_t, typename target_aborter_t = SurfaceReached, typename path_aborter_t = PathLimitReached>
auto makeState(const parameters_t &start, const Surface &target, const propagator_options_t &options) const
-
template<typename parameters_t, typename propagator_options_t, typename path_aborter_t = PathLimitReached>
Result<action_list_t_result_t<StepperCurvilinearTrackParameters, typename propagator_options_t::action_list_type>> propagate(const parameters_t &start, const propagator_options_t &options, bool makeCurvilinear = true) const Propagate track parameters.
This function performs the propagation of the track parameters using the internal stepper implementation, until at least one abort condition is fulfilled or the maximum number of steps/path length provided in the propagation options is reached.
- Template Parameters:
parameters_t – Type of initial track parameters to propagate
propagator_options_t – Type of the propagator options
path_aborter_t – The path aborter type to be added
- Parameters:
start – [in] initial track parameters to propagate
options – [in] Propagation options, type Options<,>
makeCurvilinear – [in] Produce curvilinear parameters at the end of the propagation
- Returns:
Propagation result containing the propagation status, final track parameters, and output of actions (if they produce any)
-
template<typename parameters_t, typename propagator_options_t, typename target_aborter_t = SurfaceReached, typename path_aborter_t = PathLimitReached>
Result<action_list_t_result_t<StepperBoundTrackParameters, typename propagator_options_t::action_list_type>> propagate(const parameters_t &start, const Surface &target, const propagator_options_t &options) const Propagate track parameters - User method.
This function performs the propagation of the track parameters according to the internal implementation object until at least one abort condition is fulfilled, the destination surface is hit or the maximum number of steps/path length as given in the propagation options is reached.
- Template Parameters:
parameters_t – Type of initial track parameters to propagate
propagator_options_t – Type of the propagator options
target_aborter_t – The target aborter type to be added
path_aborter_t – The path aborter type to be added
- Parameters:
start – [in] Initial track parameters to propagate
target – [in] Target surface of to propagate to
options – [in] Propagation options
- Returns:
Propagation result containing the propagation status, final track parameters, and output of actions (if they produce any)
-
template<typename propagator_state_t>
Result<void> propagate(propagator_state_t &state) const Propagate track parameters.
This function performs the propagation of the track parameters according to the internal implementation object until at least one abort condition is fulfilled, the destination surface is hit or the maximum number of steps/path length as given in the propagation options is reached.
Note
Does not (yet) convert into the return_type of the propagation
- Template Parameters:
propagator_state_t – Type of the propagator state with options
- Parameters:
state – [inout] the propagator state object
- Returns:
Propagation result
-
template<typename propagator_options_t, typename ...extension_state_t>
struct State : private detail::Extendable<extension_state_t...> private Propagator state for navigation and debugging
This struct holds the common state information for propagating which is independent of the actual stepper implementation.
- Template Parameters:
propagator_options_t – Type of the Objections object
Public Types
-
using options_type = propagator_options_t
Public Functions
Create the propagator state from the options.
- Template Parameters:
propagator_options_t – the type of the propagator options
- Parameters:
topts – The options handed over by the propagate call
steppingIn – Stepper state instance to begin with
navigationIn – Navigator state instance to begin with
Public Members
-
std::reference_wrapper<const GeometryContext> geoContext
Context object for the geometry.
Navigation state - internal state of the Navigator.
-
propagator_options_t options
These are the options - provided for each propagation step.
-
double pathLength = 0.
Signed distance over which the parameters were propagated.
-
PropagatorStage stage = PropagatorStage::invalid
Propagation stage.
-
StepperState stepping
Stepper state - internal state of the Stepper.
-
unsigned int steps = 0
Number of propagation steps that were carried out.
-
template<typename BinningType>
class ProtoSurfaceMaterialT : public Acts::ISurfaceMaterial Public Functions
-
ProtoSurfaceMaterialT() = default
Constructor without binningType - homogeneous material.
-
inline ProtoSurfaceMaterialT(const BinningType &binning, MappingType mappingType = MappingType::Default)
Constructor with BinningType.
- Parameters:
binning – a binning description for the material map binning
mappingType – is the type of surface mapping associated to the surface
-
ProtoSurfaceMaterialT(const ProtoSurfaceMaterialT<BinningType> &smproxy) = default
Copy constructor.
- Parameters:
smproxy – The source proxy
-
ProtoSurfaceMaterialT(ProtoSurfaceMaterialT<BinningType> &&smproxy) = default
Copy move constructor.
- Parameters:
smproxy – The source proxy
-
~ProtoSurfaceMaterialT() override = default
Destructor.
-
inline const BinningType &binning() const
Return the BinUtility.
-
inline virtual const MaterialSlab &materialSlab(const Vector2&) const final
Return method for full material description of the Surface - from local coordinates.
- Returns:
will return dummy material
-
inline virtual const MaterialSlab &materialSlab(const Vector3&) const final
Return method for full material description of the Surface - from the global coordinates.
- Returns:
will return dummy material
-
inline virtual ProtoSurfaceMaterialT<BinningType> &operator*=(double) final
Scale operator - dummy implementation.
-
ProtoSurfaceMaterialT<BinningType> &operator=(const ProtoSurfaceMaterialT<BinningType> &smproxy) = default
Assignment operator.
- Parameters:
smproxy – The source proxy
-
ProtoSurfaceMaterialT<BinningType> &operator=(ProtoSurfaceMaterialT<BinningType> &&smproxy) = default
Assignment move operator.
- Parameters:
smproxy – The source proxy
-
inline virtual std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &sl) const final
Output Method for std::ostream, to be overloaded by child classes.
- Parameters:
sl – is the output stream
-
ProtoSurfaceMaterialT() = default
-
class RadialBounds : public Acts::DiscBounds
Class to describe the bounds for a planar DiscSurface.
By providing an argument for hphisec, the bounds can be restricted to a phi-range around the center position.
Public Types
Public Functions
-
RadialBounds() = delete
-
inline RadialBounds(const std::array<double, eSize> &values) noexcept(false)
Constructor from array values.
- Parameters:
values – The bound values
-
inline RadialBounds(double minR, double maxR, double halfPhi = M_PI, double avgPhi = 0.) noexcept(false)
Constructor for full disc of symmetric disc around phi=0.
- Parameters:
minR – The inner radius (0 for full disc)
maxR – The outer radius
halfPhi – The half opening angle (Pi for full angular coverage)
avgPhi – The average phi for the disc/ring sector
-
~RadialBounds() override = default
-
inline virtual double binningValuePhi() const final
Return a reference radius for binning.
-
inline virtual double binningValueR() const final
Return a reference radius for binning.
-
inline virtual bool coversFullAzimuth() const final
Returns true for full phi coverage.
-
inline double get(BoundValues bValue) const
Access to the bound values.
- Parameters:
bValue – the class nested enum for the array access
-
virtual bool inside(const Vector2 &lposition, const BoundaryCheck &bcheck) const final
For disc surfaces the local position in (r,phi) is checked.
- Parameters:
lposition – local position to be checked
bcheck – boundary check directive
- Returns:
is a boolean indicating the operation success
-
inline virtual bool insideRadialBounds(double R, double tolerance = 0.) const final
Checks if this is inside the radial coverage given the a tolerance.
-
inline virtual double rMax() const final
Return method for outer Radius.
-
inline virtual double rMin() const final
Return method for inner Radius.
-
virtual std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &sl) const final
Outstream operator.
- Parameters:
sl – is the ostream to be dumped into
-
virtual SurfaceBounds::BoundsType type() const final
Return the bounds type - for persistency optimization.
- Returns:
is a BoundsType enum
-
inline virtual std::vector<double> values() const final
Return the bound values as dynamically sized vector.
- Returns:
this returns a copy of the internal values
-
RadialBounds() = delete
-
class RectangleBounds : public Acts::PlanarBounds
Bounds for a rectangular, planar surface - it can be used to for rectangles that are symmetrically centered around (0./0.) and for generic shifted rectangles
Public Types
Public Functions
-
RectangleBounds() = delete
-
inline RectangleBounds(const std::array<double, eSize> &values) noexcept(false)
Constructor - from fixed size array - generic.
- Parameters:
values – The parameter values
-
inline RectangleBounds(const Vector2 &min, const Vector2 &max) noexcept(false)
Constructor - from min/max - generic.
- Parameters:
min – The left bottom corner
max – The right top corning
-
inline RectangleBounds(double halfX, double halfY) noexcept(false)
Constructor with halflength in x and y - symmetric.
- Parameters:
halfX – halflength in X
halfY – halflength in Y
-
~RectangleBounds() override = default
-
virtual const RectangleBounds &boundingBox() const final
Bounding box parameters.
- Returns:
rectangle bounds for a bounding box
-
inline double get(BoundValues bValue) const
Access to the bound values.
- Parameters:
bValue – the class nested enum for the array access
-
inline double halfLengthX() const
Access to the half length in X.
-
inline double halfLengthY() const
Access to the half length in Y.
-
virtual bool inside(const Vector2 &lposition, const BoundaryCheck &bcheck) const final
Inside check for the bounds object driven by the boundary check directive Each Bounds has a method inside, which checks if a LocalPosition is inside the bounds Inside can be called without/with tolerances.
- Parameters:
lposition – Local position (assumed to be in right surface frame)
bcheck – boundary check directive
- Returns:
boolean indicator for the success of this operation
-
virtual std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &sl) const final
Output Method for std::ostream.
- Parameters:
sl – is the ostream for the dump
-
inline virtual BoundsType type() const final
Return the bounds type - for persistency optimization.
- Returns:
is a BoundsType enum
-
inline virtual std::vector<double> values() const final
Access method for bound values, this is a dynamically sized vector containing the parameters needed to describe these bounds.
- Returns:
of the stored values for this SurfaceBounds object
-
RectangleBounds() = delete
-
class RegularSurface : public Acts::Surface
A physical surface which does not depend on the direction you look at it from.
As such it narrows the interface of
Surfaceand allows inspection without providing a global position and direction.Subclassed by Acts::ConeSurface, Acts::CylinderSurface, Acts::DiscSurface, Acts::PlaneSurface
Public Functions
-
virtual Result<Vector2> globalToLocal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction, double tolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance) const final
Convert a global position to a local one this is the most generic interface, which is implemented by all surfaces.
Note
The
positionis required to be on-surface, which is indicated by theResultreturn value.- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – is the global position to be converted
direction – is the direction of the local position (ignored for
RegularSurface)tolerance – is the tolerance for the on-surface check
- Returns:
Result type containing local position by value
-
virtual Result<Vector2> globalToLocal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, double tolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance) const = 0
Convert a global position to a local one.
Note
The
positionis required to be on-surface, which is indicated by theResultreturn value.- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – is the global position to be converted
tolerance – is the tolerance for the on-surface check
- Returns:
Result type containing local position by value
-
virtual Vector3 localToGlobal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector2 &lposition) const = 0
Local to global transformation.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lposition – local 2D position in specialized surface frame
- Returns:
The global position by value
-
virtual Vector3 localToGlobal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector2 &lposition, const Vector3 &direction) const final
Local to global transformation.
This is the most generic interface, which is implemented by all surfaces.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lposition – local 2D position in specialized surface frame
direction – global 3D momentum direction (ignored for
RegularSurface)
- Returns:
The global position by value
-
virtual Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector2 &lposition) const = 0
Calculate the normal vector of the surface This overload requires an on-surface local position.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lposition – is the local position where the normal vector is constructed
- Returns:
normal vector by value
-
virtual Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &pos, const Vector3 &direction) const final
Calculate the normal vector of the surface This overload is fully generic, fulfills the Surface interface and accepts a global position and a direction.
For
RegularSurfacethis is equivalent to the normal overload, ignoring thedirection- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
pos – is the global position where the normal vector is constructed
direction – is the direction of the normal vector (ignored for
RegularSurface)
-
virtual Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position) const = 0
Calculate the normal vector of the surface This overload accepts a global position.
- Parameters:
position – is the global position where the normal vector is constructed
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
- Returns:
normal vector by value
-
Surface(const DetectorElementBase &detelement)
Constructor from DetectorElementBase: Element proxy.
- Parameters:
detelement – Detector element which is represented by this surface
-
Surface(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Surface &other, const Transform3 &shift)
Copy constructor with optional shift.
Note
copy construction invalidates the association to detector element and layer
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
other – Source surface for copy
shift – Additional transform applied as: shift * transform
-
Surface(const Surface &other)
Copy constructor.
Note
copy construction invalidates the association to detector element and layer
- Parameters:
other – Source surface for copy.
-
Surface(const Transform3 &transform = Transform3::Identity())
Constructor with Transform3 as a shared object.
Note
also acts as default constructor
- Parameters:
transform – Transform3 positions the surface in 3D global space
-
virtual Result<Vector2> globalToLocal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction, double tolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance) const final
-
template<typename T, typename E = std::error_code>
class Result Class which encapsulates either a valid result, or an error.
- Template Parameters:
T – The valid result value
E – The error, defaults to
std::error_code
Public Functions
-
Result() = delete
Default construction is disallowed.
-
template<typename T2, typename _E = E, typename _T = T, typename = std::enable_if_t<(!std::is_same_v<_T, _E> && !std::is_constructible_v<_T, _E> && !std::is_convertible_v<_T, _E> && !std::is_constructible_v<_E, _T> && !std::is_convertible_v<_E, _T> && !(std::is_convertible_v<T2, _T> && std::is_convertible_v<T2, _E>))>>
inline Result(T2 value) noexcept Constructor from arbitrary value This constructor allows construction from any value.
This constructor is only enabled if T and E are unambiguous, meaning they cannot be implicitly converted and there is T cannot be constructed from E and vice-versa. This means that when this is invoked, the value can be propagated to the underlying variant, and the assignment will be correct, and error will be an error, and a value will be a value.
Note
If T and E are ambiguous, use the
successandfailurestatic factory methods.- Template Parameters:
T2 – Type of the potential assignment
- Parameters:
value – The potential value, could be an actual valid value or an error.
-
inline E error() && noexcept
Returns the error by-value.
Note
If
res.ok()this method will abort (noexcept)- Returns:
The error
-
inline E &error() & noexcept
Returns a reference to the error stored in the result.
Note
If
res.ok()this method will abort (noexcept)- Returns:
Reference to the error
-
inline const E &error() const & noexcept
Returns a reference to the error stored in the result.
Note
If
res.ok()this method will abort (noexcept)- Returns:
Reference to the error
-
inline bool ok() const noexcept
Checks whether this result contains a valid value, and no error.
- Returns:
bool Whether result contains an error or not.
-
inline const T &operator*() const noexcept
Returns a reference into the variant to the valid value.
Note
If
!res.ok(), this method will abort (noexcept)- Returns:
Reference to value stored in the variant.
-
inline T &operator*() noexcept
Returns a reference into the variant to the valid value.
Note
If
!res.ok(), this method will abort (noexcept)- Returns:
Reference to value stored in the variant.
-
inline const T *operator->() const noexcept
Allows to access members of the stored object with
res->foosimilar tostd::optional.Note
If
!res.ok(), this method will abort (noexcept)- Returns:
Pointer to value stored in the variant.
-
inline T *operator->() noexcept
Allows to access members of the stored object with
res->foosimilar tostd::optional.Note
If
!res.ok(), this method will abort (noexcept)- Returns:
Pointer to value stored in the variant.
-
inline Result<T, E> &operator=(Result<T, E> &&other)
Move assignment is allowed.
- Parameters:
other – The other result instance, rvalue reference
- Returns:
The assigned instance
-
template<typename T2, typename _E = E, typename _T = T, typename = std::enable_if_t<(!std::is_same_v<_T, _E> && !std::is_constructible_v<_T, _E> && !std::is_convertible_v<_T, _E> && !std::is_constructible_v<_E, _T> && !std::is_convertible_v<_E, _T> && !(std::is_convertible_v<T2, _T> && std::is_convertible_v<T2, _E>))>>
inline Result<T, E> &operator=(T2 value) noexcept Assignment operator from arbitrary value This operator allows construction from any value.
The same rules as for the
Result(T2 value)constructor apply.- Template Parameters:
T2 – Type of the potential assignment
- Parameters:
value – The potential value, could be an actual valid value or an error.
- Returns:
The assigned instance
-
inline T &value() &
Retrieves the valid value from the result object.
Note
This is the lvalue version, returns a reference to the value
- Returns:
The valid value as a reference
-
template<typename external_spacepoint_t>
class SeedFilter Filter seeds at various stages with the currently available information.
Public Functions
-
SeedFilter() = delete
-
SeedFilter(SeedFilterConfig config, IExperimentCuts<external_spacepoint_t> *expCuts = nullptr)
-
virtual ~SeedFilter() = default
-
virtual void filterSeeds_1SpFixed(Acts::SpacePointData &spacePointData, CandidatesForMiddleSp<const InternalSpacePoint<external_spacepoint_t>> &candidates_collector, const std::size_t numQualitySeeds, std::back_insert_iterator<std::vector<Seed<external_spacepoint_t>>> outIt) const
Filter seeds once all seeds for one middle space point have been created.
- Parameters:
spacePointData – Auxiliary variables used by the seeding
candidates_collector – collection of seed candidates
numQualitySeeds – number of high quality seeds in seed confirmation
outIt – Output iterator for the seeds for all seeds with the same middle space point
-
virtual void filterSeeds_1SpFixed(Acts::SpacePointData &spacePointData, std::vector<typename CandidatesForMiddleSp<const InternalSpacePoint<external_spacepoint_t>>::value_type> &candidates, const std::size_t numQualitySeeds, std::back_insert_iterator<std::vector<Seed<external_spacepoint_t>>> outIt) const
Filter seeds once all seeds for one middle space point have been created.
- Parameters:
spacePointData – Auxiliary variables used by the seeding
candidates – collection of seed candidates
numQualitySeeds – number of high quality seeds in seed confirmation
outIt – Output iterator for the seeds for all seeds with the same middle space point
-
virtual void filterSeeds_2SpFixed(Acts::SpacePointData &spacePointData, const InternalSpacePoint<external_spacepoint_t> &bottomSP, const InternalSpacePoint<external_spacepoint_t> &middleSP, const std::vector<const InternalSpacePoint<external_spacepoint_t>*> &topSpVec, const std::vector<float> &invHelixDiameterVec, const std::vector<float> &impactParametersVec, SeedFilterState &seedFilterState, CandidatesForMiddleSp<const InternalSpacePoint<external_spacepoint_t>> &candidates_collector) const
Create InternalSeeds for the all seeds with the same bottom and middle space point and discard all others.
- Parameters:
spacePointData – Auxiliary variables used by the seeding
bottomSP – fixed bottom space point
middleSP – fixed middle space point
topSpVec – vector containing all space points that may be compatible with both bottom and middle space point
invHelixDiameterVec – vector containing 1/(2*r) values where r is the helix radius
impactParametersVec – vector containing the impact parameters
seedFilterState – holds quantities used in seed filter
candidates_collector – container for the seed candidates
-
inline const IExperimentCuts<external_spacepoint_t> *getExperimentCuts() const
-
inline const SeedFilterConfig getSeedFilterConfig() const
-
SeedFilter() = delete
-
class SinglyChargedParticleHypothesis : public Acts::GenericParticleHypothesis<SinglyCharged>
Specialized particle hypothesis for singly charged particles.
Note
This serves as a factory for common singly charge particles.
Public Functions
-
template<typename other_charge_t>
inline constexpr SinglyChargedParticleHypothesis(const GenericParticleHypothesis<other_charge_t> &other)
-
inline SinglyChargedParticleHypothesis(PdgParticle absPdg)
-
inline constexpr SinglyChargedParticleHypothesis(PdgParticle absPdg, float mass)
Public Static Functions
-
static inline SinglyChargedParticleHypothesis chargedGeantino()
-
static inline SinglyChargedParticleHypothesis electron()
-
static inline SinglyChargedParticleHypothesis kaon()
-
static inline SinglyChargedParticleHypothesis muon()
-
static inline SinglyChargedParticleHypothesis pion()
-
static inline SinglyChargedParticleHypothesis proton()
-
template<typename other_charge_t>
-
class SolenoidBField : public Acts::MagneticFieldProvider
Implements a multi-coil solenoid magnetic field.
On every call, the field is evaluated at that exact position. The field has radially symmetry, the field vectors point in +z direction. The config exposes a target field value in the center. This value is used to empirically determine a scale factor which reproduces this field value in the center.
E_1(k^2) = complete elliptic integral of the 1st kind E_2(k^2) = complete elliptic integral of the 2nd kind
E_1(k^2) and E_2(k^2) are usually indicated as K(k^2) and E(k^2) in literature, respectively _ 2 / pi / 2 2 2 - 1 / 2 E (k ) = | ( 1 - k sin {theta} ) dtheta 1 _/ 0
2 / pi / 2| / 2 2 E (k ) = | |/ 1 - k sin {theta} dtheta 2 _/ 0_ ____________________
k^2 = is a function of the point (r, z) and of the radius of the coil R
2 4Rr k = ————— 2 2 (R + r) + z Using these, you can evaluate the two components B_r and B_z of the magnetic field: _ _ mu I | / 2 \ | 0 kz | |2 - k | 2 2 | B (r, z) = –— —— | |—-—|E (k ) - E (k ) | r 4pi ___ | | 2| 2 1 | | / 3 |_ \2 - 2k / _| |/ Rr
mu I | / 2 \ | 0 k | | (R + r)k - 2r | 2 2 | B (r,z) = –— -— | | ———–— | E (k ) + E (k ) | z 4pi __ | | 2 | 2 1 | |/Rr |_ \ 2r(1 - k ) / _|_ _
Public Functions
-
SolenoidBField(Config config)
the constructor with a shared pointer
Note
since it is a shared field, we enforce it to be const
- Template Parameters:
bField – is the shared BField to be stored
-
Vector2 getField(const Vector2 &position) const
Retrieve magnetic field value in local (r,z) coordinates.
- Parameters:
position – [in] local 2D position
-
Vector3 getField(const Vector3 &position) const
Get the B field at a position.
- Parameters:
position – The position to query at
-
virtual Result<Vector3> getField(const Vector3 &position, MagneticFieldProvider::Cache &cache) const override
Retrieve magnetic field value at a given location.
Requires a cache object created through makeCache().
- Parameters:
position – [in] global 3D position for the lookup
cache – [inout] Field provider specific cache object
- Returns:
magnetic field vector at given position
-
virtual Result<Vector3> getFieldGradient(const Vector3 &position, ActsMatrix<3, 3> &derivative, MagneticFieldProvider::Cache &cache) const override
Retrieve magnetic field value its its gradient.
Requires a cache object created through makeCache().
Note
currently the derivative is not calculated
- Parameters:
position – [in] global 3D position
derivative – [out] gradient of magnetic field vector as (3x3) matrix
cache – [inout] Field provider specific cache object
- Returns:
magnetic field vector
-
virtual MagneticFieldProvider::Cache makeCache(const MagneticFieldContext &mctx) const override
Make an opaque cache for the magnetic field.
Instructs the specific implementation to generate a
Cacheinstance for magnetic field lookup.- Parameters:
mctx – The magnetic field context to generate cache for
- Returns:
Cache The opaque cache object
-
struct Cache
Public Functions
-
inline Cache(const MagneticFieldContext&)
Constructor with magnetic field context.
-
inline Cache(const MagneticFieldContext&)
-
struct Config
Config struct for the SolenoidBfield.
Public Members
-
double bMagCenter
The target magnetic field strength at the center.
This will be used to scale coefficients
-
double length
Extent of the solenoid in z.
It goes from -length/2 to +length/2 by convention
-
std::size_t nCoils
The number of coils that make up the solenoid.
-
double radius
Radius at which the coils are located.
-
double bMagCenter
-
SolenoidBField(Config config)
-
class SourceLink
Public Functions
-
SourceLink(const SourceLink &other) = default
-
SourceLink(SourceLink &&other) = default
-
template<typename T, typename = std::enable_if_t<!std::is_same_v<std::decay_t<T>, SourceLink>>>
inline explicit SourceLink(T &&upstream) Constructor from concrete sourcelink.
- Template Parameters:
T – The source link type
- Parameters:
upstream – The upstream source link to store
-
template<typename T>
inline T &get() Concrete source link class getter.
- Template Parameters:
T – The source link type to retrieve
- Returns:
Reference to the stored source link
-
template<typename T>
inline const T &get() const Concrete source link class getter, const version.
- Template Parameters:
T – The source link type to retrieve
- Returns:
Const reference to the stored source link
-
SourceLink &operator=(const SourceLink &other) = default
-
SourceLink &operator=(SourceLink &&other) = default
-
SourceLink(const SourceLink &other) = default
-
class StraightLineStepper
straight line stepper based on Surface intersection
The straight line stepper is a simple navigation stepper to be used to navigate through the tracking geometry. It can be used for simple material mapping, navigation validation
Public Types
-
using BField = NullBField
-
using BoundState = std::tuple<BoundTrackParameters, Jacobian, double>
-
using Covariance = BoundSquareMatrix
-
using Jacobian = BoundMatrix
Public Functions
-
StraightLineStepper() = default
-
inline double absoluteMomentum(const State &state) const
Absolute momentum accessor.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
Result<BoundState> boundState(State &state, const Surface &surface, bool transportCov = true, const FreeToBoundCorrection &freeToBoundCorrection = FreeToBoundCorrection(false)) const
Create and return the bound state at the current position.
It does not check if the transported state is at the surface, this needs to be guaranteed by the propagator
- Parameters:
state – [in] State that will be presented as
BoundStatesurface – [in] The surface to which we bind the state
transportCov – [in] Flag steering covariance transport
freeToBoundCorrection – [in] Correction for non-linearity effect during transform from free to bound
- Returns:
A bound state:
the parameters at the surface
the stepwise jacobian towards it (from last bound)
and the path length (from start - for ordering)
-
inline double charge(const State &state) const
Charge access.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
CurvilinearState curvilinearState(State &state, bool transportCov = true) const
Create and return a curvilinear state at the current position.
This creates a curvilinear state.
- Parameters:
state – [in] State that will be presented as
CurvilinearStatetransportCov – [in] Flag steering covariance transport
- Returns:
A curvilinear state:
the curvilinear parameters at given position
the stepweise jacobian towards it (from last bound)
and the path length (from start - for ordering)
-
inline Vector3 direction(const State &state) const
Momentum direction accessor.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
inline Result<Vector3> getField(State&, const Vector3&) const
Get the field for the stepping, this gives back a zero field.
-
inline double getStepSize(const State &state, ConstrainedStep::Type stype) const
Get the step size.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
stype – [in] The step size type to be returned
-
inline State makeState(std::reference_wrapper<const GeometryContext> gctx, std::reference_wrapper<const MagneticFieldContext> mctx, const BoundTrackParameters &par, double ssize = std::numeric_limits<double>::max(), double stolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance) const
-
inline Vector3 momentum(const State &state) const
Momentum accessor.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
inline std::string outputStepSize(const State &state) const
Output the Step Size - single component.
- Parameters:
state – [in,out] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
inline const ParticleHypothesis &particleHypothesis(const State &state) const
Particle hypothesis.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
inline Vector3 position(const State &state) const
Global particle position accessor.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
If necessary fill additional members needed for curvilinearState.
Compute path length derivatives in case they have not been computed yet, which is the case if no step has been executed yet.
- Parameters:
prop_state – [inout] State that will be presented as
BoundStatenavigator – [in] the navigator of the propagation
- Returns:
true if nothing is missing after this call, false otherwise.
-
inline double qOverP(const State &state) const
QoP direction accessor.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
inline void releaseStepSize(State &state, ConstrainedStep::Type stype) const
Release the Step size.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
stype – [in] The step size type to be released
-
void resetState(State &state, const BoundVector &boundParams, const BoundSquareMatrix &cov, const Surface &surface, const double stepSize = std::numeric_limits<double>::max()) const
Resets the state.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] State of the stepper
boundParams – [in] Parameters in bound parametrisation
cov – [in] Covariance matrix
surface – [in] The reset
Statewill be on this surfacestepSize – [in] Step size
Perform a straight line propagation step.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] is the propagation state associated with the track parameters that are being propagated. The state contains the desired step size, it can be negative during backwards track propagation, and since we’re using an adaptive algorithm, it can be modified by the stepper class during propagation.
- Returns:
the step size taken
-
inline double time(const State &state) const
Time access.
- Parameters:
state – [in] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
-
void transportCovarianceToBound(State &state, const Surface &surface, const FreeToBoundCorrection &freeToBoundCorrection = FreeToBoundCorrection(false)) const
Method for on-demand transport of the covariance to a new curvilinear frame at current position, or direction of the state - for the moment a dummy method.
Note
no check is done if the position is actually on the surface
- Template Parameters:
surface_t – the surface type - ignored here
- Parameters:
state – [inout] The stepper state
surface – [in] is the surface to which the covariance is forwarded to
freeToBoundCorrection – [in] Correction for non-linearity effect during transform from free to bound
-
void transportCovarianceToCurvilinear(State &state) const
Method for on-demand transport of the covariance to a new curvilinear frame at current position, or direction of the state - for the moment a dummy method.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] State of the stepper
-
void update(State &state, const FreeVector &freeParams, const BoundVector &boundParams, const Covariance &covariance, const Surface &surface) const
Method to update a stepper state to the some parameters.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] State object that will be updated
freeParams – [in] Free parameters that will be written into
stateboundParams – [in] Corresponding bound parameters used to update jacToGlobal in
statecovariance – [in] Covariance that will be written into
statesurface – [in] The surface used to update the jacToGlobal
-
void update(State &state, const Vector3 &uposition, const Vector3 &udirection, double qop, double time) const
Method to update the stepper state.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] State object that will be updated
uposition – [in] the updated position
udirection – [in] the updated direction
qop – [in] the updated qop value
time – [in] the updated time value
-
template<typename object_intersection_t>
inline void updateStepSize(State &state, const object_intersection_t &oIntersection, Direction, bool release = true) const Update step size.
It checks the status to the reference surface & updates the step size accordingly
- Parameters:
state – [in,out] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
oIntersection – [in] The ObjectIntersection to layer, boundary, etc
release – [in] boolean to trigger step size release
-
inline void updateStepSize(State &state, double stepSize, ConstrainedStep::Type stype = ConstrainedStep::actor, bool release = true) const
Update step size - explicitly with a double.
- Parameters:
state – [in,out] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
stepSize – [in] The step size value
stype – [in] The step size type to be set
release – [in] Do we release the step size?
-
inline Intersection3D::Status updateSurfaceStatus(State &state, const Surface &surface, std::uint8_t index, Direction navDir, const BoundaryCheck &bcheck, ActsScalar surfaceTolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance, const Logger &logger = getDummyLogger()) const
Update surface status.
This method intersects the provided surface and update the navigation step estimation accordingly (hence it changes the state). It also returns the status of the intersection to trigger onSurface in case the surface is reached.
- Parameters:
state – [inout] The stepping state (thread-local cache)
surface – [in] The surface provided
index – [in] The surface intersection index
navDir – [in] The navigation direction
bcheck – [in] The boundary check for this status update
surfaceTolerance – [in] Surface tolerance used for intersection
logger – [in] A logger instance
-
struct State
State for track parameter propagation.
Public Functions
-
State() = delete
-
inline explicit State(const GeometryContext &gctx, const MagneticFieldContext&, const BoundTrackParameters &par, double ssize = std::numeric_limits<double>::max(), double stolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance)
Constructor from the initial bound track parameters.
Note
the covariance matrix is copied when needed
- Parameters:
gctx – [in] is the context object for the geometry
par – [in] The track parameters at start
ssize – [in] is the maximum step size
stolerance – [in] is the stepping tolerance
Public Members
-
Covariance cov = Covariance::Zero()
-
bool covTransport = false
Boolean to indicate if you need covariance transport.
-
FreeVector derivative = FreeVector::Zero()
The propagation derivative.
-
std::reference_wrapper<const GeometryContext> geoContext
-
BoundToFreeMatrix jacToGlobal = BoundToFreeMatrix::Zero()
Jacobian from local to the global frame.
-
FreeMatrix jacTransport = FreeMatrix::Identity()
Pure transport jacobian part from runge kutta integration.
-
FreeVector pars = FreeVector::Zero()
Internal free vector parameters.
-
ParticleHypothesis particleHypothesis = ParticleHypothesis::pion()
Particle hypothesis.
-
double pathAccumulated = 0.
accummulated path length state
-
double previousStepSize = 0.
-
ConstrainedStep stepSize
adaptive step size of the runge-kutta integration
-
double tolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance
The tolerance for the stepping.
-
State() = delete
-
using BField = NullBField
-
class StrawSurface : public Acts::LineSurface
Class for a StrawSurface in the TrackingGeometry to describe dirft tube and straw like detectors.

Public Functions
-
StrawSurface() = delete
-
~StrawSurface() override = default
-
inline virtual std::string name() const final
Return properly formatted class name for screen output */.
-
StrawSurface &operator=(const StrawSurface &other)
Assignment operator.
- Parameters:
other – is the source surface for copying
-
virtual Polyhedron polyhedronRepresentation(const GeometryContext &gctx, std::size_t lseg) const final
Return a Polyhedron for the surfaces.
Note
if lseg is set to 1 then only the straw is created
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lseg – Number of segments along curved lines, it represents the full 2*M_PI coverange, if lseg is set to 1 only the extrema are given
- Returns:
A list of vertices and a face/facett description of it
-
inline virtual SurfaceType type() const final
Return the surface type.
-
StrawSurface() = delete
-
class Surface : public virtual Acts::GeometryObject, public std::enable_shared_from_this<Surface>
Abstract Base Class for tracking surfaces.
The Surface class builds the core of the Acts Tracking Geometry. All other geometrical objects are either extending the surface or are built from it.
Surfaces are either owned by Detector elements or the Tracking Geometry, in which case they are not copied within the data model objects.
Subclassed by Acts::LineSurface, Acts::RegularSurface
Public Types
Public Functions
-
virtual ~Surface()
-
AlignmentToBoundMatrix alignmentToBoundDerivative(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction, const FreeVector &pathDerivative) const
The derivative of bound track parameters w.r.t.
alignment parameters of its reference surface (i.e. local frame origin in global 3D Cartesian coordinates and its rotation represented with extrinsic Euler angles)
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment change of alignment parameters
position – global 3D position
direction – global 3D momentum direction
pathDerivative – is the derivative of free parameters w.r.t. path length
- Returns:
Derivative of bound track parameters w.r.t. local frame alignment parameters
-
virtual AlignmentToPathMatrix alignmentToPathDerivative(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction) const
Calculate the derivative of path length at the geometry constraint or point-of-closest-approach w.r.t.
alignment parameters of the surface (i.e. local frame origin in global 3D Cartesian coordinates and its rotation represented with extrinsic Euler angles)
Note
Re-implementation is needed for surface whose intersection with track is not its local xy plane, e.g. LineSurface, CylinderSurface and ConeSurface
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – global 3D position
direction – global 3D momentum direction
- Returns:
Derivative of path length w.r.t. the alignment parameters
-
void assignDetectorElement(const DetectorElementBase &detelement)
Assign a detector element.
- Parameters:
detelement – Detector element which is represented by this surface
Assign the surface material description.
The material is usually derived in a complicated way and loaded from a framework given source. As various surfaces may share the same source this is provided by a shared pointer
- Parameters:
material – Material description associated to this surface
-
const DetectorElementBase *associatedDetectorElement() const
Return method for the associated Detector Element.
- Returns:
plain pointer to the DetectorElement, can be nullptr
-
const Layer *associatedLayer() const
Return method for the associated Layer in which the surface is embedded.
- Returns:
Layer by plain pointer, can be nullptr
-
void associateLayer(const Layer &lay)
Set Associated Layer Many surfaces can be associated to a Layer, but it might not be known yet during construction of the layer, this can be set afterwards.
- Parameters:
lay – the assignment Layer by reference
-
virtual const SurfaceBounds &bounds() const = 0
Return method for SurfaceBounds.
- Returns:
SurfaceBounds by reference
-
virtual BoundToFreeMatrix boundToFreeJacobian(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction) const
Calculate the jacobian from local to global which the surface knows best, hence the calculation is done here.
Note
In principle, the input could also be a free parameters vector as it could be transformed to a bound parameters. But the transform might fail in case the parameters is not on surface. To avoid the check inside this function, it takes directly the bound parameters as input (then the check might be done where this function is called).
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – global 3D position
direction – global 3D momentum direction
- Returns:
Jacobian from local to global
-
virtual Vector3 center(const GeometryContext &gctx) const
Return method for the surface center by reference.
Note
the center is always recalculated in order to not keep a cache
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
- Returns:
center position by value
-
virtual FreeToBoundMatrix freeToBoundJacobian(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction) const
Calculate the jacobian from global to local which the surface knows best, hence the calculation is done here.
Note
It assumes the input free parameters is on surface, hence no onSurface check is done inside this function.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – global 3D position
direction – global 3D momentum direction
- Returns:
Jacobian from global to local
-
virtual FreeToPathMatrix freeToPathDerivative(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction) const
Calculate the derivative of path length at the geometry constraint or point-of-closest-approach w.r.t.
free parameters. The calculation is identical for all surfaces where the reference frame does not depend on the direction
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – global 3D position
direction – global 3D momentum direction
- Returns:
Derivative of path length w.r.t. free parameters
Retrieve a
std::shared_ptrfor this surface (non-const version)Note
Will error if this was not created through the
makeSharedfactory since it needs access to the original reference. In C++14 this is undefined behavior (but most likely implemented as abad_weak_ptrexception), in C++17 it is defined as that exception.Note
Only call this if you need shared ownership of this object.
- Returns:
The shared pointer
Retrieve a
std::shared_ptrfor this surface (const version)Note
Will error if this was not created through the
makeSharedfactory since it needs access to the original reference. In C++14 this is undefined behavior, but most likely implemented as abad_weak_ptrexception, in C++17 it is defined as that exception.Note
Only call this if you need shared ownership of this object.
- Returns:
The shared pointer
-
virtual Result<Vector2> globalToLocal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction, double tolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance) const = 0
Global to local transformation Generalized global to local transformation for the surface types.
Since some surface types need the global momentum/direction to resolve sign ambiguity this is also provided
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – global 3D position - considered to be on surface but not inside bounds (check is done)
direction – global 3D momentum direction
tolerance – optional tolerance within which a point is considered valid on surface
- Returns:
a Result<Vector2> which can be !ok() if the operation fails
-
virtual bool insideBounds(const Vector2 &lposition, const BoundaryCheck &bcheck = BoundaryCheck(true)) const
The insideBounds method for local positions.
- Parameters:
lposition – The local position to check
bcheck – BoundaryCheck directive for this onSurface check
- Returns:
boolean indication if operation was successful
-
virtual SurfaceMultiIntersection intersect(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction, const BoundaryCheck &bcheck = BoundaryCheck(false), ActsScalar tolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance) const = 0
Straight line intersection schema from position/direction.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – The position to start from
direction – The direction at start
bcheck – the Boundary Check
tolerance – the tolerance used for the intersection
- Returns:
SurfaceMultiIntersectionobject (contains intersection & surface)
-
bool isOnSurface(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction, const BoundaryCheck &bcheck = BoundaryCheck(true)) const
The geometric onSurface method.
Geometrical check whether position is on Surface
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – global position to be evaludated
direction – global momentum direction (required for line-type surfaces)
bcheck – BoundaryCheck directive for this onSurface check
- Returns:
boolean indication if operation was successful
-
virtual ActsMatrix<2, 3> localCartesianToBoundLocalDerivative(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position) const = 0
Calculate the derivative of bound track parameters local position w.r.t.
position in local 3D Cartesian coordinates
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – The position of the parameters in global
- Returns:
Derivative of bound local position w.r.t. position in local 3D cartesian coordinates
-
virtual Vector3 localToGlobal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector2 &lposition, const Vector3 &direction) const = 0
Local to global transformation Generalized local to global transformation for the surface types.
Since some surface types need the global momentum/direction to resolve sign ambiguity this is also provided
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lposition – local 2D position in specialized surface frame
direction – global 3D momentum direction
- Returns:
The global position by value
-
virtual std::string name() const = 0
Return properly formatted class name.
-
virtual Vector3 normal(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &pos, const Vector3 &direction) const = 0
Return the surface normal at a given
positionanddirection.This method is fully generic, and valid for all surface types.
Note
For some surface types, the
directionis ignored, but it is not safe to pass in a zero vector!- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
pos – The position at which to calculate the normal
direction – The direction at which to calculate the normal
- Returns:
The normal vector at the given position and direction
-
virtual bool operator!=(const Surface &sf) const
Comparison (non-equality) operator.
- Parameters:
sf – Source surface for the comparison
-
Surface &operator=(const Surface &other)
Assignment operator.
Note
copy construction invalidates the association to detector element and layer
- Parameters:
other – Source surface for the assignment
-
virtual bool operator==(const Surface &other) const
Comparison (equality) operator The strategy for comparison is (a) first pointer comparison (b) then type comparison (c) then bounds comparison (d) then transform comparison.
- Parameters:
other – source surface for the comparison
-
virtual double pathCorrection(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction) const = 0
Calucation of the path correction for incident.
Note
The
positionis either ignored, or it is coerced to be on the surface, depending on the surface type.- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – global 3D position
direction – global 3D momentum direction
- Returns:
Path correction with respect to the nominal incident.
-
virtual Polyhedron polyhedronRepresentation(const GeometryContext &gctx, std::size_t lseg) const = 0
Return a Polyhedron for this object.
Note
An internal surface transform can invalidate the extrema in the transformed space
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
lseg – Number of segments along curved lines, if the lseg is set to one, only the corners and the extrema are given, otherwise it represents the number of segments for a full 2*M_PI circle and is scaled to the relevant sector
- Returns:
A list of vertices and a face/facett description of it
-
virtual Acts::RotationMatrix3 referenceFrame(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const Vector3 &direction) const
Return method for the reference frame This is the frame in which the covariance matrix is defined (specialized by all surfaces)
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – global 3D position - considered to be on surface but not inside bounds (check is done)
direction – global 3D momentum direction (optionally ignored)
- Returns:
RotationMatrix3 which defines the three axes of the measurement frame
-
const ISurfaceMaterial *surfaceMaterial() const
Return method for the associated Material to this surface.
- Returns:
SurfaceMaterial as plain pointer, can be nullptr
Return method for the shared pointer to the associated Material.
- Returns:
SurfaceMaterial as shared_pointer, can be nullptr
-
virtual std::ostream &toStream(const GeometryContext &gctx, std::ostream &sl) const
Output Method for std::ostream, to be overloaded by child classes.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
sl – is the ostream to be dumped into
-
std::string toString(const GeometryContext &gctx) const
Output into a std::string.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
-
virtual const Transform3 &transform(const GeometryContext &gctx) const
Return method for the surface Transform3 by reference In case a detector element is associated the surface transform is just forwarded to the detector element in order to keep the (mis-)alignment cache cetrally handled.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
- Returns:
the contextual transform
-
virtual SurfaceType type() const = 0
Return method for the Surface type to avoid dynamic casts.
Public Static Functions
Factory for producing memory managed instances of Surface.
Will forward all parameters and will attempt to find a suitable constructor.
Public Static Attributes
-
static std::array<std::string, SurfaceType::Other> s_surfaceTypeNames
Helper strings for screen output.
-
virtual ~Surface()
-
class SurfaceArray
Provides Surface binning in N dimensions.
Uses
Gridunder the hood to implement the storage and lookup Contains a lookup struct which talks to theGridand performs utility actions. This struct needs to be initialised externally and passed toSurfaceArrayon construction.Public Functions
Constructor with a single surface.
- Parameters:
srf – The one and only surface
Default constructor which takes a
SurfaceLookupand a vector of surfaces.- Parameters:
gridLookup – The grid storage.
SurfaceArraydoes not fill it on its ownsurfaces – The input vector of surfaces. This is only for bookkeeping, so we can ask
transform – Optional additional transform for this SurfaceArray
-
inline SurfaceVector &at(const Vector3 &position)
Get all surfaces in bin given by position.
- Parameters:
position – the lookup position
- Returns:
reference to
SurfaceVectorcontained in bin at that position
-
inline const SurfaceVector &at(const Vector3 &position) const
Get all surfaces in bin given by position
pos.- Parameters:
position – the lookup position
- Returns:
const reference to
SurfaceVectorcontained in bin at that position
-
inline SurfaceVector &at(std::size_t bin)
Get all surfaces in bin given by global bin index
bin.- Parameters:
bin – the global bin index
- Returns:
reference to
SurfaceVectorcontained in bin
-
inline const SurfaceVector &at(std::size_t bin) const
Get all surfaces in bin given by global bin index.
- Parameters:
bin – the global bin index
- Returns:
const reference to
SurfaceVectorcontained in bin
-
inline std::vector<BinningValue> binningValues() const
The binning values described by this surface grid lookup They are in order of the axes.
-
inline std::vector<const IAxis*> getAxes() const
Get vector of axes spanning the grid as
AnyAxis.Note
The axes in the vector are copies. Only use for introspection and querying.
- Returns:
vector of
AnyAxis
-
inline Vector3 getBinCenter(std::size_t bin)
Get the center of the bin identified by global bin index
bin.- Parameters:
bin – the global bin index
- Returns:
Center position of the bin in global coordinates
-
inline bool isValidBin(std::size_t bin) const
Checks if global bin is valid.
Note
Valid means that the index points to a bin which is not a under or overflow bin or out of range in any axis.
- Parameters:
bin – the global bin index
- Returns:
bool if the bin is valid
-
inline const SurfaceVector &neighbors(const Vector3 &position) const
Get all surfaces in bin at
posand its neighbors.Note
The
SurfaceVectorwill be combined. For technical reasons, the different bin content vectors have to be copied, so the resulting vector contains copies.- Parameters:
position – The position to lookup as nominal
- Returns:
Merged
SurfaceVectorof neighbors and nominal
-
inline std::size_t size() const
Get the size of the underlying grid structure including under/overflow bins.
- Returns:
the size
-
inline const SurfaceVector &surfaces() const
Get all surfaces attached to this
SurfaceArray.Note
This does not reflect the actual state of the grid. It only returns what was given in the constructor, without any checks if that is actually what’s in the grid.
- Returns:
Reference to
SurfaceVectorcontaining all surfaces
-
std::ostream &toStream(const GeometryContext &gctx, std::ostream &sl) const
String representation of this
SurfaceArray.- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
sl – Output stream to write to
- Returns:
the output stream given as
sl
-
inline const Transform3 &transform() const
-
struct ISurfaceGridLookup
Base interface for all surface lookups.
Subclassed by Acts::SurfaceArray::SingleElementLookup, Acts::SurfaceArray::SurfaceGridLookup< Axes >
Public Functions
-
virtual ~ISurfaceGridLookup() = 0
Pure virtual destructor.
-
inline virtual std::vector<BinningValue> binningValues() const
The binning values described by this surface grid lookup They are in order of the axes (optional) and empty for eingle lookups.
-
virtual std::size_t completeBinning(const GeometryContext &gctx, const SurfaceVector &surfaces) = 0
Attempts to fix sub-optimal binning by filling closest Surfaces into empty bin.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
surfaces – The surface pointers to fill
- Returns:
number of bins that were filled
-
virtual std::size_t dimensions() const = 0
Get the number of dimensions of the grid.
- Returns:
number of dimensions
-
virtual void fill(const GeometryContext &gctx, const SurfaceVector &surfaces) = 0
Fill provided surfaces into the contained
Grid.- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
surfaces – Input surface pointers
-
virtual std::vector<const IAxis*> getAxes() const = 0
Returns copies of the axes used in the grid as
AnyAxis.Note
This returns copies. Use for introspection and querying.
- Returns:
The axes
-
virtual Vector3 getBinCenter(std::size_t bin) const = 0
Gets the center position of bin
binin global coordinates.- Parameters:
bin – the global bin index
- Returns:
The bin center
-
virtual bool isValidBin(std::size_t bin) const = 0
Checks if global bin is valid.
Note
Valid means that the index points to a bin which is not a under or overflow bin or out of range in any axis.
- Parameters:
bin – the global bin index
- Returns:
bool if the bin is valid
-
virtual const SurfaceVector &lookup(const Vector3 &position) const = 0
Performs lookup at
posand returns bin content as const reference.- Parameters:
position – Lookup position
- Returns:
SurfaceVectorat given bin
-
virtual SurfaceVector &lookup(const Vector3 &position) = 0
Performs lookup at
posand returns bin content as reference.- Parameters:
position – Lookup position
- Returns:
SurfaceVectorat given bin
-
virtual const SurfaceVector &lookup(std::size_t bin) const = 0
Performs lookup at global bin and returns bin content as const reference.
- Parameters:
bin – Global lookup bin
- Returns:
SurfaceVectorat given bin
-
virtual SurfaceVector &lookup(std::size_t bin) = 0
Performs lookup at global bin and returns bin content as reference.
- Parameters:
bin – Global lookup bin
- Returns:
SurfaceVectorat given bin
-
virtual const SurfaceVector &neighbors(const Vector3 &position) const = 0
Performs a lookup at
pos, but returns neighbors as well.- Parameters:
position – Lookup position
- Returns:
SurfaceVectorat given bin. Copy of all bins selected
-
virtual std::size_t size() const = 0
Returns the total size of the grid (including under/overflow bins)
- Returns:
Size of the grid data structure
-
virtual ~ISurfaceGridLookup() = 0
-
struct SingleElementLookup : public Acts::SurfaceArray::ISurfaceGridLookup
Lookup implementation which wraps one element and always returns this element when lookup is called.
Public Functions
-
inline SingleElementLookup(const SurfaceVector &elements)
Default constructor.
- Parameters:
elements – the surfaces that are provided through a single lookup
-
inline SingleElementLookup(SurfaceVector::value_type element)
Default constructor.
- Parameters:
element – the one and only element.
-
inline virtual std::size_t completeBinning(const GeometryContext&, const SurfaceVector&) override
Comply with concept and provide completeBinning method.
Note
Does nothing
-
inline virtual std::size_t dimensions() const override
Get the number of dimensions.
- Returns:
always 0
-
inline virtual void fill(const GeometryContext&, const SurfaceVector&) override
Comply with concept and provide fill method.
Note
Does nothing
-
inline virtual std::vector<const IAxis*> getAxes() const override
Returns an empty vector of
AnyAxis.- Returns:
empty vector
-
inline virtual Vector3 getBinCenter(std::size_t) const override
Gets the bin center, but always returns (0, 0, 0)
- Returns:
(0, 0, 0)
-
inline virtual bool isValidBin(std::size_t) const override
Returns if the bin is valid (it is)
- Returns:
always true
-
inline virtual const SurfaceVector &lookup(const Vector3&) const override
Lookup, always returns
element.- Returns:
reference to vector containing only
element
-
inline virtual SurfaceVector &lookup(const Vector3&) override
Lookup, always returns
element.- Returns:
reference to vector containing only
element
-
inline virtual const SurfaceVector &lookup(std::size_t) const override
Lookup, always returns
element.- Returns:
reference to vector containing only
element
-
inline virtual SurfaceVector &lookup(std::size_t) override
Lookup, always returns
element.- Returns:
reference to vector containing only
element
-
inline virtual const SurfaceVector &neighbors(const Vector3&) const override
Lookup, always returns
element.- Returns:
reference to vector containing only
element
-
inline virtual std::size_t size() const override
returns 1
- Returns:
1
-
inline SingleElementLookup(const SurfaceVector &elements)
-
template<class ...Axes>
struct SurfaceGridLookup : public Acts::SurfaceArray::ISurfaceGridLookup Lookup helper which encapsulates a
Grid.- Template Parameters:
Axes – The axes used for the grid
Public Types
-
using Grid_t = Grid<SurfaceVector, Axes...>
-
using point_t = std::conditional_t<DIM == 1, std::array<double, 1>, ActsVector<DIM>>
Specifies the local coordinate type.
This resolves to
ActsVector<DIM>for DIM > 1, elsestd::array<double, 1>
Public Functions
-
inline SurfaceGridLookup(std::function<point_t(const Vector3&)> globalToLocal, std::function<Vector3(const point_t&)> localToGlobal, std::tuple<Axes...> axes, std::vector<BinningValue> bValues = {})
Default constructor.
Note
Signature of localToGlobal and globalToLocal depends on
DIM. If DIM > 1, local coords areActsVector<DIM>elsestd::array<double, 1>.- Parameters:
globalToLocal – Callable that converts from global to local
localToGlobal – Callable that converts from local to global
axes – The axes to build the grid data structure.
bValues – What the axes represent (optional)
-
inline virtual std::vector<BinningValue> binningValues() const override
The binning values described by this surface grid lookup They are in order of the axes.
-
inline virtual std::size_t completeBinning(const GeometryContext &gctx, const SurfaceVector &surfaces) override
Attempts to fix sub-optimal binning by filling closest Surfaces into empty bins.
Note
This does not always do what you want.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
surfaces – The surface pointers to fill
- Returns:
number of bins that were filled
-
inline virtual std::size_t dimensions() const override
Get the number of dimensions of the grid.
- Returns:
number of dimensions
-
inline virtual void fill(const GeometryContext &gctx, const SurfaceVector &surfaces) override
Fill provided surfaces into the contained
Grid.This is done by iterating, accessing the binningPosition, lookup and append. Also populates the neighbor map by combining the filled bins of all bins around a given one.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
surfaces – Input surface pointers
-
inline virtual std::vector<const IAxis*> getAxes() const override
Returns copies of the axes used in the grid as
AnyAxis.Note
This returns copies. Use for introspection and querying.
- Returns:
The axes
-
inline virtual Vector3 getBinCenter(std::size_t bin) const override
Gets the center position of bin
binin global coordinates.- Parameters:
bin – the global bin index
- Returns:
The bin center
-
inline virtual bool isValidBin(std::size_t bin) const override
Checks if global bin is valid.
Note
Valid means that the index points to a bin which is not a under or overflow bin or out of range in any axis.
- Parameters:
bin – the global bin index
- Returns:
bool if the bin is valid
-
inline virtual const SurfaceVector &lookup(const Vector3 &position) const override
Performs lookup at
posand returns bin content as const reference.- Parameters:
position – Lookup position
- Returns:
SurfaceVectorat given bin
-
inline virtual SurfaceVector &lookup(const Vector3 &position) override
Performs lookup at
posand returns bin content as reference.- Parameters:
position – Lookup position
- Returns:
SurfaceVectorat given bin
-
inline virtual const SurfaceVector &lookup(std::size_t bin) const override
Performs lookup at global bin and returns bin content as const reference.
- Parameters:
bin – Global lookup bin
- Returns:
SurfaceVectorat given bin
-
inline virtual SurfaceVector &lookup(std::size_t bin) override
Performs lookup at global bin and returns bin content as reference.
- Parameters:
bin – Global lookup bin
- Returns:
SurfaceVectorat given bin
-
inline virtual const SurfaceVector &neighbors(const Vector3 &position) const override
Performs a lookup at
pos, but returns neighbors as well.- Parameters:
position – Lookup position
- Returns:
SurfaceVectorat given bin. Copy of all bins selected
-
inline virtual std::size_t size() const override
Returns the total size of the grid (including under/overflow bins)
- Returns:
Size of the grid data structure
-
class SurfaceArrayCreator
It is designed create sub surface arrays to be ordered on Surfaces.
Public Functions
-
inline SurfaceArrayCreator(const Config &cfg, std::unique_ptr<const Logger> logger = getDefaultLogger("SurfaceArrayCreator", Logging::INFO))
Constructor with explicit config.
- Parameters:
cfg – Explicit config struct
logger – logging instance
-
inline SurfaceArrayCreator(std::unique_ptr<const Logger> logger = getDefaultLogger("SurfaceArrayCreator", Logging::INFO))
Constructor with default config.
- Parameters:
logger – logging instance
-
virtual ~SurfaceArrayCreator() = default
Destructor.
-
inline void setLogger(std::unique_ptr<const Logger> logger)
Set logging instance.
- Parameters:
logger – is the logging instance to be set
SurfaceArrayCreator interface method.
create an array in a cylinder, binned in phi, z when extremas and bin numbers are unknown - this method goes through the surfaces and finds out the needed information
Warning
This function requires the cylinder aligned with the z-axis
- Parameters:
surfaces – is the vector of pointers to sensitive surfaces to be ordered on the cylinder
gctx – [in] The gometry context for this building call
protoLayerOpt – The proto layer containing the layer size
bTypePhi – the binning type in phi direction (equidistant/arbitrary)
bTypeZ – the binning type in z direction (equidistant/arbitrary)
transform – is the (optional) additional transform applied
- Pre:
the pointers to the sensitive surfaces in the surfaces vectors all need to be valid, since no check is performed
- Returns:
a unique pointer a new SurfaceArray
SurfaceArrayCreator interface method.
create an array in a cylinder, binned in phi, z when extremas and bin numbers are known
Warning
This function requires the cylinder aligned with the z-axis
- Parameters:
surfaces – is the vector of pointers to sensitive surfaces to be ordered on the cylinder
gctx – [in] The gometry context for this building call
protoLayerOpt – The proto layer containing the layer size
binsPhi – is the number of bins in phi for the surfaces
binsZ – is the number of bin in Z for the surfaces
transform – is the (optional) additional transform applied
- Pre:
the pointers to the sensitive surfaces in the surfaces vectors all need to be valid, since no check is performed
- Returns:
a unique pointer to a new SurfaceArray
SurfaceArrayCreator interface method.
create an array in a cylinder, binned in phi, r when extremas and bin numbers are unknown - this method goes through the surfaces and finds out the needed information
Note
If there is more than on R-Ring, number of phi bins will be set to lowest number of surfaces of any R-ring. This ignores bTypePhi and produces equidistant binning in phi
Warning
This function requires the disc aligned with the z-axis
- Parameters:
surfaces – is the vector of pointers to sensitive surfaces to be ordered on the disc
gctx – [in] The gometry context for this building call
protoLayerOpt – The proto layer containing the layer size
bTypeR – the binning type in r direction (equidistant/arbitrary)
bTypePhi – the binning type in phi direction (equidistant/arbitrary)
transform – is the (optional) additional transform applied
- Pre:
the pointers to the sensitive surfaces in the surfaces vectors all need to be valid, since no check is performed
- Returns:
a unique pointer a new SurfaceArray
SurfaceArrayCreator interface method.
create an array on a disc, binned in r, phi when extremas and bin numbers are known
Warning
This function requires the disc aligned with the z-axis
- Parameters:
surfaces – is the vector of pointers to sensitive surfaces to be ordered on the disc
gctx – [in] The gometry context for this building call
protoLayerOpt – The proto layer containing the layer size
binsPhi – is the number of bins in phi for the surfaces
binsR – is the number of bin in R for the surfaces
transform – is the (optional) additional transform applied
- Pre:
the pointers to the sensitive surfaces in the surfaces vectors all need to be valid, since no check is performed
- Returns:
a unique pointer a new SurfaceArray
SurfaceArrayCreator interface method.
create an array on a plane
Warning
This function requires the plane aligned with either the x-, y- or z-axis
- Parameters:
gctx – [in] The gometry context for this building call
surfaces – [in] is the vector of pointers to sensitive surfaces to be ordered on the plane
bins1 – [in] is the number of bins in the orthogonal direction to
bValuebins2 – [in] is the number of bins in the orthogonal direction to
bValuebValue – [in] Direction of the aligned surfaces
protoLayerOpt – [in] Optional
ProtoLayerinstancetransform – [in] is the (optional) additional transform applied
- Pre:
the pointers to the sensitive surfaces in the surfaces vectors all need to be valid, since no check is performed
- Returns:
a unique pointer a new SurfaceArray
Public Static Functions
-
static inline bool isSurfaceEquivalent(const GeometryContext &gctx, BinningValue bValue, const Surface *a, const Surface *b)
Static check function for surface equivalent.
- Parameters:
gctx – [in] the geometry context for this check
bValue – the binning value for the binning
a – first surface for checking
b – second surface for checking
Friends
- friend class Acts::SurfaceArray
- friend struct Acts::Test::SurfaceArrayCreatorFixture
-
struct Config
Public Members
-
bool doPhiBinningOptimization = true
Optimize the binning in phi for disc layers.
Reduces the number of bins to the lowest number of non-equivalent phi surfaces of all r-bins. If false, this step is skipped.
-
SurfaceMatcher surfaceMatcher = SurfaceArrayCreator::isSurfaceEquivalent
Type-erased function which determines whether two surfaces are supposed to be considered equivalent in terms of the binning.
-
bool doPhiBinningOptimization = true
-
struct ProtoAxis
Public Functions
-
inline std::size_t getBin(AxisScalar x) const
Public Members
-
std::vector<AxisScalar> binEdges
-
BinningType bType = BinningType::equidistant
-
BinningValue bValue = BinningValue::binX
-
AxisScalar max = 0
-
AxisScalar min = 0
-
std::size_t nBins = 0
-
inline std::size_t getBin(AxisScalar x) const
-
inline SurfaceArrayCreator(const Config &cfg, std::unique_ptr<const Logger> logger = getDefaultLogger("SurfaceArrayCreator", Logging::INFO))
-
class SurfaceBounds
Interface for surface bounds.
Surface bounds provide:
inside() checks
distance to boundary calculations
the BoundsType and a set of parameters to simplify persistency
Subclassed by Acts::ConeBounds, Acts::CylinderBounds, Acts::DiscBounds, Acts::InfiniteBounds, Acts::LineBounds, Acts::PlanarBounds
Public Types
-
enum BoundsType
This is nested to the SurfaceBounds, as also VolumeBounds will have Bounds Type.
Values:
-
enumerator eCone
-
enumerator eCylinder
-
enumerator eDiamond
-
enumerator eDisc
-
enumerator eEllipse
-
enumerator eLine
-
enumerator eRectangle
-
enumerator eTrapezoid
-
enumerator eTriangle
-
enumerator eDiscTrapezoid
-
enumerator eConvexPolygon
-
enumerator eAnnulus
-
enumerator eBoundless
-
enumerator eOther
-
enumerator eCone
Public Functions
-
virtual ~SurfaceBounds() = default
-
virtual bool inside(const Vector2 &lposition, const BoundaryCheck &bcheck) const = 0
Inside check for the bounds object driven by the boundary check directive Each Bounds has a method inside, which checks if a LocalPosition is inside the bounds Inside can be called without/with tolerances.
- Parameters:
lposition – Local position (assumed to be in right surface frame)
bcheck – boundary check directive
- Returns:
boolean indicator for the success of this operation
-
virtual std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &os) const = 0
Output Method for std::ostream, to be overloaded by child classes.
- Parameters:
os – is the outstream in which the string dump is done
-
virtual BoundsType type() const = 0
Return the bounds type - for persistency optimization.
- Returns:
is a BoundsType enum
-
virtual std::vector<double> values() const = 0
Access method for bound values, this is a dynamically sized vector containing the parameters needed to describe these bounds.
- Returns:
of the stored values for this SurfaceBounds object
-
class TGeoDetectorElement : public Acts::IdentifiedDetectorElement
DetectorElement plugin for ROOT TGeo shapes.
Added possibility to hand over transformation matrix.
Subclassed by Acts::DD4hepDetectorElement
Public Types
-
using ContextType = GeometryContext
Broadcast the context type.
Public Functions
Constructor.
Note
this constructor used auto-translation
Note
This parameter only needs to be set for plane modules
Note
In the translation from a 3D geometry (TGeo) which only knows tubes to a 2D geometry (Tracking geometry) a distinction if the module should be described as a cylinder or a disc surface needs to be done. Since this information can not be taken just from the geometry description (both can be described as TGeoTubeSeg), one needs to set the flag ‘isDisc’ in case a volume with shape
TGeoTubeSegshould be translated to a disc surface. Per default it will be translated into a cylindrical surface.- Parameters:
identifier – is the detector identifier
tGeoNode – is the TGeoNode which should be represented
tGeoMatrix – The Matrix to global (i.e. ACTS transform)
axes – is the axis orientation with respect to the tracking frame it is a string of the three characters x, y and z (standing for the three axes) there is a distinction between capital and lower case characters :
capital -> positive orientation of the axis
lower case -> negative orientation of the axis example options are “XYZ” -> identical frame definition (default value) “YZX” -> node y axis is tracking x axis, etc. “XzY” -> negative node z axis is tracking y axis, etc.
scalor – is the scale factor for unit conversion if needed
material – Possible material of detector element
Constructor with pre-computed disk surface.
Note
this detector element constructor needs everything pre-computed.
- Parameters:
identifier – is the detector identifier
tGeoNode – is the TGeoNode which should be represented
tgTransform – the transform of this detector element
tgBounds – the bounds of this surface
tgThickness – the thickness of this detector element
Constructor with pre-computed surface.
Note
this detector element constructor needs everything pre-computed.
- Parameters:
identifier – is the detector identifier
tGeoNode – is the TGeoNode which should be represented
tgTransform – the transform of this detector element
tgBounds – the bounds of this surface
tgThickness – the thickness of this detector element
-
~TGeoDetectorElement() override
-
inline virtual const std::shared_ptr<const DigitizationModule> digitizationModule() const final
Retrieve the DigitizationModule.
-
inline virtual Identifier identifier() const final
Retrieve the Identifier.
-
inline virtual const Surface &surface() const override
Return surface associated with this detector element.
-
inline virtual Surface &surface() override
Return surface associated with this detector element.
Note
this is the non-const access
-
inline const TGeoNode &tgeoNode() const
Return the TGeoNode for back navigation.
-
inline virtual double thickness() const override
Returns the thickness of the module.
-
inline virtual const Transform3 &transform(const GeometryContext &gctx) const override
Return local to global transform associated with this identifier.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
-
using ContextType = GeometryContext
-
template<ACTS_CONCEPT track_container_t(TrackContainerBackend), typename traj_t, template<typename> class holder_t = detail::RefHolder>
class TrackContainer Track container interface class.
This type represents a collections of tracks. It uses a backend to store both the actual tracks and the associated track states.
- Template Parameters:
track_container_t – the track container backend
traj_t – the track state container backend
holder_t – ownership management class for the backend
TrackContainer construction
Constructors for the track container by using a set of backends (track + track state). The container can either take ownership of the backends or just hold references to them. This is driven by the
holder_ttemplate parameter, where you can also supply a custom holder type. Template deduction is used to try to guess the correct holder type.-
inline TrackContainer(holder_t<track_container_t> container, holder_t<traj_t> traj)
Constructor from a track container backend and a track state container backend.
- Parameters:
container – the track container backend
traj – the track state container backend
-
template<template<typename> class H = holder_t, typename = std::enable_if_t<detail::is_same_template<H, detail::RefHolder>::value>>
inline TrackContainer(track_container_t &container, traj_t &traj) Constructor from references to a track container backend and to a track state container backend.
Note
The track container will not assume ownership over the backends in this case. You need to ensure suitable lifetime
- Parameters:
container – the track container backend
traj – the track state container backend
-
template<template<typename> class H = holder_t, bool RO = (IsReadOnlyTrackContainer<track_container_t>::value && IsReadOnlyMultiTrajectory<traj_t>::value), typename = std::enable_if_t<detail::is_same_template<H, detail::ConstRefHolder>::value && RO>>
inline TrackContainer(const track_container_t &container, const traj_t &traj) Constructor from const references to a track container backend and to a track state container backend.
Note
The track container will not assume ownership over the backends in this case. You need to ensure suitable lifetime
- Parameters:
container – the track container backend
traj – the track state container backend
TrackContainer track (proxy) access and manipulation
These methods allow accessing tracks, i.e. adding or retrieving a track proxy that points at a specific track in the container.
-
inline ConstTrackProxy getTrack(IndexType itrack) const
Get a const track proxy for a track index.
- Parameters:
itrack – the track index in the container
- Returns:
A const track proxy for the index
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline TrackProxy getTrack(IndexType itrack) Get a mutable track proxy for a track index.
Note
Only available if the track container is not read-only
- Parameters:
itrack – the track index in the container
- Returns:
A mutable track proxy for the index
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline IndexType addTrack() Add a track to the container.
Note this only creates the logical track and allocates memory. You can combine this with
getTrackto obtain a track proxyNote
Only available if the track container is not read-only
- Returns:
the index to the newly added track
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline TrackProxy makeTrack() Add a track to the container and return a track proxy to it This effectively calls
addTrackandgetTrack.Note
Only available if the track container is not read-only
- Returns:
a track proxy to the newly added track
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline void removeTrack(IndexType itrack) Remove a track at index
itrackfrom the container.Note
Only available if the track container is not read-only
Note
This invalidates track proxies that point to tracks with larger indices than
itrack!- Parameters:
itrack – The index of the track to remove
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline auto begin() Get a mutable iterator to the first track in the container.
Note
Only available if the track container is not read-only
- Returns:
a mutable iterator to the first track
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline auto end() Get a past-the-end iterator for this container.
Note
Only available if the track container is not read-only
- Returns:
a past-the-end iterator
-
inline auto begin() const
Get an const iterator to the first track in the container.
- Returns:
a const iterator to the first track
-
inline auto end() const
Get a past-the-end iterator for this container.
- Returns:
a past-the-end iterator
TrackContainer column management
TrackContainer can manage a set of common static columns, and dynamic columns that can be added at runtime.
This set of methods allows you to manage the dynamic columns.
-
template<typename T, bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline constexpr void addColumn(const std::string &key) Add a dymanic column to the track container.
Note
Only available if the track container is not read-only
- Parameters:
key – the name of the column to be added
-
inline constexpr bool hasColumn(const std::string &key) const
Check if this track container has a specific dynamic column.
- Parameters:
key – the key to check for
-
inline constexpr bool hasColumn(HashedString key) const
Check if a this track container has a specific dynamic column.
- Parameters:
key – the key to check for
-
template<typename other_track_container_t, bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline void ensureDynamicColumns(const other_track_container_t &other) Helper function to make this track container match the dynamic columns of another one.
This will only work if the track container supports this source, and depends on the implementation details of the dynamic columns of the container
Note
Only available if the track container is not read-only
- Template Parameters:
other_track_container_t – Type of the other track container
- Parameters:
other – The other track container
TrackContainer backend access
These methods allow accessing the backend of the track container.
In most cases, this is not necessary for interacting with the container.
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline auto &container() Get a mutable reference to the track container backend.
Note
Only available if the track container is not read-only
- Returns:
a mutable reference to the backend
-
inline const auto &container() const
Get a const reference to the track container backend.
- Returns:
a const reference to the backend
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline auto &trackStateContainer() Get a mutable reference to the track state container backend.
Note
Only available if the track container is not read-only
- Returns:
a mutable reference to the backend
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline auto &trackStateContainerHolder() Retrieve the holder of the track state container.
Note
Only available if the track container is not read-only
- Returns:
The track state container including it’s holder
-
inline const auto &trackStateContainer() const
Get a const reference to the track state container backend.
- Returns:
a const reference to the backend
-
inline const auto &trackStateContainerHolder() const
Retrieve the holder of the track state container.
- Returns:
The track state container including it’s holder
Public Types
-
using ConstTrackProxy = Acts::TrackProxy<track_container_t, traj_t, holder_t, true>
Alias for the const version of a track proxy, with the same backends as this container.
-
using IndexType = TrackIndexType
The index type of the track container, taken from the container backend.
-
using TrackProxy = Acts::TrackProxy<track_container_t, traj_t, holder_t, false>
Alias for the mutable version of a track proxy, with the same backends as this container.
Public Functions
Public Static Attributes
-
static constexpr IndexType kInvalid = kTrackIndexInvalid
Sentinel value that indicates an invalid index.
-
static constexpr bool ReadOnly = IsReadOnlyTrackContainer<track_container_t>::value
Indicates if this track container is read-only, or if it can be modified.
-
template<typename track_container_t, typename trajectory_t, template<typename> class holder_t, bool read_only = true>
class TrackProxy Proxy class representing a single track.
This class provides a view into an associated TrackContainer, and has reference semantics. You can think of it as a pointer to a vector of tracks, which exposes an object-oriented interface for accessing the track properties.
- Template Parameters:
track_container_t – the container backend
trajectory_t – the track state container backend
holder_t – ownership management class for the backend
read_only – true if this track container is not mutable
Constructors and assignment operator
Public constructors and assignment operators for
TrackProxyonly allow construction from anotherTrackProxy. You should generally not have to constructTrackProxymanually.-
inline TrackProxy(const MutableTrackProxy &other)
Copy constructor from a mutable track proxy.
This is always valid, either mutable to mutable or mutable to const
- Parameters:
other – the other track state proxy
-
inline TrackProxy &operator=(const MutableTrackProxy &other)
Copy assignment operator from mutable track proxy.
This is always valid, either mutable to mutable or mutable to const
- Parameters:
other – the other track state proxy
TrackProxy properties
Methods that give access to the properties of a track represented by
TrackProxy.Many of these methods come in a
constand a non-constversion. The non-constversion is only available if you have an instance ofTrackProxythat does not have theread_onlytemplate parameter set totrue, even if you hold it as an lvalue.-
inline IndexType tipIndex() const
Get the tip index, i.e.
the entry point into the track state container
- Returns:
the tip index by value
-
inline IndexType stemIndex() const
Index of the stem, i.e.
the innermost track state of the track. This might be invalid, signifying that the track state is not forward-linked.
- Returns:
the stem index
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline IndexType &tipIndex() Get a mutable reference to the tip index, i.e.
the entry point into the track container
Note
Only available if the track proxy is not read-only
- Returns:
mutable reference to the tip index
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline IndexType &stemIndex() Index of the stem, i.e.
the innermost track state of the track. This might be invalid, signifying that the track state is not forward-linked.
Note
Only available if the track proxy is not read-only
- Returns:
mutable reference to the stem index
-
inline const Surface &referenceSurface() const
Get the reference surface of the track (e.g.
the perigee)
- Returns:
the reference surface
Set a new reference surface for this track.
- Parameters:
srf – The surface to set
-
inline bool hasReferenceSurface() const
Returns whether the track has a reference surface or not.
- Returns:
whether a surface exists or not
-
inline ConstParameters parameters() const
Get the parameters of the track at the reference surface (e.g.
perigee). Const version
- Returns:
Proxy vector for the parameters
-
inline ConstCovariance covariance() const
Get the covariance of the track at the reference surface (e.g.
perigee). Const version
- Returns:
Proxy matrix for the covariance
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline Parameters parameters() Get the parameters of the track at the reference surface (e.g.
perigee). Mutable version
Note
Only available if the track proxy is not read-only
- Returns:
Proxy vector for the parameters
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline Covariance covariance() Get the covariance of the track at the reference surface (e.g.
perigee). Mutable version
Note
Only available if the track proxy is not read-only
- Returns:
Proxy matrix for the covariance
-
inline ActsScalar theta() const
Access the theta parameter of the track at the reference surface.
- Returns:
The theta parameter
-
inline ActsScalar phi() const
Access the phi parameter of the track at the reference surface.
- Returns:
The phi parameter
-
inline ActsScalar loc0() const
Access the loc0 parameter of the track at the reference surface.
- Returns:
The loc0 parameter
-
inline ActsScalar loc1() const
Access the loc1 parameter of the track at the reference surface.
- Returns:
The loc1 parameter
-
inline ActsScalar time() const
Access the time parameter of the track at the reference surface.
- Returns:
The time parameter
-
inline ActsScalar qOverP() const
Access the q/p (curvature) parameter of the track at the reference surface.
- Returns:
The q/p parameter
-
inline ParticleHypothesis particleHypothesis() const
Get the particle hypothesis.
- Returns:
the particle hypothesis
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline void setParticleHypothesis(const ParticleHypothesis &particleHypothesis) Set a new particle hypothesis for this track.
Note
Only available if the track proxy is not read-only
- Parameters:
particleHypothesis – The particle hypothesis to set
-
inline ActsScalar charge() const
Get the charge of the tack.
Note
this depends on the charge hypothesis
- Returns:
The absolute track momentum
-
inline ActsScalar absoluteMomentum() const
Get the absolute momentum of the tack.
- Returns:
The absolute track momentum
-
inline ActsScalar transverseMomentum() const
Get the transverse momentum of the track.
- Returns:
The track transverse momentum value
-
inline Vector3 direction() const
Get a unit vector along the track direction at the reference surface.
- Returns:
The direction unit vector
-
inline Vector3 momentum() const
Get the global momentum vector.
- Returns:
the global momentum vector
-
inline unsigned int nTrackStates() const
Return the number of track states associated to this track.
Note
This is calculated by iterating over the track states which is somewhat expensive. Consider caching this value if you need It more than once.
- Returns:
The number of track states
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline unsigned int &nMeasurements() Return the number of measurements for the track.
Const version
Note
Only available if the track proxy is not read-only
- Returns:
The number of measurements
-
inline unsigned int nMeasurements() const
Return a mutable reference to the number of measurements for the track.
Mutable version
- Returns:
The number of measurements
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline unsigned int &nHoles() Return a mutable reference to the number of holes for the track.
Mutable version
Note
Only available if the track proxy is not read-only
- Returns:
The number of holes
-
inline unsigned int nHoles() const
Return the number of measurements for the track.
Const version
- Returns:
The number of measurements
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline unsigned int &nOutliers() Return a mutable reference to the number of outliers for the track.
Mutable version
Note
Only available if the track proxy is not read-only
- Returns:
The number of outliers
-
inline unsigned int nOutliers() const
Return the number of outliers for the track.
Const version
- Returns:
The number of outliers
Return a mutable reference to the number of shared hits for the track.
Mutable version
Note
Only available if the track proxy is not read-only
- Returns:
The number of shared hits
Return the number of shared hits for the track.
Const version
- Returns:
The number of shared hits
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline float &chi2() Return a mutable reference to the chi squared Mutable version.
Note
Only available if the track proxy is not read-only
- Returns:
The chi squared
-
inline float chi2() const
Return the chi squared for the track.
Const version
- Returns:
The chi squared
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline unsigned int &nDoF() Return a mutable reference to the number of degrees of freedom for the track.
Mutable version
Note
Only available if the track proxy is not read-only
- Returns:
The number of degrees of freedom
-
inline unsigned int nDoF() const
Return the number of degrees of freedom for the track.
Const version
- Returns:
The number of degrees of freedom
TrackProxy track state access
Methods that give access to the track states of a track represented by
TrackProxy.-
inline auto innermostTrackState() const
Return a const track state proxy to the innermost track state.
Note
This is only available, if the track is forward linked
- Returns:
The innermost track state proxy
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline auto innermostTrackState() Return a mutable track state proxy to the innermost track state.
Note
This is only available, if the track is forward linked
Note
Only available if the track proxy is not read-only
- Returns:
The innermost track state proxy
-
inline auto trackStatesReversed() const
Get a range over the track states of this track.
Return value is compatible with range based for loop. Const version
Note
This range is from the outside inwards!
- Returns:
Track state range to iterate over
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline auto trackStatesReversed() Get a range over the track states of this track.
Return value is compatible with range based for loop. Mutable version
Note
Only available if the track proxy is not read-only
Note
This range is from the outside inwards!
- Returns:
Track state range to iterate over
-
inline auto trackStates() const
Get a range over the track states of this track.
Return value is compatible with range based for loop. This overload returns a const-only track state range, which means you cannot modify the track states obtained in the iteration.
Note
This range is from the inside out!
Warning
This access direction is only possible if the track states are forward-linked.
- Returns:
Track state range to iterate over
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline auto trackStates() Get a range over the track states of this track.
Return value is compatible with range based for loop. This overload returns a mutable track state range, which means you can modify the track states obtained in the iteration.
Note
Only available if the track proxy is not read-only
Note
This range is from the inside out!
Warning
This access direction is only possible if the track states are forward-linked.
- Returns:
Track state range to iterate over
TrackProxy track state manipulation
Methods that manipulate the track states of a track represented by
TrackProxy.-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline void linkForward() Forward connect a track.
This means setting indices from the inside out on all track states.
Note
Only available if the track proxy is not read-only
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline auto appendTrackState(TrackStatePropMask mask = TrackStatePropMask::All) Append a track state to this track.
This will modify the tip index to point at the newly created track state, which will be directly after the previous track state at tip index.
Note
Only available if the track proxy is not read-only
- Parameters:
mask – The allocation prop mask for the new track state
- Returns:
The newly added track state
-
template<typename track_proxy_t, bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline void copyFrom(const track_proxy_t &other, bool copyTrackStates = true) Copy the content of another track proxy into this one.
Note
Only available if the track proxy is not read-only
- Template Parameters:
track_proxy_t – the other track proxy’s type
- Parameters:
other – The track proxy
copyTrackStates – Copy the track state sequence from
other
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline void reverseTrackStates(bool invertJacobians = false) Reverse the ordering of track states for this track Afterwards, the previous endpoint of the track state sequence will be the “innermost” track state.
Note
Only available if the track proxy is not read-only
Note
This is dangerous with branching track state sequences, as it will break them
Note
This also automatically forward-links the track!
- Parameters:
invertJacobians – Whether to invert the Jacobians of the track states
TrackProxy generic component access
Methods that give access to generic components of a track represented by
TrackProxy.Internally, a compile-time hash of the component name is used to identify which component is being requested. Most of the named methods in TrackProxy properties use these methods to retrieve the actual data.
A number of overloads exist, where you can either supply the HashedString
keyas a template parameter or a runtime argument. The former has the advantage of being guaranteed to be evaluated at compile-time.-
template<typename T, HashedString key, bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline constexpr T &component() Retrieve a mutable reference to a component.
- Template Parameters:
T – The type of the component to access
key – String key for the component to access
- Returns:
Mutable reference to the component given by
key
-
template<typename T, bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline constexpr T &component(HashedString key) Retrieve a mutable reference to a component.
- Template Parameters:
T – The type of the component to access
- Parameters:
key – String key for the component to access
- Returns:
Mutable reference to the component given by
key
-
template<typename T, bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline constexpr T &component(std::string_view key) Retrieve a mutable reference to a component.
Note
This might hash the
keyat runtime instead of compile-time- Template Parameters:
T – The type of the component to access
- Parameters:
key – String key for the component to access
- Returns:
Mutable reference to the component given by
key
-
template<typename T, HashedString key>
inline constexpr const T &component() const Retrieve a const reference to a component.
- Template Parameters:
T – The type of the component to access
key – String key for the component to access
- Returns:
Const reference to the component given by
key
-
template<typename T>
inline constexpr const T &component(HashedString key) const Retrieve a const reference to a component.
- Template Parameters:
T – The type of the component to access
- Parameters:
key – String key for the component to access
- Returns:
Const reference to the component given by
key
-
template<typename T>
inline constexpr const T &component(std::string_view key) const Retrieve a const reference to a component.
Note
This might hash the
keyat runtime instead of compile-time- Template Parameters:
T – The type of the component to access
- Parameters:
key – String key for the component to access
- Returns:
Const reference to the component given by
key
Public Types
-
using ConstCovariance = typename detail_lt::Types<eBoundSize, true>::CovarianceMap
Same as Covariance, but with const semantics.
-
using ConstParameters = typename detail_lt::Types<eBoundSize, true>::CoefficientsMap
Same as Parameters, but with const semantics.
-
using ConstProxyType = ConstTrackProxy
Alias for an associated const track proxy, with the same backends.
-
using ConstTrackProxy = TrackProxy<track_container_t, trajectory_t, holder_t, true>
Alias for the const version of this track proxy, with the same backends.
-
using ConstTrackStateProxy = typename Trajectory::ConstTrackStateProxy
Alias for an associated const track state proxy, with the same backends.
-
using Container = track_container_t
The track container backend given as a template parameter.
-
using Covariance = typename detail_lt::Types<eBoundSize, false>::CovarianceMap
Map-type for a bound covariance.
This has reference semantics, i.e. points at a matrix by an internal pointer.
-
using MutableTrackProxy = TrackProxy<track_container_t, trajectory_t, holder_t, false>
Alias for the mutable version of this track proxy, with the same backends.
-
using Parameters = typename detail_lt::Types<eBoundSize, false>::CoefficientsMap
Map-type for a bound parameter vector.
This has reference semantics, i.e. points at a matrix by an internal pointer.
-
using TrackStateProxy = typename Trajectory::TrackStateProxy
Alias for an associated mutable track state proxy, with the same backends.
-
using Trajectory = trajectory_t
The track state container backend given as a template parameter.
Public Functions
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline auto &container() Return a reference to the track container backend, mutable version.
Note
Only available if the track proxy is not read-only
- Returns:
reference to the track container backend
-
inline const auto &container() const
Return a reference to the track container backend, const version.
- Returns:
reference to the track container backend
-
inline BoundTrackParameters createParametersAtReference() const
Return the track parameters at the reference surface.
Note
The parameters are created on the fly
- Returns:
the track parameters
-
inline BoundTrackParameters createParametersFromState(const ConstTrackStateProxy &trackState) const
Convert a track state into track parameters.
Note
The parameters are created on the fly
- Returns:
the track parameters
-
inline bool operator==(const TrackProxy &other) const
Equality operator with another track proxy Checks the container identity and the track index.
- Returns:
True if the track proxies refer to the same track
-
template<typename trajectory_t, std::size_t M, bool read_only = true>
class TrackStateProxy Proxy object to access a single point on the trajectory.
- Template Parameters:
SourceLink – Type to link back to an original measurement
M – Maximum number of measurement dimensions
read_only – true for read-only access to underlying storage
Constructors and assignment operator
Public constructors and assignment operators for
TrackStateProxyonly allow construction from anotherTrackStateProxy. You should generally not have to constructTrackStateProxymanually.-
inline TrackStateProxy(const TrackStateProxy<Trajectory, M, false> &other)
Constructor and assignment operator to construct TrackStateProxy from mutable.
- Parameters:
other – The other TrackStateProxy to construct from
-
inline TrackStateProxy &operator=(const TrackStateProxy<Trajectory, M, false> &other)
Assignment operator to from mutable
TrackStateProxy.- Parameters:
other – The other TrackStateProxy to construct from
- Returns:
Reference to this TrackStateProxy
Track state properties
Properties of the track state represented by
TrackStateProxy.Many of these methods come in a
constand a non-constversion. The non-constversion is only available if you have an instance ofTrackStateProxythat does not have theread_onlytemplate parameter set totrue, even if you hold it as an lvalue.The track states each have an index in the track state container. The sequence of track states is implemented as a one or two-way linked list, which uses indices into the same container.
Each track state has a
previousindex, which points at the track state immediately preceding. A track state with apreviousindex ofkInvalidis the first (innermost) track state in a track or track candidate. This is also referred to as a stem at the track level.During track finding and fitting, track states are usually appended to the sequence, populating the
previousindex of the new track state. Combinatorial track finding can produce track states which fork in this way, by having more than one track state with the samepreviousindex.The track states have static, optional and dynamic properties. Static properties are always present, and can always be retrieved. Optional components use an extra indirection mechanism that coordinates with the backend to allow both not having the component set, or sharing it with other track states. An example is a branching trajectory from track finding which shares the same predicted parameter vector and associated covariance.
Optional components are
predicted parameters and covariance
filtered parameters and covariance
smoothed parameters and covariance
jacobian
calibrated measurement info including projector
They can be unset via unset, getMask can be used to check which components are present. The first four are shareable between track states via shareFrom.
-
inline IndexType previous() const
Return the index of the track state
previousin the track sequence.- Returns:
The index of the previous track state.
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline IndexType &previous() Return a mutable reference to the index of the track state ‘previous’ in the track sequence.
Note
Only available if the track state proxy is not read-only
- Returns:
The index of the previous track state.
-
inline bool hasPrevious() const
Return whether this track state has a previous (parent) track state.
- Returns:
Boolean indicating whether a previous track state exists
-
TrackStatePropMask getMask() const
Build a mask that represents all the allocated components of this track state proxy.
- Returns:
The generated mask
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline void unset(TrackStatePropMask target) Unset an optional track state component.
Note
Only available if the track state proxy is not read-only
- Parameters:
target – The component to unset
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline void addComponents(TrackStatePropMask mask) Add additional components to the track state.
Note
Only available if the track state proxy is not read-only
- Parameters:
mask – The bitmask that instructs which components to allocate
-
inline bool hasReferenceSurface() const
Returns if the track state has a non nullptr surface associated.
- Returns:
whether a surface exists or not
Set the reference surface to a given value.
Note
This overload is only present in case
ReadOnlyis false.- Parameters:
srf – Shared pointer to the surface to set
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline float &chi2() Getter/setter for chi2 value associated with the track state This overload returns a mutable reference, which allows setting a new value directly into the backing store.
Note
this overload is only enabled in case the proxy is not read-only
- Returns:
Mutable reference to the chi2 value
-
inline float chi2() const
Getter for the chi2 value associated with the track state.
This overload returns a copy of the chi2 value, and thus does not allow modification of the value in the backing storage.
- Returns:
the chi2 value of the track state
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline double &pathLength() Getter for the path length associated with the track state.
This overloaded is only enabled if not read-only, and returns a mutable reference.
- Returns:
Mutable reference to the pathlength.
-
inline double pathLength() const
Getter for the path length.
Returns a copy of the path length value.
- Returns:
The path length of this track state
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline TrackStateType typeFlags() Getter for the type flags associated with the track state.
This overloaded is only enabled if not read-only, and returns a mutable reference.
- Returns:
reference to the type flags.
-
inline ConstTrackStateType typeFlags() const
Getter for the type flags.
Returns a copy of the type flags value.
- Returns:
The type flags of this track state
Track state parameters
-
ConstParameters parameters() const
Track parameters vector.
This tries to be somewhat smart and return the first parameters that are set in this order: predicted -> filtered -> smoothed
- Returns:
one of predicted, filtered or smoothed parameters
-
ConstCovariance covariance() const
Track parameters covariance matrix.
This tries to be somewhat smart and return the first parameters that are set in this order: predicted -> filtered -> smoothed
- Returns:
one of predicted, filtered or smoothed covariances
-
inline ConstParameters predicted() const
Predicted track parameters vector.
- Returns:
The predicted parameters
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline Parameters predicted()
-
inline ConstCovariance predictedCovariance() const
Predicted track parameters covariance matrix.
- Returns:
The predicted track parameter covariance
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline Covariance predictedCovariance()
-
inline bool hasPredicted() const
Check whether the predicted parameters+covariance is set.
- Returns:
Whether it is set or not
-
inline ConstParameters filtered() const
Filtered track parameters vector.
Note
Const version
- Returns:
The filtered parameters
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline Parameters filtered() Filtered track parameters vector.
Note
Mutable version
- Returns:
The filtered parameters
-
inline ConstCovariance filteredCovariance() const
Filtered track parameters covariance matrix.
Note
Const version
- Returns:
The filtered parameters covariance
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline Covariance filteredCovariance() Filtered track parameters covariance matrix.
Note
Mutable version
- Returns:
The filtered parameters covariance
-
inline bool hasFiltered() const
Return whether filtered parameters+covariance is set.
- Returns:
Whether it is set
-
inline ConstParameters smoothed() const
Smoothed track parameters vector.
Note
Const version
- Returns:
The smoothed parameters
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline Parameters smoothed() Smoothed track parameters vector.
Note
Mutable version
- Returns:
The smoothed parameters
-
inline ConstCovariance smoothedCovariance() const
Smoothed track parameters covariance matrix.
Note
Const version
- Returns:
the parameter covariance matrix
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline Covariance smoothedCovariance() Smoothed track parameters covariance matrix.
Note
Mutable version
- Returns:
the parameter covariance matrix
-
inline bool hasSmoothed() const
Return whether smoothed parameters+covariance is set.
- Returns:
Whether it is set
-
inline ConstCovariance jacobian() const
Returns the jacobian from the previous trackstate to this one.
Note
Const version
- Returns:
The jacobian matrix
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline Covariance jacobian() Returns the jacobian from the previous trackstate to this one.
Note
Mutable version
- Returns:
The jacobian matrix
-
inline bool hasJacobian() const
Returns whether a jacobian is set for this trackstate.
- Returns:
Whether it is set
Track state measurement properties
Properties of the measurement associated with the track state represented. This consists of a vector and an associated square matrix of a measurement dimension which is between one and the size of the track parametrization. The measurement coordinate frame is required to be a strict subset of the bound track parametrization on the local geometry coordinate frame, i.e. using a pure projector matrix to convert from the bound parametrization to the measurement frame is possible.
The track state stores the parameter vector and covariance, and the backend is given the possibility to do so in a jagged way, i.e. only storing the number of values needed. This requires calling allocateCalibrated before storing the measurements (even if it might be a no-op).
The projector matrix is packed as a bitset, which is converted to a matrix on-demand (and therefore returned by value).
A convenience function to assign this from the Measurement class is provided, although it’s use is discouraged.
The track state also includes a SourceLink which acts as a proxy to the original uncalibrated measurement that the calibrated measurement was derived from. It is set and returned by value, to allow unpacking / repacking by the backend, if needed.
-
Projector projector() const
Returns the projector (measurement mapping function) for this track state.
It is derived from the uncalibrated measurement
Note
This function returns the overallocated projector. This means it is of dimension MxM, where M is the maximum number of measurement dimensions. The NxM submatrix, where N is the actual dimension of the measurement, is located in the top left corner, everything else is zero.
- Returns:
The overallocated projector
-
inline bool hasProjector() const
Returns whether a projector is set.
- Returns:
Whether it is set
-
inline EffectiveProjector effectiveProjector() const
Returns the projector (measurement mapping function) for this track state.
It is derived from the uncalibrated measurement
Warning
This function returns the effective projector. This means it is of dimension \(N\times M\), where \(N\) is the actual dimension of the measurement.
- Returns:
The effective projector
-
template<typename Derived, bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline void setProjector(const Eigen::MatrixBase<Derived> &projector) Set the projector on this track state This will convert the projector to a more compact bitset representation and store it.
Note
projectoris assumed to only have 0s or 1s as components.- Parameters:
projector – The projector in the form of a dense matrix
-
inline ProjectorBitset projectorBitset() const
Directly get the projector bitset, a compressed form of a projection matrix.
Note
This is mainly to copy explicitly a projector from one state to another. Use the
projectororeffectiveProjectormethod if you want to access the matrix.- Returns:
The projector bitset
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline void setProjectorBitset(ProjectorBitset proj) Set the projector bitset, a compressed form of a projection matrix.
Note
This is mainly to copy explicitly a projector from one state to another. If you have a projection matrix, set it with
setProjector.- Parameters:
proj – The projector bitset
-
SourceLink getUncalibratedSourceLink() const
Uncalibrated measurement in the form of a source link.
Const version
- Returns:
The uncalibrated measurement source link
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline void setUncalibratedSourceLink(SourceLink sourceLink) Set an uncalibrated source link.
- Parameters:
sourceLink – The uncalibrated source link to set
-
inline bool hasUncalibratedSourceLink() const
Check if the point has an associated uncalibrated measurement.
- Returns:
Whether it is set
-
inline bool hasCalibrated() const
Check if the point has an associated calibrated measurement.
- Returns:
Whether it is set
-
template<std::size_t measdim>
inline ConstMeasurement<measdim> calibrated() const Full calibrated measurement vector.
Might contain additional zeroed dimensions.
Note
Const version
- Returns:
The measurement vector
-
template<std::size_t measdim, bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline Measurement<measdim> calibrated() Full calibrated measurement vector.
Might contain additional zeroed dimensions.
Note
Mutable version
- Returns:
The measurement vector
-
template<std::size_t measdim>
inline ConstMeasurementCovariance<measdim> calibratedCovariance() const Const full calibrated measurement covariance matrix.
The effective covariance is located in the top left corner, everything else is zeroed.
- Returns:
The measurement covariance matrix
-
template<std::size_t measdim, bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline MeasurementCovariance<measdim> calibratedCovariance() Mutable full calibrated measurement covariance matrix.
The effective covariance is located in the top left corner, everything else is zeroed.
- Returns:
The measurement covariance matrix
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline auto effectiveCalibrated() Mutable dynamic measurement vector with only the valid dimensions.
Warning
The dynamic vector has a runtime overhead!
- Returns:
The effective calibrated measurement vector
-
inline auto effectiveCalibrated() const
Const dynamic measurement vector with only the valid dimensions.
Warning
The dynamic matrix has a runtime overhead!
- Returns:
The effective calibrated measurement vector
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline auto effectiveCalibratedCovariance() Mutable dynamic measurement covariance matrix with only the valid dimensions.
Warning
The dynamic matrix has a runtime overhead!
- Returns:
The effective calibrated covariance matrix
-
inline auto effectiveCalibratedCovariance() const
Const dynamic measurement covariance matrix with only the valid dimensions.
Warning
The dynamic matrix has a runtime overhead!
- Returns:
The effective calibrated covariance matrix
-
inline IndexType calibratedSize() const
Return the (dynamic) number of dimensions stored for this measurement.
Note
Depending on the backend, this size is used to determine the memory range of the measurement vector and covariance.
- Returns:
The number of dimensions
-
template<std::size_t kMeasurementSize, bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline void setCalibrated(const Acts::Measurement<BoundIndices, kMeasurementSize> &meas) Set the calibrated measurement of this track state from a measurement object.
This is a convenience function to set the calibrated measurement from the
Acts::Measurementobject. In general, you should implement this functionality specifically for an (experiment-specific) uncalibrated measurement EDM.Note
This does not set the reference surface.
Warning
This assumes this TrackState stores it’s own calibrated measurement. If storage is shared with another TrackState, both will be overwritten!. Also assumes none of the calibrated components is invalid (i.e. unset) for this TrackState.
- Template Parameters:
kMeasurementSize – Size of the calibrated measurement
- Parameters:
meas – The measurement object to set
-
inline void allocateCalibrated(std::size_t measdim)
Allocate storage to be able to store a measurement of size
measdim.This must be called before setting the measurement content.
Sharing and copying
Methods to share and copy track state components. Sharing means setting up more than one track state to point to the same component.
Shareable components are
predicted parameters and covariance
filtered parameters and covariance
smoothed parameters and covariance
jacobian
See TrackStatePropMask.
Share a shareable component within this track state.
- Parameters:
shareSource – Which component to share from
shareTarget – Which component to share as. This should be different from as
shareSource, e.g. predicted can be shared as filtered.
Share a shareable component from another track state.
Note
The track states both need to be stored in the same
MultiTrajectoryinstance- Parameters:
other – Track state proxy to share component from
component – Which component to share.
Share a shareable component from another track state.
Note
Shareable components are predicted, filtered, smoothed, calibrated, jacobian, or projector. See
TrackStatePropMask.- Parameters:
other – Track state proxy to share component(s) from
shareSource – Which component to share from
shareTarget – Which component to share as. This can be be different from as
shareSource, e.g. predicted can be shared as filtered.
-
template<ACTS_CONCEPT track_state_proxy_t(TrackStateProxyConcept), bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline void copyFrom(const track_state_proxy_t &other, TrackStatePropMask mask = TrackStatePropMask::All, bool onlyAllocated = true) Copy the contents of another track state proxy into this one.
Note
If the this track state proxy does not have compatible allocations with the source track state proxy, and
onlyAllocatedis false, an exception is thrown.Note
The mask parameter will not cause a copy of components that are not allocated in the source track state proxy.
- Parameters:
other – The other track state to copy from
mask – An optional mask to determine what to copy from
onlyAllocated – Whether to only copy allocated components
Track state proxy Generic component access
-
template<HashedString key>
inline constexpr bool has() const Check if a component is set.
- Template Parameters:
key – Hashed string key to check for
- Returns:
true if the component exists, false if not
-
inline constexpr bool has(HashedString key) const
Check if a component is set.
- Parameters:
key – Hashed string key to check for
- Returns:
true if the component exists, false if not
-
inline constexpr bool has(std::string_view key) const
Check if a component is set.
Note
This might hash the
keyat runtime instead of compile-time- Parameters:
key – String key to check for
- Returns:
true if the component exists, false if not
-
template<typename T, HashedString key, bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline constexpr T &component() Retrieve a mutable reference to a component.
- Template Parameters:
T – The type of the component to access
key – String key for the component to access
- Returns:
Mutable reference to the component given by
key
-
template<typename T, bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline constexpr T &component(HashedString key) Retrieve a mutable reference to a component.
- Template Parameters:
T – The type of the component to access
- Parameters:
key – String key for the component to access
- Returns:
Mutable reference to the component given by
key
-
template<typename T, bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline constexpr T &component(std::string_view key) Retrieve a mutable reference to a component.
Note
This might hash the
keyat runtime instead of compile-time- Template Parameters:
T – The type of the component to access
- Parameters:
key – String key for the component to access
- Returns:
Mutable reference to the component given by
key
-
template<typename T, HashedString key>
inline constexpr const T &component() const Retrieve a const reference to a component.
- Template Parameters:
T – The type of the component to access
key – String key for the component to access
- Returns:
Const reference to the component given by
key
-
template<typename T>
inline constexpr const T &component(HashedString key) const Retrieve a const reference to a component.
- Template Parameters:
T – The type of the component to access
- Parameters:
key – String key for the component to access
- Returns:
Const reference to the component given by
key
-
template<typename T>
inline constexpr const T &component(std::string_view key) const Retrieve a const reference to a component.
Note
This might hash the
keyat runtime instead of compile-time- Template Parameters:
T – The type of the component to access
- Parameters:
key – String key for the component to access
- Returns:
Const reference to the component given by
key
Public Types
-
using ConstCovariance = typename TrackStateTraits<M, true>::Covariance
Same as Covariance, but with const semantics.
-
template<std::size_t N>
using ConstMeasurement = typename TrackStateTraits<N, true>::Measurement Same as
Measurement, but with const semantics.
-
template<std::size_t N>
using ConstMeasurementCovariance = typename TrackStateTraits<N, true>::MeasurementCovariance Same as MeasurementCovariance, but with const semantics.
-
using ConstParameters = typename TrackStateTraits<M, true>::Parameters
Same as Parameters, but with const semantics.
-
using ConstProxyType = TrackStateProxy<trajectory_t, M, true>
Alias for an associated const track state proxy, with the same backends.
-
using Covariance = typename TrackStateTraits<M, ReadOnly>::Covariance
Map-type for a bound covariance.
This has reference semantics, i.e. points at a matrix by an internal pointer.
-
using EffectiveProjector = Eigen::Matrix<typename Projector::Scalar, Eigen::Dynamic, Eigen::Dynamic, TrackStateTraits<M, ReadOnly>::ProjectorFlags, M, eBoundSize>
Dynamic variant of the projector matrix.
Warning
Using this type is discouraged, as it has a runtime overhead
-
using IndexType = TrackIndexType
The index type of the track state container.
-
template<std::size_t N>
using Measurement = typename TrackStateTraits<N, ReadOnly>::Measurement Map-type for a measurement vector, where the local measurement dimension is variable.
-
template<std::size_t N>
using MeasurementCovariance = typename TrackStateTraits<N, ReadOnly>::MeasurementCovariance Map-type for a measurement covariance matrix, where the local measurement dimension is variable.
-
using Parameters = typename TrackStateTraits<M, ReadOnly>::Parameters
Map-type for a bound parameter vector.
This has reference semantics, i.e. points at a matrix by an internal pointer.
-
using Projector = typename TrackStateTraits<M, ReadOnly>::Projector
Matrix representing the projector (measurement mapping function) for a measurement.
This is not a map type, but an actual matrix. This matrix is always \(M \times M\), even if the local measurement dimension is lower. The actual \(N\times M\) projector is given by the top \(N\) rows.
-
using Trajectory = trajectory_t
The track state container backend given as a template parameter.
Public Functions
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline auto &container() Get a mutable reference to the track state container backend.
- Returns:
a mutable reference to the backend
-
inline const auto &container() const
Get a const reference to the track state container backend.
- Returns:
a const reference to the backend
-
template<bool RO = ReadOnly, typename = std::enable_if_t<!RO>>
inline MultiTrajectory<Trajectory> &trajectory() Return a mutable reference to the underlying backend container.
- Returns:
A reference to the backend container
-
inline const MultiTrajectory<Trajectory> &trajectory() const
Return a const reference to the underlying backend container.
- Returns:
A const reference to the backend container
Public Static Attributes
Friends
- friend class Acts::MultiTrajectory< Trajectory >
-
class TrackingGeometry
The TrackingGeometry class is the owner of the constructed TrackingVolumes.
It enables both, a global search for an asociatedVolume (respectively, if existing, a global search of an associated Layer or the next associated Layer), such as a continuous navigation by BoundarySurfaces between the confined TrackingVolumes.
Public Functions
-
TrackingGeometry(const MutableTrackingVolumePtr &highestVolume, const IMaterialDecorator *materialDecorator = nullptr, const GeometryIdentifierHook &hook = {}, const Logger &logger = getDummyLogger())
Constructor.
- Parameters:
highestVolume – is the world volume
materialDecorator – is a dediated decorator that can assign surface or volume based material to the TrackingVolume
hook – Identifier hook to be applied to surfaces
logger – instance of a logger (defaulting to the “silent” one)
-
~TrackingGeometry()
Destructor.
-
const Layer *associatedLayer(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &gp) const
Forward the associated Layer information.
- Parameters:
gctx – is the context for this request (e.g. alignment)
gp – is the global position of the call
- Returns:
plain pointer to assocaiated layer
-
const Surface *findSurface(GeometryIdentifier id) const
Search for a surface with the given identifier.
- Parameters:
id – is the geometry identifier of the surface
- Return values:
nullptr – if no such surface exists
pointer – to the found surface otherwise.
-
const TrackingVolume *findVolume(GeometryIdentifier id) const
Search for a volume with the given identifier.
- Parameters:
id – is the geometry identifier of the volume
- Return values:
nullptr – if no such volume exists
pointer – to the found volume otherwise.
-
const Surface *getBeamline() const
surface representing the beam pipe
Note
The ownership is not passed, e.g. do not delete the pointer
- Returns:
raw pointer to surface representing the beam pipe (could be a null pointer)
-
const TrackingVolume *highestTrackingVolume() const
Access to the world volume.
- Returns:
plain pointer to the world volume
Access to the world volume.
- Returns:
shared pointer to the world volume
-
const TrackingVolume *lowestTrackingVolume(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &gp) const
return the lowest tracking Volume
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
gp – is the global position of the call
- Returns:
plain pointer to the lowest TrackingVolume
Register the beam tube.
- Parameters:
beam – is the beam line surface
-
template<ACTS_CONCEPT visitor_t(SurfaceVisitor)>
inline void visitSurfaces(visitor_t &&visitor) const Visit all sensitive surfaces.
Note
If a context is needed for the visit, the vistitor has to provide this, e.g. as a private member
- Template Parameters:
visitor_t – Type of the callable visitor
- Parameters:
visitor – The callable. Will be called for each sensitive surface that is found, a selection of the surfaces can be done in the visitor
-
template<ACTS_CONCEPT visitor_t(SurfaceVisitor)>
inline void visitSurfaces(visitor_t &&visitor, bool restrictToSensitives) const Visit all reachable surfaces.
Note
If a context is needed for the visit, the vistitor has to provide this, e.g. as a private member
- Template Parameters:
visitor_t – Type of the callable visitor
- Parameters:
visitor – The callable. Will be called for each reachable surface that is found, a selection of the surfaces can be done in the visitor
restrictToSensitives – If true, only sensitive surfaces are visited
-
template<ACTS_CONCEPT visitor_t(TrackingVolumeVisitor)>
inline void visitVolumes(visitor_t &&visitor) const Visit all reachable tracking volumes.
Note
If a context is needed for the visit, the vistitor has to provide this, e.g. as a private member
- Template Parameters:
visitor_t – Type of the callable visitor
- Parameters:
visitor – The callable. Will be called for each reachable volume that is found, a selection of the volumes can be done in the visitor
-
TrackingGeometry(const MutableTrackingVolumePtr &highestVolume, const IMaterialDecorator *materialDecorator = nullptr, const GeometryIdentifierHook &hook = {}, const Logger &logger = getDummyLogger())
-
class TrackingVolume : public Acts::Volume
Full Volume description used in Tracking, it inherits from Volume to get the geometrical structure.
information / internal navigation with in 5 different ways:A TrackingVolume at navigation level can provide the (layer) material
The TrackingVolume can also be a simple container of other TrackingVolumes--- a) Static confinement of Layers --- b) detached sub volumes --- b) unordered (arbitrarily oriented) layers --- d) unordered sub volumes --- e) unordered layers AND unordered subvolumes
In addition it is capable of holding a subarray of Layers and TrackingVolumes.
Unnamed Group
-
const Layer *associatedLayer(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position) const
Interface of
TrackingVolumein the Gen1 geometry model.Note
This interface is being replaced, and is subject to removal Return the associated Layer to the global position
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – is the associated global position
- Returns:
plain pointer to layer object
Resolves the volume into (compatible) Layers.
This is the method for the propagator/extrapolator
- Template Parameters:
options_t – Type of navigation options object for decomposition
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – Position for the search
direction – Direction for the search
options – The templated navigation options
- Returns:
vector of compatible intersections with layers
Returns all boundary surfaces sorted by the user.
- Template Parameters:
options_t – Type of navigation options object for decomposition
sorter_t – Type of the boundary surface sorter
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – The position for searching
direction – The direction for searching
options – The templated navigation options
logger – A
Loggerinstance
- Returns:
is the templated boundary intersection
-
const LayerArray *confinedLayers() const
Return the confined static layer array - if it exists.
- Returns:
the BinnedArray of static layers if exists
-
std::shared_ptr<const TrackingVolumeArray> confinedVolumes() const
Return the confined volumes of this container array - if it exists.
-
const MutableTrackingVolumeVector denseVolumes() const
Return the confined dense volumes.
-
const TrackingVolumeBoundaries &boundarySurfaces() const
Method to return the BoundarySurfaces.
Set the boundary surface material description.
The material is usually derived in a complicated way and loaded from a framework given source. As various volumes could potentially share the the same material description, it is provided as a shared object
- Parameters:
surfaceMaterial – Material description of this volume
bsFace – Specifies which boundary surface to assign the material to
-
void glueTrackingVolume(const GeometryContext &gctx, BoundarySurfaceFace bsfMine, TrackingVolume *neighbor, BoundarySurfaceFace bsfNeighbor)
Glue another tracking volume to this one.
if common face is set the glued volumes are sharing the boundary, down to the last navigation volume
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
bsfMine – is the boundary face indicater where to glue
neighbor – is the TrackingVolume to be glued
bsfNeighbor – is the boundary surface of the neighbor
Glue another tracking volume to this one.
if common face is set the glued volumes are sharing the boundary, down to the last navigation volume
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
bsfMine – is the boundary face indicater where to glue
neighbors – are the TrackingVolumes to be glued
bsfNeighbor – are the boundary surface of the neighbors
Provide a new BoundarySurface from the glueing.
- Parameters:
bsf – is the boundary face indicater where to glue
bs – is the new boundary surface
checkmaterial – is a flag how to deal with material, if true:
if the old boundary surface had a material description but the new one has not, keep the current one
in all other cases just assign the new boundary surface
-
void registerGlueVolumeDescriptor(GlueVolumesDescriptor *gvd)
Register the outside glue volumes - ordering is in the TrackingVolume Frame:
negativeFaceXY
(faces YZ, ZY, radial faces)
positiveFaceXY
- Parameters:
gvd – register a new GlueVolumeDescriptor
-
GlueVolumesDescriptor &glueVolumesDescriptor()
Register the outside glue volumes - ordering is in the TrackingVolume Frame:
negativeFaceXY
(faces YZ, ZY, radial faces)
positiveFaceXY
Public Types
-
using MutableVolumeRange = detail::TransformRange<detail::Dereference, std::vector<std::unique_ptr<TrackingVolume>>>
-
using VolumeRange = detail::TransformRange<detail::ConstDereference, const std::vector<std::unique_ptr<TrackingVolume>>>
Public Functions
-
TrackingVolume() = delete
-
TrackingVolume(const TrackingVolume&) = delete
Constructor for a container Volume.
vacuum filled volume either as a for other tracking volumes
- Parameters:
transform – is the global 3D transform to position the volume in space
volbounds – is the description of the volume boundaries
containedVolumeArray – are the static volumes that fill this volume
volumeName – is a string identifier
Constructor for a full equipped Tracking Volume.
- Parameters:
transform – is the global 3D transform to position the volume in space
volumeBounds – is the description of the volume boundaries
volumeMaterial – is are materials of the tracking volume
staticLayerArray – is the confined layer array (optional)
containedVolumeArray – are the sub volumes if the volume is a container
denseVolumeVector – The contained dense volumes
volumeName – is a string identifier
-
TrackingVolume(const Volume &volume, const std::string &volumeName = "undefined")
Constructor from a regular volume.
- Parameters:
volume – is the volume to be converted
volumeName – is a string identifier
-
~TrackingVolume() override
-
TrackingVolume &addVolume(std::unique_ptr<TrackingVolume> volume)
Add a child volume to this tracking volume.
Note
The
volumewill have its mother volume assigned tothis. It will throw ifvolumealready has a mother volume set- Parameters:
volume – The volume to add
- Returns:
Reference to the added volume
Set the volume material description.
The material is usually derived in a complicated way and loaded from a framework given source. As various volumes could potentially share the the same material description, it is provided as a shared object
- Parameters:
material – Material description of this volume
-
const TrackingVolume *lowestTrackingVolume(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position, const double tol = 0.) const
Return the associated sub Volume, returns THIS if no subVolume exists.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
position – is the global position associated with that search
tol – Search position tolerance for dense volumes
- Returns:
plain pointer to associated with the position
-
TrackingVolume *motherVolume()
Return the MotherVolume - if it exists.
-
const TrackingVolume *motherVolume() const
Return the MotherVolume - if it exists.
-
TrackingVolume &operator=(const TrackingVolume&) = delete
-
void setMotherVolume(TrackingVolume *mvol)
Set the MotherVolume.
- Parameters:
mvol – is the mother volume
-
template<ACTS_CONCEPT visitor_t(SurfaceVisitor)>
inline void visitSurfaces(visitor_t &&visitor) const Visit all sensitive surfaces.
Note
If a context is needed for the visit, the vistitor has to provide this, e.g. as a private member
- Template Parameters:
visitor_t – Type of the callable visitor
- Parameters:
visitor – The callable. Will be called for each sensitive surface that is found, a selection of the surfaces can be done in the visitor
-
template<ACTS_CONCEPT visitor_t(SurfaceVisitor)>
inline void visitSurfaces(visitor_t &&visitor, bool restrictToSensitives) const Visit all reachable surfaces.
Note
If a context is needed for the visit, the vistitor has to provide this, e.g. as a private member
- Template Parameters:
visitor_t – Type of the callable visitor
- Parameters:
visitor – The callable. Will be called for each reachable surface that is found, a selection of the surfaces can be done in the visitor
restrictToSensitives – If true, only sensitive surfaces are visited
-
template<ACTS_CONCEPT visitor_t(TrackingVolumeVisitor)>
inline void visitVolumes(visitor_t &&visitor) const Visit all reachable tracking volumes.
Note
If a context is needed for the visit, the vistitor has to provide this, e.g. as a private member
- Template Parameters:
visitor_t – Type of the callable visitor
- Parameters:
visitor – The callable. Will be called for each reachable volume that is found, a selection of the volumes can be done in the visitor
-
const IVolumeMaterial *volumeMaterial() const
Return the material of the volume.
Return the material of the volume as shared pointer.
-
const std::string &volumeName() const
Returns the VolumeName - for debug reason, might be depreciated later.
-
MutableVolumeRange volumes()
Return mutable view of the registered volumes under this tracking volume.
- Returns:
the range of volumes
-
VolumeRange volumes() const
Return all volumes registered under this tracking volume.
- Returns:
the range of volumes
-
const Layer *associatedLayer(const GeometryContext &gctx, const Vector3 &position) const
-
class TrapezoidBounds : public Acts::PlanarBounds
Bounds for a trapezoidal, planar Surface.
Public Types
Public Functions
-
TrapezoidBounds() = delete
-
TrapezoidBounds(const std::array<double, eSize> &values) noexcept(false)
Constructor for symmetric Trapezoid - from fixed size array.
- Parameters:
values – the values to be stream in
-
TrapezoidBounds(double halfXnegY, double halfXposY, double halfY, double rotAngle = 0.) noexcept(false)
Constructor for symmetric Trapezoid.
- Parameters:
halfXnegY – minimal half length X, definition at negative Y
halfXposY – maximal half length X, definition at positive Y
halfY – half length Y - defined at x=0
rotAngle – rotation angle of the bounds w.r.t coordinate axes
-
~TrapezoidBounds() override
-
virtual const RectangleBounds &boundingBox() const final
Bounding box parameters.
- Returns:
rectangle bounds for a bounding box
-
inline double get(BoundValues bValue) const
Access to the bound values.
- Parameters:
bValue – the class nested enum for the array access
-
virtual bool inside(const Vector2 &lposition, const BoundaryCheck &bcheck) const final
The orientation of the Trapezoid is according to the figure above, in words: the shorter of the two parallel sides of the trapezoid intersects with the negative \( y \) - axis of the local frame.
The cases are:
(0)
\( y \) or \( x \)bounds are 0 || 0
(1) the local position is outside
\( y \)bounds
(2) the local position is inside
\( y \) bounds, but outside maximum \( x \)bounds
(3) the local position is inside
\( y \) bounds AND inside minimum \( x \)bounds
(4) the local position is inside
\( y \) bounds AND inside maximum \( x \) bounds, so that it depends on the \( eta \) coordinate (5) the local position fails test of (4)The inside check is done using single equations of straight lines and one has to take care if a point lies on the positive \( x \) half area(I) or the negative one(II). Denoting \( |x_{min}| \) and \( | x_{max} | \) as
minHalfXrespectivelymaxHalfX, such as \( | y_{H} | \) ashalfY, the equations for the straing lines in (I) and (II) can be written as:(I): \( y = \kappa_{I} x + \delta_{I} \)
(II): \( y = \kappa_{II} x + \delta_{II} \)
,
where
\( \kappa_{I} = - \kappa_{II} = 2 \frac{y_{H}}{x_{max} - x_{min}} \) and \( \delta_{I} = \delta_{II} = - \frac{1}{2}\kappa_{I}(x_{max} + x_{min}) \)
- Parameters:
lposition – Local position (assumed to be in right surface frame)
bcheck – boundary check directive
- Returns:
boolean indicator for the success of this operation
-
virtual std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &sl) const final
Output Method for std::ostream.
- Parameters:
sl – is the ostream to be dumped into
-
virtual BoundsType type() const final
Return the bounds type - for persistency optimization.
- Returns:
is a BoundsType enum
-
virtual std::vector<double> values() const final
Access method for bound values, this is a dynamically sized vector containing the parameters needed to describe these bounds.
- Returns:
of the stored values for this SurfaceBounds object
-
TrapezoidBounds() = delete
-
class TrapezoidVolumeBounds : public Acts::VolumeBounds
Bounds for a trapezoidal shaped Volume, the orientedSurface(…) method creates a vector of 6 surfaces:
BoundarySurfaceFace [index]:
negativeFaceXY [0] : Trazpezoidal Acts::PlaneSurface, parallel to \( xy \) plane at negative \(z\)
positiveFaceXY [1] : Trazpezoidal Acts::PlaneSurface, parallel to \( xy \) plane at positive \(z\)
trapezoidFaceAlpha [2] : Rectangular Acts::PlaneSurface, attached to [0] and [1] at negative \(x\) (associated to alpha)
trapezoidFaceBeta [3] : Rectangular Acts::PlaneSurface, attached to [0] and [1] at positive \( x\) (associated to beta)
negativeFaceZX [4] : Rectangular Acts::PlaneSurface, parallel to \( zx \) plane at negative \(y\)
positiveFaceZX [5] : Rectangular Acts::PlaneSurface, parallel to \( zx \) plane at positive \(y\)
Public Types
-
enum BoundValues
for access / streaming
Values:
-
enumerator eHalfLengthXnegY
halflength in x at negative y
-
enumerator eHalfLengthXposY
halflength in x at positive y
-
enumerator eHalfLengthY
halflength in y
-
enumerator eHalfLengthZ
halflength in z
-
enumerator eAlpha
opening angle alpha (in point A)
-
enumerator eBeta
opening angle beta (in point B)
-
enumerator eSize
length of the bounds vector
-
enumerator eHalfLengthXnegY
Public Functions
-
TrapezoidVolumeBounds() = delete
-
TrapezoidVolumeBounds(ActsScalar minhalex, ActsScalar haley, ActsScalar halez, ActsScalar alpha, ActsScalar beta) noexcept(false)
Constructor - the trapezoid boundaries (arbitrary trapezoid)
- Parameters:
minhalex – is the half length in x at minimal y
haley – is the half length in y
halez – is the half length in z
alpha – is the opening angle at -x,-y
beta – is the opening angle at +x,-y
-
TrapezoidVolumeBounds(ActsScalar minhalex, ActsScalar maxhalex, ActsScalar haley, ActsScalar halez) noexcept(false)
Constructor - the trapezoid boundaries (symmetric trapezoid)
- Parameters:
minhalex – is the half length in x at minimal y
maxhalex – is the half length in x at maximal y
haley – is the half length in y
halez – is the half length in z
-
inline TrapezoidVolumeBounds(const std::array<ActsScalar, eSize> &values) noexcept(false)
Constructor - from a fixed size array.
- Parameters:
values – The bound values
-
TrapezoidVolumeBounds(const TrapezoidVolumeBounds &trabo) = default
-
~TrapezoidVolumeBounds() override = default
-
virtual Volume::BoundingBox boundingBox(const Transform3 *trf = nullptr, const Vector3 &envelope = {0, 0, 0}, const Volume *entity = nullptr) const final
Construct bounding box for this shape.
- Parameters:
trf – Optional transform
envelope – Optional envelope to add / subtract from min/max
entity – Entity to associate this bounding box with
- Returns:
Constructed bounding box
-
inline ActsScalar get(BoundValues bValue) const
Access to the bound values.
- Parameters:
bValue – the class nested enum for the array access
-
virtual bool inside(const Vector3 &pos, ActsScalar tol = 0.) const override
This method checks if position in the 3D volume frame is inside the cylinder.
- Parameters:
pos – is the global position to be checked
tol – is the tolerance applied
- Returns:
boolean indicator if position is inside
-
TrapezoidVolumeBounds &operator=(const TrapezoidVolumeBounds &trabo) = default
-
virtual std::vector<OrientedSurface> orientedSurfaces(const Transform3 &transform = Transform3::Identity()) const override
Oriented surfaces, i.e.
the decomposed boundary surfaces and the according navigation direction into the volume given the normal vector on the surface
It will throw an exception if the orientation prescription is not adequate
- Parameters:
transform – is the 3D transform to be applied to the boundary surfaces to position them in 3D space
- Returns:
a vector of surfaces bounding this volume
-
virtual std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &os) const override
Output Method for std::ostream.
- Parameters:
os – is the output stream
-
inline virtual VolumeBounds::BoundsType type() const final
Return the bounds type - for persistency optimization.
- Returns:
is a BoundsType enum
-
virtual std::vector<ActsScalar> values() const final
Return the bound values as dynamically sized vector.
- Returns:
this returns a copy of the internal values
-
class VectorMultiTrajectory : public Acts::detail_vmt::VectorMultiTrajectoryBase, public Acts::MultiTrajectory<VectorMultiTrajectory>
Public Functions
-
VectorMultiTrajectory() = default
-
inline VectorMultiTrajectory(const VectorMultiTrajectory &other)
-
inline VectorMultiTrajectory(VectorMultiTrajectory &&other)
-
template<typename T>
inline void addColumn_impl(const std::string &key)
-
IndexType addTrackState_impl(TrackStatePropMask mask = TrackStatePropMask::All, IndexType iprevious = kInvalid)
-
void addTrackStateComponents_impl(IndexType istate, TrackStatePropMask mask)
-
inline void allocateCalibrated_impl(IndexType istate, std::size_t measdim)
-
void clear_impl()
-
inline std::any component_impl(HashedString key, IndexType istate)
-
inline std::any component_impl(HashedString key, IndexType istate) const
-
void copyDynamicFrom_impl(IndexType dstIdx, HashedString key, const std::any &srcPtr)
-
inline TrackStateProxy::Covariance covariance_impl(IndexType parIdx)
-
inline ConstTrackStateProxy::Covariance covariance_impl(IndexType parIdx) const
-
inline bool has_impl(HashedString key, IndexType istate) const
-
inline bool hasColumn_impl(HashedString key) const
-
inline TrackStateProxy::Covariance jacobian_impl(IndexType istate)
-
inline ConstTrackStateProxy::Covariance jacobian_impl(IndexType istate) const
-
template<std::size_t measdim>
inline TrackStateProxy::Measurement<measdim> measurement_impl(IndexType istate)
-
template<std::size_t measdim>
inline ConstTrackStateProxy::Measurement<measdim> measurement_impl(IndexType istate) const
-
template<std::size_t measdim>
inline TrackStateProxy::MeasurementCovariance<measdim> measurementCovariance_impl(IndexType istate)
-
template<std::size_t measdim>
inline ConstTrackStateProxy::MeasurementCovariance<measdim> measurementCovariance_impl(IndexType istate) const
-
inline TrackStateProxy::Parameters parameters_impl(IndexType parIdx)
-
inline ConstTrackStateProxy::Parameters parameters_impl(IndexType parIdx) const
-
void reserve(std::size_t n)
-
inline void setUncalibratedSourceLink_impl(IndexType istate, SourceLink sourceLink)
-
inline IndexType size_impl() const
-
inline Statistics statistics() const
-
void unset_impl(TrackStatePropMask target, IndexType istate)
-
VectorMultiTrajectory() = default
-
class Volume : public Acts::GeometryObject
It inherits from GeometryObject for geometry identification.
Base class for all volumes inside the tracking realm, it defines the interface for inherited Volume classes regarding the geometrical information.
Subclassed by Acts::TrackingVolume
Public Types
-
using BoundingBox = AxisAlignedBoundingBox<Volume, ActsScalar, 3>
Public Functions
-
Volume() = delete
Explicit constructor with shared arguments.
- Parameters:
transform – is the transform to position the volume in 3D space
volbounds – is the volume boundary definitions
-
Volume(const Volume &vol, const Transform3 &shift = Transform3::Identity())
Copy Constructor - with optional shift.
- Parameters:
vol – is the source volume for the copy
shift – is the optional shift applied as : shift * vol.transform()
-
virtual ~Volume() = default
Set volume bounds and update volume bounding boxes implicitly.
- Parameters:
volbounds – The volume bounds to be assigned
-
virtual Vector3 binningPosition(const GeometryContext &gctx, BinningValue bValue) const override
The binning position method.
as default the center is given, but may be overloaded
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
bValue – is the binning value schema
- Returns:
vector 3D that can be used for the binning
-
BoundingBox boundingBox(const Vector3 &envelope = {0, 0, 0}) const
Construct bounding box for this shape.
- Parameters:
envelope – Optional envelope to add / subtract from min/max
- Returns:
Constructed bounding box pointing to this volume
-
bool inside(const Vector3 &gpos, ActsScalar tol = 0.) const
Inside() method for checks.
- Parameters:
gpos – is the position to be checked
tol – is the tolerance parameter
- Returns:
boolean indicator if the position is inside
-
const Transform3 &itransform() const
Returns the inverted transform of this volume.
-
Volume &operator=(const Volume &vol)
Assignment operator.
- Parameters:
vol – is the source volume to be copied
-
BoundingBox orientedBoundingBox() const
Construct oriented bounding box for this shape.
Note
This will build an oriented bounding box with an envelope value of (0.05, 0.05, 0.05)mm
- Returns:
Constructed oriented bounding box pointing to this volume
-
void setTransform(const Transform3 &transform)
-
const Transform3 &transform() const
Return methods for geometry transform.
Set the volume bounds and optionally also update the volume transform.
- Parameters:
volbounds – The volume bounds to be assigned
transform – The transform to be assigned, can be optional
-
const VolumeBounds &volumeBounds() const
Returns const reference to the volume bounds.
-
std::shared_ptr<const VolumeBounds> volumeBoundsPtr() const
Returns shared pointer to the volume bounds.
-
using BoundingBox = AxisAlignedBoundingBox<Volume, ActsScalar, 3>
-
class VolumeBounds
Pure Absract Base Class for Volume bounds.
Acts::VolumeBounds are a set of up to six confining Surfaces that are stored in a std::vector. Each type of Acts::VolumeBounds has to implement a orientedSurfaces() and a inside() method.
The Volume, retrieving a set of Surfaces from the VolumeBounds, can turn the Surfaces into BoundarySurfaces.
Subclassed by Acts::ConeVolumeBounds, Acts::CuboidVolumeBounds, Acts::CutoutCylinderVolumeBounds, Acts::CylinderVolumeBounds, Acts::GenericCuboidVolumeBounds, Acts::TrapezoidVolumeBounds
Public Types
Public Functions
-
VolumeBounds() = default
-
virtual ~VolumeBounds() = default
-
inline virtual double binningBorder(BinningValue bValue) const
Binning borders in double.
- Parameters:
bValue – is the binning schema used
- Returns:
float offset to be used for the binning
-
inline virtual Vector3 binningOffset(BinningValue bValue) const
Binning offset - overloaded for some R-binning types.
- Parameters:
bValue – is the binning schema used
- Returns:
vector 3D to be used for the binning
-
virtual Volume::BoundingBox boundingBox(const Transform3 *trf = nullptr, const Vector3 &envelope = {0, 0, 0}, const Volume *entity = nullptr) const = 0
Construct bounding box for this shape.
- Parameters:
trf – Optional transform
envelope – Optional envelope to add / subtract from min/max
entity – Entity to associate this bounding box with
- Returns:
Constructed bounding box
-
inline virtual std::vector<Acts::BinningValue> canonicalBinning() const
Get the canonical binning values, i.e.
the binning values for that fully describe the shape’s extent
Note
This is the default implementation that returns the bounding box binning. Individual shapes should override this method
- Returns:
vector of canonical binning values
-
virtual bool inside(const Vector3 &gpos, double tol = 0.) const = 0
Checking if position given in volume frame is inside.
- Parameters:
gpos – is the global position to be checked
tol – is the tolerance applied for the inside check
- Returns:
boolean indicating if the position is inside
-
virtual std::vector<OrientedSurface> orientedSurfaces(const Transform3 &transform = Transform3::Identity()) const = 0
Oriented surfaces, i.e.
the decomposed boundary surfaces and the according navigation direction into the volume given the normal vector on the surface
It will throw an exception if the orientation prescription is not adequate
- Parameters:
transform – is the 3D transform to be applied to the boundary surfaces to position them in 3D space
- Returns:
a vector of surfaces bounding this volume
-
virtual std::ostream &toStream(std::ostream &sl) const = 0
Output Method for std::ostream, to be overloaded by child classes.
- Parameters:
sl – is the output stream to be dumped into
-
virtual BoundsType type() const = 0
Return the bounds type - for persistency optimization.
- Returns:
is a BoundsType enum
-
virtual std::vector<double> values() const = 0
Access method for bound values, this is a dynamically sized vector containing the parameters needed to describe these bounds.
- Returns:
of the stored values for this SurfaceBounds object
Public Static Attributes
-
static const std::vector<std::string> s_boundsTypeNames
Static member to get the name of the BoundsType.
-
VolumeBounds() = default
Enums
-
enum Acts::BinningType
, BinningOption & BinningAccess
BinningType:
Enumeration to qualify the binning type for the use of the LayerArrayCreator and the TrackingVolumeArrayCreator
BinningOption: open: [0,max] closed: 0 -> nextbin -> max -> 0
BinningValue necessary access to global positions
Values:
-
enumerator equidistant
-
enumerator arbitrary
-
enum Acts::BinningValue
how to take the global / local position
Values:
-
enumerator binX
-
enumerator binY
-
enumerator binZ
-
enumerator binR
-
enumerator binPhi
-
enumerator binRPhi
-
enumerator binH
-
enumerator binEta
-
enumerator binMag
-
enumerator binValues
-
enumerator binX
-
enum Acts::BoundIndices
Components of a bound track parameters vector.
To be used to access components by named indices instead of just numbers. This must be a regular
enumand not a scopedenum classto allow implicit conversion to an integer. The enum value are thus visible directly innamespace Actsand are prefixed to avoid naming collisions.Values:
-
enumerator eBoundLoc0
-
enumerator eBoundLoc1
-
enumerator eBoundPhi
-
enumerator eBoundTheta
-
enumerator eBoundQOverP
-
enumerator eBoundTime
-
enumerator eBoundSize
-
enumerator eBoundLoc0
-
enum class Acts::ComponentMergeMethod
Available reduction methods for the reduction of a Gaussian mixture.
Values:
-
enumerator eMean
-
enumerator eMaxWeight
-
enumerator eMean
-
enum Acts::FreeIndices
Components of a free track parameters vector.
To be used to access components by named indices instead of just numbers. This must be a regular
enumand not a scopedenum classto allow implicit conversion to an integer. The enum value are thus visible directly innamespace Actsand are prefixed to avoid naming collisions.Values:
-
enumerator eFreePos0
-
enumerator eFreePos1
-
enumerator eFreePos2
-
enumerator eFreeTime
-
enumerator eFreeDir0
-
enumerator eFreeDir1
-
enumerator eFreeDir2
-
enumerator eFreeQOverP
-
enumerator eFreeSize
-
enumerator eFreePos0
-
enum class Acts::TrackStatePropMask : std::uint8_t
Collection of bit masks to enable steering which components of a track state should be initialized, and which should be left invalid.
These mask values can be combined using binary operators, so (TrackStatePropMask::Predicted | TrackStatePropMask::Jacobian) will instruct allocating storage for both predicted parameters (including covariance) and a jacobian. The enum is used as a strong type wrapper around the bits to prevent autoconversion from integer
Values:
-
enumerator None
-
enumerator Predicted
-
enumerator Filtered
-
enumerator Smoothed
-
enumerator Jacobian
-
enumerator Calibrated
-
enumerator All
-
enumerator None
Functions
-
inline const Logger &Acts::CylinderVolumeBuilder::logger() const
Private access to the logger.
- Returns:
a const reference to the logger
Global method which creates the TrackingGeometry from DD4hep input.
This method returns a std::unique_ptr of the TrackingGeometry from the World DD4hep DetElement.
- Attention
The default thickness should be set thin enough that no touching or overlapping with the next layer can happen.
Note
Possible binningtypes:
arbitrary - of the sizes if the surfaces and the distance in between vary. This mode finds out the bin boundaries by scanning through the surfaces.
equidistant - if the sensitive surfaces are placed equidistantly
Note
equidistant binningtype is recommended because it is faster not only while building the geometry but also for look up during the extrapolation
Note
Layers containing surfaces per default are not allowed to be attached to each other (navigation will fail at this point). However, to allow material layers (not containing surfaces) to be attached to each other, this default thickness is needed. In this way, the layer will be thin (with space to the next layer), but the material will have the ‘real’ thickness.
- Parameters:
worldDetElement – [in] the DD4hep DetElement of the world
logger – [in] A logger instance geometry building
bTypePhi – [in] is how the sensitive surfaces (modules) should be binned in a layer in phi direction.
bTypeR – [in] is how the sensitive surfaces (modules) should be binned in a layer in r direction
bTypeZ – [in] is how the sensitive surfaces (modules) should be binned in a layer in z direction
layerEnvelopeR – [in] the tolerance added to the geometrical extension in r of the layers contained to build the volume envelope around
layerEnvelopeZ – [in] the tolerance added to the geometrical extension in z of the layers contained to build the volume envelope around
defaultLayerThickness – [in] In case no surfaces (to be contained by the layer) are handed over, the layer thickness will be set to this value
sortSubDetectors – [in]
std::functionwhich should be used in order to sort all sub detectors (=all Detelements collected by the methodcollectSubDetectors()) from bottom to top to ensure correct wrapping of the volumes, which is needed for navigation. Therefore the different hierarchies need to be sorted ascending. The default is sorting by ID.gctx – The geometry context to use
matDecorator – is the material decorator that loads material maps
geometryIdentifierHook – Hook to apply to surfaces during geometry closure.
- Throws:
std::logic_error – if an error in the translation occurs
- Pre:
Before using this method make sure, that the preconditions described in DD4hepPlugins are met.
- Returns:
std::unique_ptr to the full TrackingGeometry
The Tracking geometry needs to be built from bottom to top to ensure Navigation. Therefore the different hierarchies need to be sorted ascending. Per default the sub detectors are sorted by the id of their dd4hep::DetElement. In case another sorting needs to be applied, the users can provide their own function
-
std::unique_ptr<const Logger> Acts::getDefaultLogger(const std::string &name, const Logging::Level &lvl, std::ostream *log_stream = &std::cout)
get default debug output logger
This function returns a pointer to a Logger instance with the following decorations enabled:
time stamps
name of logging instance
debug level
- Parameters:
name – [in] name of the logger instance
lvl – [in] debug threshold level
log_stream – [in] output stream used for printing debug messages
- Returns:
pointer to logging instance
-
AtlasBetheHeitlerApprox<6, 5> Acts::makeDefaultBetheHeitlerApprox()
Creates a AtlasBetheHeitlerApprox object based on an ATLAS configuration, that are stored as static data in the source code.
This may not be an optimal configuration, but should allow to run the GSF without the need to load files
-
void Acts::reduceMixtureLargestWeights(std::vector<Acts::GsfComponent> &cmpCache, std::size_t maxCmpsAfterMerge, const Surface &surface)
Very simple mixture reduction method: Just removes the components with the smallest weight until the required number of components is reached.
- Parameters:
cmpCache – the component collection
maxCmpsAfterMerge – the number of components we want to reach
surface – the surface type on which the components are (unused here)
-
void Acts::reduceMixtureWithKLDistance(std::vector<GsfComponent> &cmpCache, std::size_t maxCmpsAfterMerge, const Surface &surface)
Greedy component reduction algorithm.
Reduces the components with the minimal symmetric KL-distance (applied only to the q/p-dimension) until the required number of components is reached.
- Parameters:
cmpCache – the component collection
maxCmpsAfterMerge – the number of components we want to reach
surface – the surface type on which the components are
Structs
-
template<typename ...aborters_t>
struct AbortList : public detail::Extendable<aborters_t...> AbortList object to be used in the propagation.
The abort list is a list of structs or classes that is called at each propagation step and can trigger the abort of the current propagation.
It can (optionally) depend on a result of an Actor from the actor list.
Public Functions
-
AbortList() = default
Default constructor.
-
AbortList(AbortList<aborters_t...> &&aborters) = default
Default move constructor.
- Parameters:
aborters – The source action list
-
AbortList(const AbortList<aborters_t...> &aborters) = default
Default copy constructor.
- Parameters:
aborters – The source action list
-
inline AbortList(const std::tuple<aborters_t...> &aborters)
Constructor from tuple.
- Parameters:
aborters – Source extensions tuple
-
inline AbortList(std::tuple<aborters_t...> &&aborters)
Constructor from tuple move.
- Parameters:
aborters – Source extensions tuple
-
template<typename ...appendices_t>
inline AbortList<aborters_t..., appendices_t...> append(appendices_t... aps) const Append new entries and return a new condition.
This is the call signature for the abort list, it broadcasts the call to the tuple() members of the list.
- Template Parameters:
propagator_state_t – is the state type of the propagator
stepper_t – Type of the stepper
navigator_t – Type of the navigator
- Parameters:
state – [inout] is the state object from the propagator
stepper – [in] Stepper used for the propagation
navigator – [in] Navigator used for the propagation
args – [in] are the arguments to be passed to the aborters
-
AbortList<aborters_t...> &operator=(AbortList<aborters_t...> &&aborters) = default
Default move assignment operator.
- Parameters:
aborters – The source action list
-
AbortList<aborters_t...> &operator=(const AbortList<aborters_t...> &aborters) = default
Default move assignment operator.
- Parameters:
aborters – The source action list
-
AbortList() = default
-
template<typename ...actors_t>
struct ActionList : public detail::Extendable<actors_t...> ActionList implementation to be used with the propagator.
This is the ActionList struct that is used in the propagator to define a list of different actors_t that are each executed during the stepping procedure
Public Functions
-
ActionList() = default
Default constructor.
-
ActionList(ActionList<actors_t...> &&actors) = default
Default move constructor.
- Parameters:
actors – The source action list
-
ActionList(const ActionList<actors_t...> &actors) = default
Default copy constructor.
- Parameters:
actors – The source action list
Call operator that is that broadcasts the call to the tuple() members of the list.
- Template Parameters:
propagator_state_t – is the state type of the propagator
stepper_t – Type of the stepper used for the propagation
navigator_t – Type of the navigator used for the propagation
- Parameters:
state – [inout] This is the propagator state object
stepper – [in] The stepper in use
navigator – [in] The navigator in use
args – [in] The arguments to be passed to the actions
-
ActionList<actors_t...> &operator=(ActionList<actors_t...> &&actors) = default
Default move assignment operator.
- Parameters:
actors – The source action list
-
ActionList<actors_t...> &operator=(const ActionList<actors_t...> &actors) = default
Default move assignment operator.
- Parameters:
actors – The source action list
-
ActionList() = default
-
template<typename traj_t>
struct CombinatorialKalmanFilterExtensions Extension struct which holds the delegates to customize the CKF behavior.
Public Types
-
using BranchStopper = Delegate<bool(const CombinatorialKalmanFilterTipState&, typename traj_t::TrackStateProxy&)>
-
using MeasurementSelector = Delegate<Result<std::pair<typename candidate_container_t::iterator, typename candidate_container_t::iterator>>(candidate_container_t &trackStates, bool&, const Logger&)>
Public Members
-
BranchStopper branchStopper = {DelegateFuncTag<voidBranchStopper>{}}
The branch stopper is called during the filtering by the Actor.
-
Calibrator calibrator = {DelegateFuncTag<detail::voidFitterCalibrator<traj_t>>{}}
The Calibrator is a dedicated calibration algorithm that allows to calibrate measurements using track information, this could be e.g.
sagging for wires, module deformations, etc.
-
MeasurementSelector measurementSelector = {DelegateFuncTag<voidMeasurementSelector>{}}
The measurement selector is called during the filtering by the Actor.
-
using BranchStopper = Delegate<bool(const CombinatorialKalmanFilterTipState&, typename traj_t::TrackStateProxy&)>
-
template<typename source_link_iterator_t, typename traj_t>
struct CombinatorialKalmanFilterOptions Combined options for the combinatorial Kalman filter.
- Template Parameters:
source_link_iterator_t – Type of the source link iterator
traj_t – Type of the trajectory
Public Types
-
using SourceLinkAccessor = SourceLinkAccessorDelegate<source_link_iterator_t>
-
using SourceLinkIterator = source_link_iterator_t
Public Functions
-
CombinatorialKalmanFilterOptions() = delete
Contexts are required and the options must not be default-constructible.
-
inline CombinatorialKalmanFilterOptions(const GeometryContext &gctx, const MagneticFieldContext &mctx, std::reference_wrapper<const CalibrationContext> cctx, SourceLinkAccessor accessor_, CombinatorialKalmanFilterExtensions<traj_t> extensions_, const PropagatorPlainOptions &pOptions, bool mScattering = true, bool eLoss = true)
PropagatorOptions with context.
- Parameters:
gctx – The geometry context for this track finding/fitting
mctx – The magnetic context for this track finding/fitting
cctx – The calibration context for this track finding/fitting
accessor_ – The source link accessor
extensions_ – The extension struct
pOptions – The plain propagator options
mScattering – Whether to include multiple scattering
eLoss – Whether to include energy loss
Public Members
-
std::reference_wrapper<const CalibrationContext> calibrationContext
context object for the calibration
-
bool energyLoss = true
Whether to consider energy loss.
-
CombinatorialKalmanFilterExtensions<traj_t> extensions
The filter extensions.
-
std::reference_wrapper<const GeometryContext> geoContext
Context object for the geometry.
-
std::reference_wrapper<const MagneticFieldContext> magFieldContext
Context object for the magnetic field.
-
bool multipleScattering = true
Whether to consider multiple scattering.
-
PropagatorPlainOptions propagatorPlainOptions
The trivial propagator options.
-
SourceLinkAccessor sourcelinkAccessor
The source link accessor.
-
struct DefaultExtension
Default evaluater of the k_i’s and elements of the transport matrix D of the RKN4 stepping.
This is a pure implementation by textbook.
Public Types
-
using Scalar = ActsScalar
Public Functions
Control function if the step evaluation would be valid.
- Template Parameters:
propagator_state_t – Type of the state of the propagator
stepper_t – Type of the stepper
navigator_t – Type of the navigator
- Returns:
Boolean flag if the step would be valid
Veto function after a RKN4 step was accepted by judging on the error of the step.
Since the textbook does not deliver further vetos, this is a dummy function.
- Template Parameters:
propagator_state_t – Type of the state of the propagator
stepper_t – Type of the stepper
navigator_t – Type of the navigator
- Parameters:
state – [in] State of the propagator
stepper – [in] Stepper of the propagation
h – [in] Step size
- Returns:
Boolean flag if the calculation is valid
Veto function after a RKN4 step was accepted by judging on the error of the step.
Since the textbook does not deliver further vetos, this is just for the evaluation of the transport matrix.
- Template Parameters:
propagator_state_t – Type of the state of the propagator
stepper_t – Type of the stepper
navigator_t – Type of the navigator
- Parameters:
state – [in] State of the propagator
stepper – [in] Stepper of the propagation
h – [in] Step size
D – [out] Transport matrix
- Returns:
Boolean flag if the calculation is valid
Evaluater of the k_i’s of the RKN4.
For the case of i = 0 this step sets up qop, too.
- Template Parameters:
propagator_state_t – Type of the state of the propagator
stepper_t – Type of the stepper
navigator_t – Type of the navigator
- Parameters:
state – [in] State of the propagator
stepper – [in] Stepper of the propagation
knew – [out] Next k_i that is evaluated
bField – [in] B-Field at the evaluation position
kQoP – [out] k_i elements of the momenta
i – [in] Index of the k_i, i = [0, 3]
h – [in] Step size (= 0. ^ 0.5 * StepSize ^ StepSize)
kprev – [in] Evaluated k_{i - 1}
- Returns:
Boolean flag if the calculation is valid
-
using Scalar = ActsScalar
-
struct DenseEnvironmentExtension
Evaluater of the k_i’s and elements of the transport matrix D of the RKN4 stepping.
This implementation involves energy loss due to ioninisation, bremsstrahlung, pair production and photonuclear interaction in the propagation and the jacobian. These effects will only occur if the propagation is in a TrackingVolume with attached material.
Public Types
-
using Scalar = ActsScalar
Public Functions
Control function if the step evaluation would be valid.
- Template Parameters:
propagator_state_t – Type of the state of the propagator
stepper_t – Type of the stepper
navigator_t – Type of the navigator
- Parameters:
state – [in] State of the propagator
stepper – [in] Stepper of the propagator
navigator – [in] Navigator of the propagator
- Returns:
Boolean flag if the step would be valid
After a RKN4 step was accepted by the stepper this method has an additional veto on the quality of the step.
The veto lies in evaluation of the energy loss and the therewith constrained to keep the momentum after the step in reasonable values.
- Template Parameters:
propagator_state_t – Type of the state of the propagator
stepper_t – Type of the stepper
navigator_t – Type of the navigator
- Parameters:
state – [in] State of the propagator
stepper – [in] Stepper of the propagator
h – [in] Step size
- Returns:
Boolean flag if the calculation is valid
After a RKN4 step was accepted by the stepper this method has an additional veto on the quality of the step.
The veto lies in the evaluation of the energy loss, the therewith constrained to keep the momentum after the step in reasonable values and the evaluation of the transport matrix.
- Template Parameters:
propagator_state_t – Type of the state of the propagator
stepper_t – Type of the stepper
navigator_t – Type of the navigator
- Parameters:
state – [in] State of the propagator
stepper – [in] Stepper of the propagator
navigator – [in] Navigator of the propagator
h – [in] Step size
D – [out] Transport matrix
- Returns:
Boolean flag if the calculation is valid
Evaluater of the k_i’s of the RKN4.
For the case of i = 0 this step sets up member parameters, too.
- Template Parameters:
stepper_state_t – Type of the state of the propagator
stepper_t – Type of the stepper
navigator_t – Type of the navigator
- Parameters:
state – [in] State of the propagator
stepper – [in] Stepper of the propagator
navigator – [in] Navigator of the propagator
knew – [out] Next k_i that is evaluated
kQoP – [out] k_i elements of the momenta
bField – [in] B-Field at the evaluation position
i – [in] Index of the k_i, i = [0, 3]
h – [in] Step size (= 0. ^ 0.5 * StepSize ^ StepSize)
kprev – [in] Evaluated k_{i - 1}
- Returns:
Boolean flag if the calculation is valid
Public Members
-
using Scalar = ActsScalar
-
template<typename action_list_t = ActionList<>, typename aborter_list_t = AbortList<>>
struct DenseStepperPropagatorOptions : public Acts::PropagatorOptions<ActionList<>, AbortList<>> Public Functions
-
DenseStepperPropagatorOptions(const DenseStepperPropagatorOptions<action_list_t, aborter_list_t> &dspo) = default
Copy Constructor.
-
inline DenseStepperPropagatorOptions(const GeometryContext &gctx, const MagneticFieldContext &mctx)
Constructor with GeometryContext.
- Parameters:
gctx – The current geometry context object, e.g. alignment
mctx – The current magnetic fielc context object
-
template<typename extended_aborter_list_t>
inline DenseStepperPropagatorOptions<action_list_t, extended_aborter_list_t> extend(extended_aborter_list_t aborters) const Expand the Options with extended aborters.
- Template Parameters:
extended_aborter_list_t – Type of the new aborter list
- Parameters:
aborters – The new aborter list to be used (internally)
-
DenseStepperPropagatorOptions(const DenseStepperPropagatorOptions<action_list_t, aborter_list_t> &dspo) = default
-
struct Initializer
Nested Actor struct, called Initializer.
This is needed for the initialization of the surface sequence.
Public Types
-
using result_type = this_result
Public Functions
-
Initializer() = default
Defaulting the constructor.
-
template<typename propagator_state_t, typename stepper_t, typename navigator_t>
inline void operator()(propagator_state_t &state, const stepper_t&, const navigator_t&, result_type &r, const Logger&) const Actor operator call.
- Template Parameters:
statet – Type of the full propagator state
stepper_t – Type of the stepper
navigator_t – Type of the navigator
- Parameters:
state – the entire propagator state
r – the result of this Actor
Public Members
-
SurfaceSequence navSurfaces = {}
The Surface sequence.
-
struct this_result
Actor result / state.
Public Members
-
bool initialized = false
-
bool initialized = false
-
using result_type = this_result
-
struct State
Nested State struct.
It acts as an internal state which is created for every propagation/extrapolation step and keep thread-local navigation information
Public Members
-
const Surface *currentSurface = nullptr
Navigation state - external interface: the current surface.
-
const TrackingVolume *currentVolume = nullptr
Navigation state: the current volume.
-
bool navigationBreak = false
Navigation state - external interface: a break has been detected.
-
SurfaceIter navSurfaceIter = navSurfaces.begin()
Iterator the next surface.
-
SurfaceSequence navSurfaces = {}
Externally provided surfaces - expected to be ordered along the path.
-
const Layer *startLayer = nullptr
Navigation state - starting layer.
-
const Surface *startSurface = nullptr
Navigation state - external interface: the start surface.
-
const TrackingVolume *startVolume = nullptr
Navigation state: the start volume.
-
const Layer *targetLayer = nullptr
Navigation state - target layer.
-
bool targetReached = false
Navigation state - external interface: target is reached.
-
const Surface *targetSurface = nullptr
Navigation state - external interface: the target surface.
-
const TrackingVolume *targetVolume = nullptr
Navigation state: the target volume.
-
const Surface *currentSurface = nullptr
Nested State struct.
It acts as an internal state which is created for every propagation/extrapolation step and keep thread-local navigation information
Public Members
Navigation state - external state: the current surface.
Navigation state : a break has been detected.
Navigation state - external state: the start surface.
Indicator if the target is reached.
Navigation state - external state: the target surface.
A navigation state struct that is holding the current navigation information.
It relies on Surfaces and Portals, all navigation entities have to be described in these terms.
Subclassed by Acts::Experimental::DetectorNavigator::State
Public Types
Surface candidate vector alias, this allows to use e.g.
boost_small vector or other stl like containers
Public Functions
Public Members
The current absolute charge.
The current absolute momentum.
Auxiliary attached information.
The current detector in processing.
The current portal, i.e the position is on portal.
The current surface, i.e the position is on surface.
The current volume in processing, i.e. the position is inside.
The current direction.
The current magnetic field.
An overstep tolerance.
The current position.
Boundary directives for surfaces.
That are the candidate surfaces to process.
A surface candidate and its intersection.
A candidates can either be a surface or a portal (which contain a surface)
Public Members
The boundary check used for the candidate, boundary checks can differ for sensitive surfaces and portals.
A candidate intersection, in Surface view.
Or a portal.
A candidate is either a detector Surface.
-
template<typename propagator_t, typename bethe_heitler_approx_t, typename traj_t>
struct GaussianSumFitter Gaussian Sum Fitter implementation.
Note
This GSF implementation tries to be as compatible to the KalmanFitter as possible. However, strict compatibility is not garantueed.
Note
Currently there is no possibility to export the states of the individual components from the GSF, the only information returned in the MultiTrajectory are the means of the states. Therefore, also NO dedicated component smoothing is performed as described e.g. by R. Fruewirth.
- Template Parameters:
propagator_t – The propagator type on which the algorithm is built on
bethe_heitler_approx_t – The type of the Bethe-Heitler-Approximation
traj_t – The MultiTrajectory type (backend)
Public Types
-
using GsfActor = detail::GsfActor<bethe_heitler_approx_t, traj_t>
The actor type.
The navigator type.
Public Functions
-
inline GaussianSumFitter(propagator_t &&propagator, bethe_heitler_approx_t &&bha, std::unique_ptr<const Logger> _logger = getDefaultLogger("GSF", Logging::INFO))
-
template<typename source_link_it_t, typename start_parameters_t, typename track_container_t, template<typename> class holder_t>
inline auto fit(source_link_it_t begin, source_link_it_t end, const start_parameters_t &sParameters, const GsfOptions<traj_t> &options, const std::vector<const Surface*> &sSequence, TrackContainer<track_container_t, traj_t, holder_t> &trackContainer) const The fit function for the Direct navigator.
-
template<typename source_link_it_t, typename start_parameters_t, typename track_container_t, template<typename> class holder_t>
inline auto fit(source_link_it_t begin, source_link_it_t end, const start_parameters_t &sParameters, const GsfOptions<traj_t> &options, TrackContainer<track_container_t, traj_t, holder_t> &trackContainer) const The fit function for the standard navigator.
-
template<typename source_link_it_t, typename start_parameters_t, typename fwd_prop_initializer_t, typename bwd_prop_initializer_t, typename track_container_t, template<typename> class holder_t>
inline Acts::Result<typename TrackContainer<track_container_t, traj_t, holder_t>::TrackProxy> fit_impl(source_link_it_t begin, source_link_it_t end, const start_parameters_t &sParameters, const GsfOptions<traj_t> &options, const fwd_prop_initializer_t &fwdPropInitializer, const bwd_prop_initializer_t &bwdPropInitializer, TrackContainer<track_container_t, traj_t, holder_t> &trackContainer) const The generic implementation of the fit function.
TODO check what this function does with the referenceSurface is e.g. the first measurementSurface
Public Members
-
bethe_heitler_approx_t m_betheHeitlerApproximation
The fitter holds the instance of the bethe heitler approx.
-
propagator_t m_propagator
The propagator instance used by the fit function.
This allows to break the propagation by setting the navigationBreak TODO refactor once we can do this more elegantly.
Public Functions
-
struct AllSelector : public Acts::IGeant4PhysicalVolumeSelector
Struct that selects all G4VPhysicalVolume objects.
Public Functions
-
inline virtual bool select(const G4VPhysicalVolume&) const final
The main interface method.
- Parameters:
g4Phys – the physical volume to be checked
- Returns:
a boolean indicating if it should be selected or not
-
inline virtual bool select(const G4VPhysicalVolume&) const final
-
struct NameSelector : public Acts::IGeant4PhysicalVolumeSelector
Struct that selects G4VPhysicalVolume objects that match one of the provided names, exact or partially.
Public Functions
-
inline NameSelector(const std::vector<std::string> &ns, bool e = false)
Constructor with arguments.
- Parameters:
ns – the provided list of names
e – whether to select them exact or not
-
inline virtual bool select(const G4VPhysicalVolume &g4PhysVol) const final
Secect function for the volume.
- Parameters:
g4PhysVol – the volume that is checked
- Returns:
a boolean indicating the selection
-
inline NameSelector(const std::vector<std::string> &ns, bool e = false)
-
struct PositionSelector : public Acts::IGeant4PhysicalVolumeSelector
Struct that selects G4VPhysicalVolume objects based on the allowed range of their position.
Note
Can be used for preselection of volumes before a KDTree search. This way the memory consumption can be reduced, compromising the execution speed
Note
Careful with axis conventions as Geant4 uses a different one than Acts
Public Functions
-
inline PositionSelector(const std::map<unsigned int, std::tuple<double, double>> &ranges)
Constructor with arguments.
- Parameters:
ranges – the provided map of axes of ranges
-
inline virtual bool select(const G4VPhysicalVolume &g4PhysVol) const final
Secect function for the volume.
- Parameters:
g4PhysVol – the volume that is checked
- Returns:
a boolean indicating the selection
Public Members
-
std::map<unsigned int, std::tuple<double, double>> m_ranges
-
inline PositionSelector(const std::map<unsigned int, std::tuple<double, double>> &ranges)
-
template<typename traj_t>
struct GsfOptions Public Functions
-
GsfOptions() = delete
Public Members
-
bool abortOnError = false
-
std::reference_wrapper<const CalibrationContext> calibrationContext
-
ComponentMergeMethod componentMergeMethod = ComponentMergeMethod::eMaxWeight
-
bool disableAllMaterialHandling = false
-
std::string_view finalMultiComponentStateColumn = ""
-
std::reference_wrapper<const GeometryContext> geoContext
-
std::reference_wrapper<const MagneticFieldContext> magFieldContext
-
std::size_t maxComponents = 4
-
PropagatorPlainOptions propagatorPlainOptions
-
double weightCutoff = 1.e-4
-
GsfOptions() = delete
-
struct MultiStepperSurfaceReached : public Acts::SurfaceReached
Public Functions
-
MultiStepperSurfaceReached() = default
-
inline MultiStepperSurfaceReached(double oLimit)
boolean operator for abort condition without using the result
- Template Parameters:
propagator_state_t – Type of the propagator state
stepper_t – Type of the stepper
navigator_t – Type of the navigator
- Parameters:
state – [inout] The propagation state object
stepper – [in] Stepper used for propagation
navigator – [in] Navigator used for the propagation
logger – a logger instance
Public Members
-
bool averageOnSurface = true
If this is set, we are also happy if the mean of the components is on the surface.
How the averaging is performed depends on the stepper implementation
-
double averageOnSurfaceTolerance = 0.2
A configurable tolerance within which distance to the intersection we consider the surface as reached.
Has no effect if averageOnSurface is false
-
MultiStepperSurfaceReached() = default
-
struct Config
Public Members
-
bool resolveMaterial = true
stop at every material surface (whether it is passive or not)
-
bool resolvePassive = false
stop at every surface regardless what it is
-
bool resolveSensitive = true
stop at every sensitive surface (whether it has material or not)
-
std::shared_ptr<const TrackingGeometry> trackingGeometry = {nullptr}
Tracking Geometry for this Navigator.
-
bool resolveMaterial = true
-
struct State
Nested State struct.
It acts as an internal state which is created for every propagation and meant to keep thread-local navigation information.
Public Functions
-
inline auto navBoundary() const
-
inline auto navLayer() const
-
inline auto navSurface() const
Public Members
-
const Surface *currentSurface = nullptr
Navigation state - external state: the current surface.
-
const TrackingVolume *currentVolume = nullptr
Navigation state: the current volume.
-
ExternalSurfaces externalSurfaces = {}
Externally provided surfaces - these are tried to be hit.
-
bool forceIntersectBoundaries = false
Force intersection with boundaries.
-
bool lastHierarchySurfaceReached = false
Indicator that the last VolumeHierarchy surface was reached skip the next layer targeting to the next boundary/volume.
-
NavigationBoundaries navBoundaries = {}
the vector of boundary surfaces to work through
-
std::size_t navBoundaryIndex = navBoundaries.size()
the current boundary index of the navigation state
-
bool navigationBreak = false
Navigation state : a break has been detected.
-
std::size_t navLayerIndex = navLayers.size()
the current layer index of the navigation state
-
NavigationLayers navLayers = {}
the vector of navigation layers to work through
-
std::size_t navSurfaceIndex = navSurfaces.size()
the current surface index of the navigation state
-
NavigationSurfaces navSurfaces = {}
the vector of navigation surfaces to work through
-
const Layer *startLayer = nullptr
Navigation state: the start layer.
-
bool startLayerResolved = false
Indicator for start layer treatment.
-
const Surface *startSurface = nullptr
Navigation state: the start surface.
-
const TrackingVolume *startVolume = nullptr
Navigation state: the start volume.
-
const Layer *targetLayer = nullptr
Navigation state: the target layer.
-
bool targetReached = false
Indicator if the target is reached.
-
const Surface *targetSurface = nullptr
Navigation state: the target surface.
-
const TrackingVolume *targetVolume = nullptr
Navigation state: the target volume.
-
const TrackingVolume *worldVolume = nullptr
Navigation state: the world volume.
-
inline auto navBoundary() const
-
struct Neutral
Charge and momentum interpretation for neutral particles.
Public Functions
-
constexpr Neutral() = default
-
inline constexpr Neutral(float absQ) noexcept
Construct and verify the input charge magnitude (in debug builds).
This constructor is only provided to allow consistent construction.
-
inline constexpr float absQ() const noexcept
-
inline constexpr float extractCharge(ActsScalar) const noexcept
-
inline constexpr ActsScalar extractMomentum(ActsScalar qOverP) const noexcept
-
inline constexpr ActsScalar qOverP(ActsScalar momentum, float signedQ) const noexcept
Friends
- inline friend constexpr friend bool operator== (Neutral, Neutral) noexcept
Compare for equality.
This is always
trueasNeutralhas no internal state. Must be available to provide a consistent interface.
-
constexpr Neutral() = default
-
struct OrientedSurface
-
struct PathLimitReached
This is the condition that the pathLimit has been reached.
Public Functions
boolean operator for abort condition without using the result
- Template Parameters:
propagator_state_t – Type of the propagator state
stepper_t – Type of the stepper
navigator_t – Type of the navigator
- Parameters:
state – [inout] The propagation state object
stepper – [in] Stepper used for propagation
logger – a logger instance
Public Members
-
double internalLimit = std::numeric_limits<double>::max()
Boolean switch for Loop protection.
-
template<typename action_list_t = ActionList<>, typename aborter_list_t = AbortList<>>
struct PropagatorOptions : public Acts::PropagatorPlainOptions Options for propagate() call.
- Template Parameters:
action_list_t – List of action types called after each propagation step with the current propagation and stepper state
aborter_list_t – List of abort conditions tested after each propagation step using the current propagation and stepper state
Public Functions
-
PropagatorOptions() = delete
Delete default constructor.
-
inline PropagatorOptions(const GeometryContext &gctx, const MagneticFieldContext &mctx)
PropagatorOptions with context.
-
PropagatorOptions(const PropagatorOptions<action_list_t, aborter_list_t> &po) = default
PropagatorOptions copy constructor.
-
template<typename extended_aborter_list_t>
inline PropagatorOptions<action_list_t, extended_aborter_list_t> extend(extended_aborter_list_t aborters) const Expand the Options with extended aborters.
- Template Parameters:
extended_aborter_list_t – Type of the new aborter list
- Parameters:
aborters – The new aborter list to be used (internally)
-
inline void setPlainOptions(const PropagatorPlainOptions &pOptions)
Set the plain options.
- Parameters:
pOptions – The plain options
Public Members
-
aborter_list_t abortList
List of abort conditions.
-
action_list_t actionList
List of actions.
-
std::reference_wrapper<const GeometryContext> geoContext
The context object for the geometry.
-
std::reference_wrapper<const MagneticFieldContext> magFieldContext
The context object for the magnetic field.
-
struct PropagatorPlainOptions
Class holding the trivial options in propagator options.
Subclassed by Acts::PropagatorOptions< ActionList<>, AbortList<> >, Acts::PropagatorOptions< action_list_t, aborter_list_t >
Public Members
-
double loopFraction = 0.5
Allowed loop fraction, 1 is a full loop.
-
bool loopProtection = true
Loop protection step, it adapts the pathLimit.
-
unsigned int maxRungeKuttaStepTrials = 10000
Maximum number of Runge-Kutta steps for the stepper step call.
-
unsigned int maxSteps = 1000
Maximum number of steps for one propagate call.
-
double maxStepSize = std::numeric_limits<double>::max()
Absolute maximum step size.
-
double pathLimit = std::numeric_limits<double>::max()
Absolute maximum path length.
-
double stepSizeCutOff = 0.
Cut-off value for the step size.
-
double stepTolerance = 1e-4
Tolerance for the error of the integration.
-
double surfaceTolerance = s_onSurfaceTolerance
Required tolerance to reach surface.
-
double loopFraction = 0.5
-
struct ProtoDetector
A proto detector description being used to define an overall structure of either a TrackingGeometry or Experimental::Detector.
Public Functions
-
inline void harmonize(bool legacy = true)
Harmonize the detector information, this can run in two modes, steered by the.
The legacy mode prepares everything for
Acts::TrackingVolume, if off it creates a description forActs::Detector.- Parameters:
legacy – boolean
-
std::string toString(const std::string &indent = "") const
Write the tracking volume to screen.
- Parameters:
indent – the current indentation
-
inline void harmonize(bool legacy = true)
-
struct SeedConfirmationRangeConfig
Contains parameters for quality seed confirmation.
Note
Requirements on the number of compatible space-points and impact parameters can be defined for different (r, z) regions of the detector (e.g. forward or central region) by SeedConfirmationRange. Seeds are classified as “high-quality” seeds and normal quality seeds. Normal quality seeds are only selected if no other “high-quality” seed has been found for that inner-middle doublet. For optimization reasons, the algorithm only calls the seed confirmation for a certain inner-middle doublet, in case a configurable minimum number of inner-middle-outer triplets have been found.
Public Members
-
float minImpactSeedConf = 1. * Acts::UnitConstants::mm
Minimum impact parameter of seed required in quality seed confirmation.
-
std::size_t nTopForLargeR = 0
Minimum number of compatible outer space-points required in quality seed confirmation if inner space-points radius is larger than rMaxSeedConf.
-
std::size_t nTopForSmallR = 0
Minimum number of compatible outer space-points required in quality seed confirmation if inner space-points radius is smaller than rMaxSeedConf.
-
float rMaxSeedConf = std::numeric_limits<float>::max()
Radius position of inner seed component that is used to split the region of the detector for seed confirmation.
-
float seedConfMaxZOrigin = 150. * Acts::UnitConstants::mm
Maximum longitudinal impact parameter of seed required in quality seed confirmation.
-
float seedConfMinBottomRadius = 60. * Acts::UnitConstants::mm
Minimum radius for inner seed component required in quality seed confirmation.
-
float zMaxSeedConf = std::numeric_limits<float>::max()
Maximum z position of middle component of the seed used to split the region of the detector for seed confirmation.
-
float zMinSeedConf = std::numeric_limits<float>::lowest()
Minimum z position of middle component of the seed used to split the region of the detector for seed confirmation.
-
float minImpactSeedConf = 1. * Acts::UnitConstants::mm
-
struct SinglyCharged
Charge and momentum interpretation for particles with +-e charge.
Public Functions
-
constexpr SinglyCharged() = default
-
inline constexpr SinglyCharged(float absQ) noexcept
Construct and verify the input charge magnitude (in debug builds).
This constructor is only provided to allow consistent construction.
-
inline constexpr float absQ() const noexcept
-
inline constexpr float extractCharge(ActsScalar qOverP) const noexcept
-
inline constexpr ActsScalar extractMomentum(ActsScalar qOverP) const noexcept
-
inline constexpr ActsScalar qOverP(ActsScalar momentum, float signedQ) const noexcept
Friends
- inline friend constexpr friend bool operator== (SinglyCharged, SinglyCharged) noexcept
Compare for equality.
This is always
trueasSinglyChargedhas no internal state. Must be available to provide a consistent interface.
-
constexpr SinglyCharged() = default
-
template<typename ...extensions>
struct StepperExtensionList : private detail::Extendable<extensions...> Container of extensions used in the stepper of the propagation.
This struct allows a broadcast of function calls for each element in the list. The broadcasts occur for a certain function at each step in a specific order. The first function is an evaluater if an extension is or how many extensions are applicable for an upcoming step. The next functions called are the evaluations of the k_1 - k_4 or the RKN4 integration. The last function call in a step is the finalize() method. This method is an overloaded function (optionally propagates the covariance). Each method has the possibility to break the evaluation of a given step if an extension reports that something went wrong (e.g. a particle lost too much momentum during the step)
- Template Parameters:
extensions – Types of the extensions
Public Functions
This functions broadcasts the call of the method finalize().
It collects all extensions and arguments and passes them forward for evaluation and returns a boolean.
This functions broadcasts the call of the method finalize().
It collects all extensions and arguments and passes them forward for evaluation and returns a boolean.
This functions broadcasts the call for evaluating a generic k.
It collects all arguments and extensions, test their validity for the evaluation and passes them forward for evaluation and returns a boolean as indicator if the evaluation is valid.
This functions broadcasts the call for evaluating k1.
It collects all arguments and extensions, test their validity for the evaluation and passes them forward for evaluation and returns a boolean as indicator if the evaluation is valid.
This functions broadcasts the call for evaluating k2.
It collects all arguments and extensions and passes them forward for evaluation and returns a boolean as indicator if the evaluation is valid.
This functions broadcasts the call for evaluating k3.
It collects all arguments and extensions and passes them forward for evaluation and returns a boolean as indicator if the evaluation is valid.
This functions broadcasts the call for evaluating k4.
It collects all arguments and extensions and passes them forward for evaluation and returns a boolean as indicator if the evaluation is valid.
Evaluation function to set valid extensions for an upcoming integration step.
- Template Parameters:
propagator_state_t – Type of the state of the propagator
stepper_t – Type of the stepper
navigtor_t – Type of the navigator
- Parameters:
state – [in] State of the propagator
stepper – [in] Stepper of the propagation
navigator – [in] Navigator of the propagation
-
struct WeightedComponentReducerLoop
Reducer struct for the Loop MultiEigenStepper which reduces the multicomponent state to simply by summing the weighted values.
Public Static Functions
-
template<typename stepper_state_t>
static inline ActsScalar absoluteMomentum(const stepper_state_t &s)
-
template<typename stepper_state_t>
static inline ActsScalar charge(const stepper_state_t &s)
-
template<typename stepper_state_t>
static inline FreeVector cov(const stepper_state_t &s)
-
template<typename stepper_state_t>
static inline Vector3 direction(const stepper_state_t &s)
-
template<typename stepper_state_t>
static inline Vector3 momentum(const stepper_state_t &s)
-
template<typename stepper_state_t>
static inline FreeVector pars(const stepper_state_t &s)
-
template<typename stepper_state_t>
static inline Vector3 position(const stepper_state_t &s)
-
template<typename stepper_state_t>
static inline ActsScalar qOverP(const stepper_state_t &s)
-
template<typename stepper_state_t>
static inline ActsScalar time(const stepper_state_t &s)
-
template<typename component_range_t>
static inline Vector3 toVector3(const component_range_t &comps, const FreeIndices i)
-
template<typename stepper_state_t>
Types
-
template<unsigned int kRows, unsigned int kCols>
using Acts::ActsMatrix = Eigen::Matrix<ActsScalar, kRows, kCols>
-
using Acts::ActsScalar = double
Common scalar (floating point type used for the default algebra types.
Defaults to
doublebut can be customized by the user.
-
template<unsigned int kSize>
using Acts::ActsSquareMatrix = Eigen::Matrix<ActsScalar, kSize, kSize>
-
template<unsigned int kSize>
using Acts::ActsVector = Eigen::Matrix<ActsScalar, kSize, 1>
-
using Acts::AngleAxis3 = Eigen::AngleAxis<ActsScalar>
-
using Acts::BoundMatrix = ActsMatrix<eBoundSize, eBoundSize>
-
using Acts::BoundSquareMatrix = ActsSquareMatrix<eBoundSize>
-
using Acts::BoundToFreeMatrix = ActsMatrix<eFreeSize, eBoundSize>
-
using Acts::BoundTrackParameters = GenericBoundTrackParameters<ParticleHypothesis>
BoundTrackParameters can hold any kind of charge.
-
using Acts::BoundVector = ActsVector<eBoundSize>
-
using Acts::BoundarySurface = BoundarySurfaceT<TrackingVolume>
BoundarySurface of a volume.
-
using Acts::FreeMatrix = ActsMatrix<eFreeSize, eFreeSize>
-
using Acts::FreeSquareMatrix = ActsSquareMatrix<eFreeSize>
-
using Acts::FreeToBoundMatrix = ActsMatrix<eBoundSize, eFreeSize>
-
using Acts::FreeToPathMatrix = ActsMatrix<1, eFreeSize>
-
using Acts::FreeVector = ActsVector<eFreeSize>
-
using Acts::GeometryContext = ContextType
This is the central definition of the Acts payload object regarding detector geometry status (e.g.
alignment)
It is propagated through the code to allow for event/thread dependent geometry changes
-
using Acts::HashedString = std::uint32_t
-
using Acts::Intersection3D = Intersection<3>
-
typedef BinnedArray<LayerPtr> Acts::LayerArray
A BinnedArray to a std::shared_ptr of a layer.
Layers are constructed with shared_ptr factories, hence the layer array is describes as:
-
using Acts::MagneticFieldContext = ContextType
This is the central definition of the Acts payload object regarding magnetic field status.
It is propagated through the code to allow for event/thread dependent magnetic field changes
-
using Acts::RotationMatrix2 = ActsMatrix<2, 2>
-
using Acts::RotationMatrix3 = ActsMatrix<3, 3>
-
using Acts::SquareMatrix2 = ActsSquareMatrix<2>
-
using Acts::SquareMatrix3 = ActsSquareMatrix<3>
-
using Acts::SquareMatrix4 = ActsSquareMatrix<4>
-
using Acts::Transform2 = Eigen::Transform<ActsScalar, 2, Eigen::AffineCompact>
-
using Acts::Transform3 = Eigen::Transform<ActsScalar, 3, Eigen::Affine>
-
using Acts::Translation2 = Eigen::Translation<ActsScalar, 2>
-
using Acts::Translation3 = Eigen::Translation<ActsScalar, 3>
-
using Acts::Vector2 = ActsVector<2>
-
using Acts::Vector3 = ActsVector<3>
-
using Acts::Vector4 = ActsVector<4>